497Uploads
168k+Views
71k+Downloads
Physics
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Ideal Gas
OCR A level Physics: Ideal Gas is a part of the Module 5: Newtonian World and Astrophysics.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

OCR AS level Physics: Drag and Terminal Velocity
OCR AS level Physics: Drag and Terminal Velocity is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Drag and speed relationship
Free body diagrams
Net forces and acceleration
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Electrical Circuits
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 4: Energy, Power, and Resistance.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
This covers topics from Kirchhoff’s laws to potential dividers and sensing circuits.
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Nuclear Physics
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 26 Nuclear Physics is apart of the Module 6: Particle and Medical Physics
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
26.1 Einstein’s Mass-Energy Equation
26.2 Binding Energy
26.3 Nuclear Fission
26.4 Nuclear Fusion
Mass-energy is a conserved quantity
Einstein’s mass-energy equation
Particle and antiparticle annihilate each other
Rest mass and increasing mass with increased kinetic energy
Interpretation of mass-energy equivalence
Definition of mass defect
Definition of binding energy
Binding energy per nucleon
Calculating mass defect, binding energy, and binding energy per nucleon.
Explaining nuclear stability
Fuels in nuclear fission reactors
Moderators and thermal neutrons
Conservation of mass-energy
Energy released in fission reactions
Control rods
Nuclear waste management
Conditions for nuclear fusion
Binding energy and released energy
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Charge and Current
OCR AS level Physics: Charge and Current is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Fundamental charge and relative charge
Structure of a metal
Conventional current and electron flow
Measuring current with an ammeter
Ionic solutions with cations and anions.
Ions, relative charge and absolute charge
Comparing ionic solutions and metal conductors
Apply Kirchhoff’s First Law
Kirchhoff’s First Law in mathematical form
Kirchhoff’s First Law in written form
Describing conservation laws
Women in Science - Emmy Noether
CERN and jobs in physics
Number density for conductors, semi-conductors, and insulators
Calculating cross-sectional area
Apply the mean drift velocity equation.
Derivation of Mean Drift Velocity Equation
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Energy, Power, and Resistance
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 4: Energy, Power, and Resistance.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
This covers topics from circuit symbols to paying for electricity.
All circuit symbols required for OCR A level physics
Polarity of cells and batteries
Electron flow and conventional current
Calculating the base SI units for volts
Comparing potential difference and electromotive force (emf).
Circuit diagrams for measuring potential difference and emf.
Calculating energy dissipated in a circuit.
The structure of an electron gun.
The electron gun in the history of science (J.J. Thomson).
Rearranging equations to equate kinetic energy and work done.
Accelerating potential differences
Comparing the protons and electrons accelerated in a potential difference
Definition of an ohm.
Temperature and resistance for metallic conductors (wires)
The ohm in base SI units
I against V graphs and resistance
I-V Characteristics curves for ohmic components
I-V Characteristics curves for non-ohmic components
Circuit diagrams used to measure I and V.
Describing I-V Characteristics curves
Polarity of diodes
Conventional current and diodes
Plotting I-V curves for diodes
Describing I-V curves for diodes
Factors affecting resistance
Calculating resistivity
Resistivity and temperature
Experimentally determining resistivity
Using a graph to calculate resistivity
Thermistor uses
Thermistors with negative temperature coefficients
Plotting I-V curves for thermistors
Creating an experiment to test thermistors.
Materials and uses of LDRs
Creating an experiment to understand LDRs
LDRs relationship with light intensity
Converting time to hours
Using different units for electrical energy
Converting from J to kW hr
Calculating the cost of using different electrical appliances.
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Quantum Physics
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 4: Quantum Physics.
All presentations are full lesson PowerPoints with worked examples and homeworks with complete worked answers.
The Photon Model
Energy of a single photon
Converting from electron-volts to Joules.
Frequency of the electromagnetic spectrum
Determining Plank’s constant with LEDs
Threshold potential difference difference
Photoelectric Effect
Threshold frequency
Producing photoelectrons
Kinetic energy of photoelectrons
Linking frequency and wavelength
The electromagnetic spectrum, frequency and energy.
Einstein’s Photoelectric Equation
The photoelectric equation
Work function and Kinetic Energy
Determining work function from a graph
Determining threshold frequency from a from graphical analysis.
Determining Plank’s constant from graphical analysis.
Wave Particle Duality
deBroglie wavelength equation
Diffraction of electrons and protons
Comparing wavelengths of particles with different masses
Kinetic energy and wavelength

