497Uploads
168k+Views
72k+Downloads
Chemistry

GCSE Chemistry: Forming Ions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of ions
• The electronic configuration of ions
• Ions metals and nonmetals form
• Drawing electron configurations

OCR AS Chemistry: Electrophilic Addition in Alkenes
OCR AS Chemistry: 13.4 Electrophilic Addition in Alkenes
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Electrophile molecules
Electronegativity
Reaction mechanisms for addition reaction of alkenes and hydrogen halides
Carbocations and stability
Markownikoff’s Rule

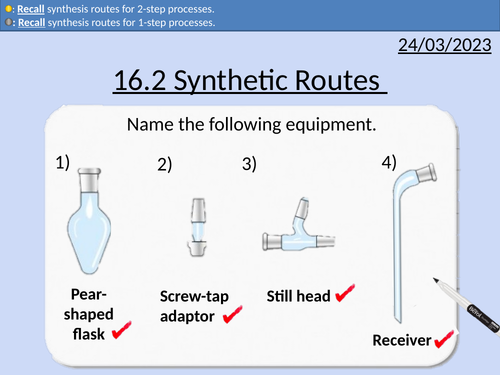
OCR AS Chemistry: Synthetic Routes
OCR AS Chemistry: 16.2 Synthetic Routes
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Functional Groups - Alkane, Alkene, Haloalkane, Alcohols, Carboxylic Acid, Ketone, Aldehyde, Ester, Amine, Nitrile.
One-step synthetic routes with reagents and conditions
Two-step synthetic routes with reagents and conditions

OCR AS Chemistry: 17.2 Infrared Spectroscopy
OCR AS Chemistry: 17.2 Infrared Spectroscopy
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Absorb infrared radiation increasing vibrations
What determines the magnitude of vibration
Fingerprint region
Identifying peaks

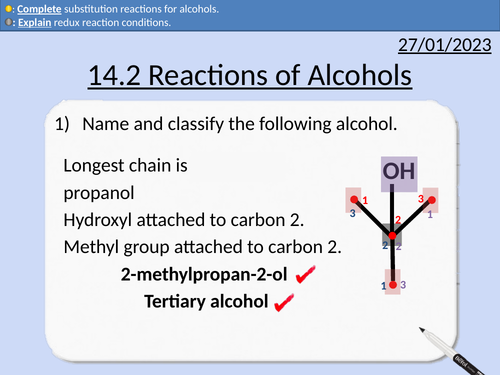
OCR AS Chemistry: Reactions of Alcohols
OCR AS Chemistry: 14.2 Reactions of Alcohols
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Combustion of alcohols
Reflux condition for reactions
Primary alcohol to aldehydes
Primary alcohols to carboxylic acids
Secondary alcohols to ketones
Dehydration of alcohols
Substitution reactions for alcohols

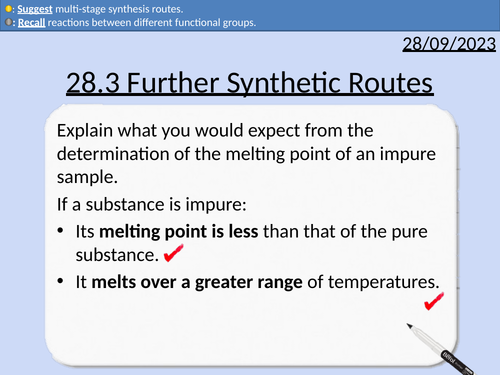
A level Chemistry: Further Synthetic Routes
OCR A level Chemistry: 28.3 Further Synthetic Routes
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Functional groups
Reactions of benzenes
Reactions of phenols
Common reactions between different functional groups
Reaction conditions and reagents

OCR Applied Science: 6.1 Mechanical Properties of Materials
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 6.1 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
• Interpreting laboratory tests for stress-strain graphs and Young’s modulus
• Awareness that repeated loading cycles may cause failure by fatigue below the yield strength
• Use of diagrams to understand that the way molecules are arranged in polymers determines the properties: chain length, crosslinking, use of plasticizers and crystallinity.
• Use and rearranging of the density equation.

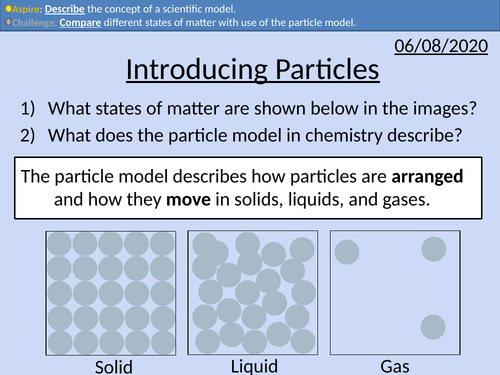
GCSE Chemistry: Introducing Particles
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Solids, liquids, and gases
• Scientific models as a concept
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry: P1.2 Atomic Structure
All resources for P1.2 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Atomic Structure
Isotopes and Ions
Developing the Atomic Model

GCSE Chemistry: Empirical Formula
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Calculate empirical formula and by finding the simplest whole-number ratio
• Calculate relative formula mass from balanced equations.

