499Uploads
171k+Views
72k+Downloads
Biology

GCSE Biology:Transcription and Translation
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.2.2 Transcription and Translation
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
The role of proteins and AI
Proteins as polymers
Explaining transcription
mRNA and complementary bases
Explaining translation

GCSE Biology: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.3.1 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
The three main macronutrients - carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
Names of enzymes - carbohydrase, amylase, protease, lipase
What the macronutrients are broken down into - simple sugars, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol.
Metabolic rate
Food tests and the positive results

GCSE Biology: Mitosis
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B2.1.4 Mitosis
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
The cell cycle
DNA replication
Movement of chromosomes
Cytokinesis (cell division)
Growth of daughter cells.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Biology: B1.2 What happens in cells?
All resources for B1.2 What happens in cells? GCSE OCR Biology Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid.
DNA is found in the nucleus of cells.
DNA is packaged into a thread-like structure called chromosomes.
Humans typically have 46 chromosomes shared from their parents.
Genes are sections of DNA that code for physical characteristics.
The structure of DNA.
DNA is comprised of monomers called nucleotides.
A nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a sugar (deoxyribose), and an organic base.
There are four organic bases: Adenine, A. Thymine, T. Cytosine, C. Guanine, G.
Hydrogen bonds in DNA.
The role of proteins and AI
Proteins as polymers
Explaining transcription
mRNA and complementary bases
Explaining translation
Enzymes are made of protein.
Enzymes are biological catalysts.
Catalysts speed up the rate of reaction without being used up themselves.
Enzymes and the lock and key hypothesis.
Enzymes breaking down and bonding substrates.
Enzymes-catalysed reactions
Rate of reaction
Denaturing of enzymes and the active site
Optimum temperature and optimum pH for enzymes
Definition of concentration
Increasing concentration of enzymes and substrates
Saturation of substrates

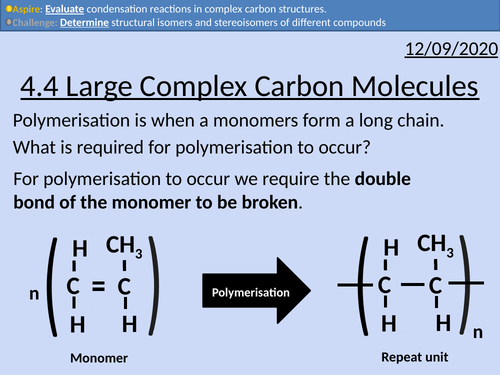
OCR Applied Science: 4.4 Large Complex Carbon Molecules
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 4.4 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Complex carbohydrates (starch, glycogen, cellulose)
• Carbohydrates found as monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides (monomers, dimers or polymers)
• Monomers held together by glycosidic bonds to form dimers and polymers, via condensation reactions
• Monosaccharides include glucose, fructose and galactose
• Disaccharides include maltose, sucrose and lactose
• Polysaccharides include starch, glycogen and cellulose
• Cellulose is found in plant cell walls where it provides strength/support and pliability
• Starch and glycogen are energy sources
Proteins and peptides from amino acids
• Dipeptides are formed from two amino acids joined by a peptide bond, via a condensation reaction
• Polypeptides are chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
• Proteins/polypeptides have physiological or functional roles, including enzymes, carrier proteins in the plasma membrane, and structural roles, including collagen and elastin fibres in connective tissue
Lipids from fatty acids, glycerol and phosphorus compounds
• Monoglycerides, diglycerides and triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and glycerol
• An ester bond forms between each fatty acid and the glycerol, via condensation reactions
• Phospholipids contain glycerol plus two fatty acids and a phosphate group
• Lipids act as an energy source within cells, as an insulation layer around animal organs, in the myelin sheath (found around some nerve fibres/axons) to increase speed of nerve transmission
• Phospholipids form a bilayer in the plasma membrane
Protein synthesis (transcription, translation) RNA, messenger, ribosomal and transfer
• The nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, are polymers of nucleotides
• Peptide bonds form between amino acids to create polypeptide chains/proteins
• Recall a simple description of protein synthesis
Bundle

OCR Applied Science: 21.2 Product Testing of Consumer Products
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.1 Types of testing i.e.:
• in-vitro
• in-vivo
• titration
• extraction and separation
2.2 Laboratory testing during development i.e.:
• formulation
• production
• quality control and assurance
• after sale monitoring.
2.3 Effectiveness of test i.e.:
• Appropriate test method
• Data collection validity and reliability
• Consistent chemical composition
• Hazards and risks of use (e.g. toxicity, possible mutagenic and
teratogenic effects, microbiological safety)

GCSE Biology: DNA
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.2.1 DNA
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid.
DNA is found in the nucleus of cells.
DNA is packaged into a thread-like structure called chromosomes.
Humans typically have 46 chromosomes shared from their parents.
Genes are sections of DNA that code for physical characteristics.
The structure of DNA.
DNA is comprised of monomers called nucleotides.
A nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a sugar (deoxyribose), and an organic base.
There are four organic bases: Adenine, A. Thymine, T. Cytosine, C. Guanine, G.
Hydrogen bonds in DNA.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Biology: B1.1 Cell Structures
All resources for B1.1 Cell Structures GCSE OCR Biology Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Cells are the building blocks of living objects.
Definition of eukaryotic cells
Typical size of eukaryotic cells
Subcellular structure of animal cells
Subcellular structure of plant cells
Organelles and their functions
Revision activities (Look, Cover, Write, Check)
Print out of animal and plant cells
Typical size of bacterial cells
Subcellular structure of bacterial cells
Functions of subcellular structure of bacterial cells
Comparing animal, plant, and bacterial cells
Revision activity - flash cards
Print out of bacterial cell
Labeling a light microscope
Defining magnification and resolution.
Explaining why stains are used for light microscope.
Calculating total magnification, objective lens magnification and eyepiece lens magnification.
Calculating actual size, magnification, and magnified size of objects.
Converting from from micrometre (µm) to millimetres (mm)
Rearranging equations
Comparing sizes of different cells
Using standard form
Using SI prefixes (nano, micro, milli, kilo, mega)
Comparing electron microscopes and light microscopes.

