484Uploads
146k+Views
64k+Downloads
All resources

GCSE Physics: Efficiency and Sankey Diagrams
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of efficiency
• Analysing and constructing Sankey diagrams
• Using the efficiency equation
• Rearranging the efficiency equation

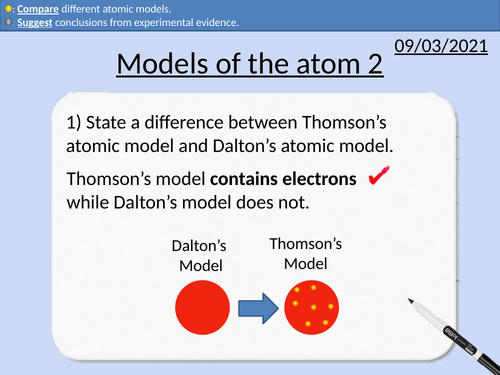
GCSE Physics: Development of the Atomic Model 1
This presentation includes:
What is a scientific model
Why scientific models change over time
The Ancient Greek Model
John Dalton’s Model
Thomson’s Plum-Pudding Model

GCSE Physics: Development of the Atomic Model 2
This presentation includes:
Why scientific models change over time
Electric charge
Rutherford’s atomic model
Rutherford’s experiment
Bohr’s atomic model

GCSE Physics Equation Tests
Included are 9 lessons with tips on how to learn the equations for GCSE Physics.

GCSE Physics: Temperature Scales and Changes.
This presentation covers:
Celsius and Kelvin temperature scales
Physical and Chemical Changes
Absolute zero

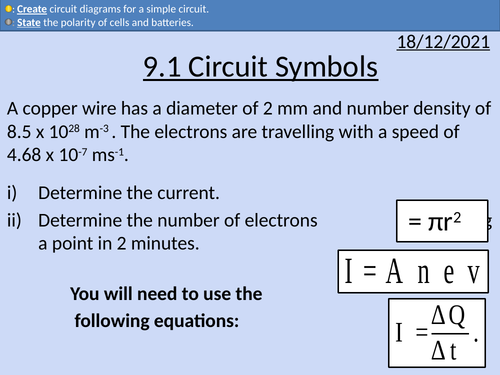
OCR AS level Physics: Circuit Symbols
OCR AS level Physics: Circuit Symbols is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
All circuit symbols required for OCR A level physics
Polarity of cells and batteries
Electron flow and conventional current

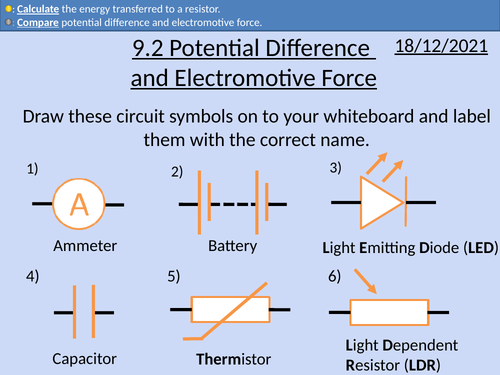
OCR AS level Physics: Potential Difference and Electromotive Force
OCR AS level Physics: Potential Difference and Electromotive Force is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Calculating the base SI units for volts
Comparing potential difference and electromotive force (emf).
Circuit diagrams for measuring potential difference and emf.
Calculating energy dissipated in a circuit.

OCR AS level Physics: More Vectors
OCR AS level Physics: More Vectors is a part of the Module 2: Foundations of Physics
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

OCR AS level Physics: Distance and Speed
OCR AS level Physics: Distance and Speed is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

OCR AS level Physics: Adding Vectors
OCR AS level Physics: Adding Vectors is a part of the Module 2: Foundations of Physics
Full lesson PowerPoint with worked examples and homework with complete worked answers.
Adding vectors in 1 D
Adding vectors in 2 D
Vector triangles
Using Pythagoras’ theorem to determine the magnitude
Using trigonometry to determine the direction