OCR Applied Science: 1.2 The Periodic Table
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 1.2 of Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Elements are based on atomic structure and can be classified by the Periodic Table i.e.:
organisation of elements within the table
groups
periods
atomic number
atomic mass atomic radius

OCR Applied Science: 2.2 Reactions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 2.2 of Module 1: Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Oxidation and reduction (redox) reactions
Addition reactions of alkenes to include full balanced symbol equations
Substitution reactions of alkanes and haloalkanes to include full balanced
equations
Addition polymerisation to include identification of monomers and repeating units
Condensation polymerisation to include identification of monomers and repeating units
Definition of a radical
The role played by UV light in producing chlorine radicals from CFCs in the
depletion of the ozone layer
Equations to show how chlorine radicals can destroy many ozone molecules
Displacement reactions to include full balanced equations for metals and halogens.

GCSE Chemistry: Simple Distillation
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Changes of state
• The technique of simple distillation
• Concentration of solute increasing in distillation
• Jobs related to chemistry
• Key word test Insoluble, Soluble, Solvent, Solute, Solution, Distillation, Filtration, and Crystallisation

GCSE Chemistry: Purification and Checking Purity
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Choosing the correct separation technique
• Comparisons of mobile and stationary phases for chromatography
• Rf Values
• Analysing chromatographs in gas chromatography

GCSE Chemistry: Electronic Structures
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Electrons reside in energy levels (shells) around the nucleus
• The electronic configuration of elements up to 20 is 2,8,8,2
• Groups and periods of the periodic table
• Drawing electron configurations

GCSE Chemistry: Metals and Non-metals
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Using the periodic table to identify metals and non-metals
• Different properties of metal and non-metals (Appearance, melting and boiling point, state of matter at room temperature, ductility, and malleability).
• Exceptions of physical properties (mercury being liquid and carbon conducting electricity).

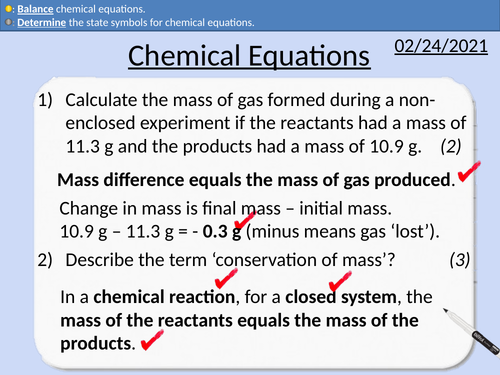
GCSE Chemistry: Chemical Equations
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Pathways into medical chemistry
• State the number of atoms from a chemical formula.
• Properties of metals and non-metals
• Determine state symbols for chemical equations
• Balancing chemical equations

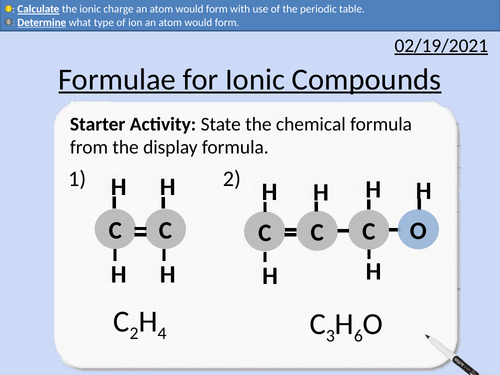
GCSE Chemistry: Formulae for Ionic Compounds
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• State the number of electrons in each energy level.
• Determine what type of ion an atom would form.
• Calculate the ionic charge an atom would form with use of the periodic table.
• Groups number, outer shell electrons, dot and cross diagrams
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry C2 Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
Resources for P2 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and Combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Relative Formula Mass
Empirical Formula
Pure and Impure Substances
Filtration and Crystallisation
Simple Distillation
Paper Chromatography
Purification and Checking Purity
Metals and Non-metals
Electronic Structures
Forming Ions
Ionic Compounds
Simple Molecules
Giant Covalent Structures
Polymer Molecules
Structure of Metals
Carbon
Changing State
Bulk Properties
Nanoparticles

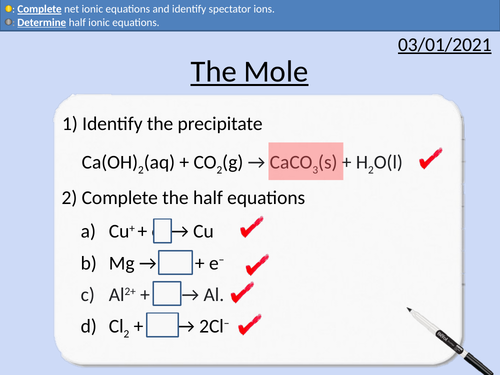
GCSE Chemistry: The Mole
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Using Standard Form
• Avogadro’s constant
• Relative Atomic Mass, Relative Formula Mass and Molar Mass
• Rearranging Equations
• Calculating the number of moles present