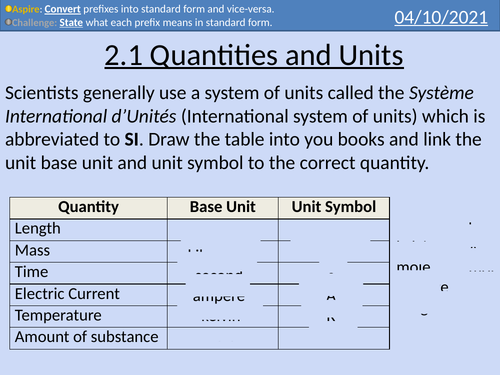
OCR AS level Physics: Quantities and Units
OCR AS level Physics: Quantities and Units is a part of the Module 2: Foundations of Physics
Full lesson PowerPoint with worked examples and homework with complete worked answers.
Overview of A level physics
Base units and quantities
Converting into base units
Converting from base units into non-base units

GCSE Physics: Forces and Fleming's Left Hand Rule
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P4.2.1 Forces, Current and Fleming’s Left Hand Rule.
This presentation includes:
Interacting Magnetic Field Lines
Increasing Magnitude of the force on a current carrying conductor
Applying Fleming’s Left Hand Rule

OCR AS level Physics: Projectile Motion
OCR AS level Physics: Projective Motion is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Includes:
Resolving vectors in 2D
Pythagoras’ theorem:
Equations of constant acceleration - suvat equations
Projectiles being dropped
Projectiles fired at and angle to the horizontal
Velocity-time graphs

GCSE Physics: Series and Parallel Circuits
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P3.2.2 Series and Parallel Circuits
Rule for current in series and parallel circuits
Rule for potential difference in series and parallel circuits.
Working scientifically
Student activities with worked solutions
Exam questions with worked solutions
Bundle

GCSE Physics: P3 Electricity Full Scheme
All resources for P3 Electricity GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Electrostatics
Electrical Current
Electrical Current Practical Activity
Circuit Symbols and Potential Difference
Series and Parallel Circuits
Resistance and Ohm’s Law
Resistance of a wire Practical Activity
I-V Characteristics and Component Graphs
Circuit Calculations
Sensing Circuits
Electrical Power and Energy

GCSE Physics: The Big-Bang
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.3.1 The Big-Bang
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Key facts about the Big-Bang model
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB, CMBR)
Doppler Red shift of light from stars in galaxies
Hubble’s evidence of absorption spectra being red shifted

OCR AS level Physics: Archimedes' Principle
OCR AS level Physics: Archimedes’ Principle is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

OCR AS level Physics: Resistance and Resistivity
OCR AS level Physics: Resistance and Resistivity is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Factors affecting resistance
Calculating resistivity
Resistivity and temperature
Experimentally determining resistivity
Using a graph to calculate resistivity

GCSE Physics: Hooke's Law Practical
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of Hooke’s Law
• Converting from centimeters to meters
• Converting from millimeters to meters
• Calculating the spring constant from a gradient of a force-extension graph
• The parallax effect and good experimental practice
• Data analysis (calculating mean and significant figures).

OCR A level Physics: Objects in the Universe
OCR A level Physics: 19.1 Objects in the Universe
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The size of astronomical objects: Universe, Galaxies, Solar systems, Stars, Planets, Planetary satellites, Comets, Artificial planetary satellites
Comparing planets and comets
The birth of stars
Stars in equilibrium during the main sequence
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics P4 Magnetism
All resources for P4 Magnetism and Magnetic Fields for GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1.Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
• Magnets and Magnetic Fields
• Currents and Fields
• Right Hand Cork-screw Rule
• Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
• Currents and Forces
• Motors
• Electromagnetic Induction
• Generators
• Transformers
• Speakers and Microphones

GCSE Physics: Hydraulic Systems
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.3.6 Hydraulic Systems
• Uses of hydraulics
• Pressure equation
• Rearranging equation
• Calculating pressure in liquids
• Describing how force multiplies in hydraulic systems
• Worked examples and student problems

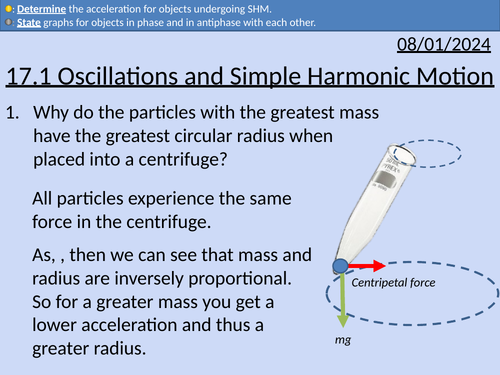
OCR A Level Physics: Simple Harmonic Motion and Oscillations
OCR A Level Physics: Simple Harmonic Motion and Oscillations presentation, homework and answers.