GCSE Biology: Aerobic Respiration
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.3.2 Aerobic Respiration
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Word equation for aerobic respiration
Balanced symbol equation for aerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration is an exothermic reaction
The structure of mitochondria
ATP and its uses
Why blood flow increases to muscles when exercising
Bundle

GCSE OCR Biology: B1.3 Respiration
All resources for B1.3 Respiration GCSE OCR Biology Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
The three main macronutrients - carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
Names of enzymes - carbohydrase, amylase, protease, lipase
What the macronutrients are broken down into - simple sugars, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol.
Metabolic rate
Food tests and the positive results
Word equation for aerobic respiration
Balanced symbol equation for aerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration is an exothermic reaction
The structure of mitochondria
ATP and its uses
Why blood flow increases to muscles when exercising
Conditions for anaerobic respiration
Word equation for anaerobic respiration in mammals
Lactic acid and its affects.
Oxygen debt
Comparing aerobic and anaerobic respiration in mammals.
Anaerobic respiration in plants - fermentation.
Fermentation word equation and symbol equation.
Exam questions.

GCSE Biology: Photosynthesis
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.4.1 Photosynthesis
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Word and symbol equation for photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide diffuses from the air through the stomata.
Water travels by osmosis through the root hair cells.
Photosynthesis occurs inside the plant’s chloroplast.
Chloroplasts contain a green pigment called chlorophyll.
Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction.
The two main stages of photosynthesis.
Comparing photosynthesis and aerobic respiration.

GCSE Biology: Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.4.3 Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Definition for rate of photosynthesis
The rate of photosynthesis affects the rate of biomass
Limiting factors include, light level, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature.
Graphs for rate of photosynthesis against light level, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature.
Plotting data graphs.
Exam questions.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Biology: B1.4 Photosynthesis
All resources for B1.4 Photosynthesis GCSE OCR Biology Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Word and symbol equation for photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide diffuses from the air through the stomata.
Water travels by osmosis through the root hair cells.
Photosynthesis occurs inside the plant’s chloroplast.
Chloroplasts contain a green pigment called chlorophyll.
Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction.
The two main stages of photosynthesis.
Comparing photosynthesis and aerobic respiration.
The positive test for starch
Experimental procedure for testing starch in leaves.
Testing for the need of chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
Testing for the need of light for photosynthesis.
Testing for the need of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
Testing oxygen produced via photosynthesis.
Testing light intensity affects photosynthesis.
Definition for rate of photosynthesis
The rate of photosynthesis affects the rate of biomass
Limiting factors include, light level, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature.
Graphs for rate of photosynthesis against light level, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature.
Plotting data graphs.
Experimental procedures to investigate how the rate of photosynthesis is affected by:
Light level
Temperature
Carbon dioxide concentration
Inverse square law for relative light intensity

GCSE Biology: Osmosis
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B2.1.2 Osmosis
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Definition of osmosis.
Explaining water potential and concentration of solution.
How cells change during osmosis - turgid, lysis, crenated, plasmolysed

OCR Applied Science: 21.2.2 Testing During Development
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 2.2 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.2 Laboratory testing during development i.e.:
• formulation
• production
• quality control and assurance
• after sale monitoring.

OCR Applied Science: 21.2.1 Types of Testing
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 2.1 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.1 Types of testing i.e.:
• in-vitro
• in-vivo
• titration
• extraction and separation

OCR Applied Science: 21.2.3 Effectiveness of Tests
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 2.3 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.3 Effectiveness of test
• Appropriate test method
• Data collection validity and reliability
• Consistent chemical composition
• Hazards and risks of use

GCSE Biology: Animal and Plant Cells
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.1.1 Animal and Plant Cells
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Cells are the building blocks of living objects.
Definition of eukaryotic cells
Typical size of eukaryotic cells
Subcellular structure of animal cells
Subcellular structure of plant cells
Organelles and their functions
Revision activities (Look, Cover, Write, Check)
Print out of animal and plant cells

GCSE Biology: Bacterial Cells
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.1.2 Bacterial Cells
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Typical size of bacterial cells
Subcellular structure of bacterial cells
Functions of subcellular structure of bacterial cells
Comparing animal, plant, and bacterial cells
Revision activity - flash cards
Print out of bacterial cell

GCSE Biology: Light Microscopy
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.1.3 Light Microscopy
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Labeling a light microscope
Defining magnification and resolution.
Explaining why stains are used for light microscope.
Calculating total magnification, objective lens magnification and eyepiece lens magnification.
Calculating actual size, magnification, and magnified size of objects.
Converting from from micrometre (µm) to millimetres (mm)
Rearranging equations