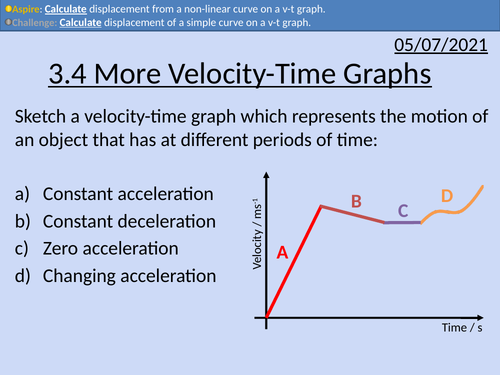
OCR AS level Physics: More Velocity-Time Graphs
OCR AS level Physics: More Velocity-time Graphs is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

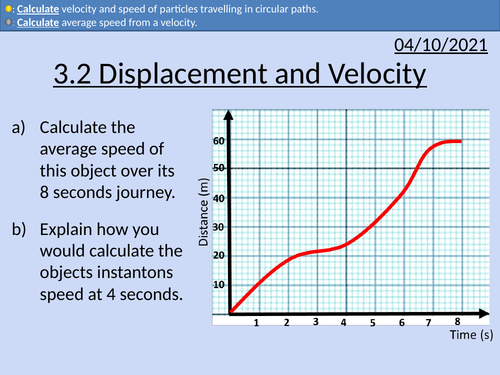
OCR AS level Physics: Displacement and Velocity
OCR AS level Physics: Displacement and Velocity is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

OCR AS level Physics: Free fall and g
OCR AS level Physics: Free fall and g is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Definition of free fall and gravitational force.
Dimensional analysis of units for acceleration and g.
Determining g with equations of constant acceleration (suvat equations).
Determining g with finding the gradient of graphs.
Determining g experimentally with stopwatches, trap doors, light gates, and cameras with strobes.

OCR AS level Physics: Newton's second law
OCR AS level Physics: Newton’s second law is a part of the Module 3: Laws of Motion and Momentum. Presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

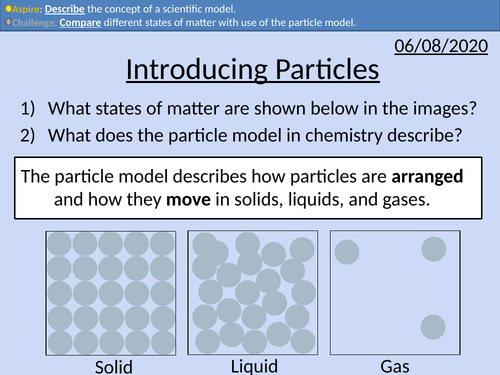
GCSE Chemistry: Introducing Particles
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Solids, liquids, and gases
• Scientific models as a concept

GCSE Chemistry: Chemical and Physical Changes
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Differences between physical and chemical changes
• Explain why physical changes are generally easier to reverse

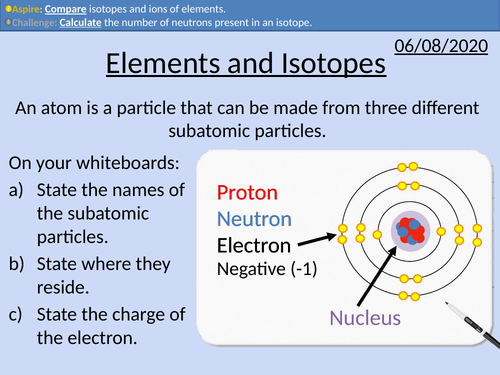
GCSE Chemistry: Isotopes and Ions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definitions of elements, isotopes, and ions
• State mass number, atomic number, and chemical symbols
• Calculate the number of neutrons
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry: P1.2 Atomic Structure
All resources for P1.2 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Atomic Structure
Isotopes and Ions
Developing the Atomic Model

GCSE Chemistry: Relative Formula Mass
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Relative atomic mass
• Understanding chemical formulas
• Relative formula mass

GCSE Chemistry: Pure and Impure Substances
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Definitions of pure and impure substances
Definition of an alloy
Identification of purity with melting points
Plotting graphs and data analysis