497Uploads
169k+Views
72k+Downloads
Chemistry
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry C2 Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
Resources for P2 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and Combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Relative Formula Mass
Empirical Formula
Pure and Impure Substances
Filtration and Crystallisation
Simple Distillation
Paper Chromatography
Purification and Checking Purity
Metals and Non-metals
Electronic Structures
Forming Ions
Ionic Compounds
Simple Molecules
Giant Covalent Structures
Polymer Molecules
Structure of Metals
Carbon
Changing State
Bulk Properties
Nanoparticles

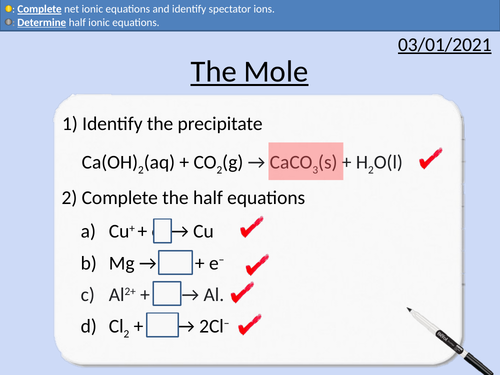
GCSE Chemistry: The Mole
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Using Standard Form
• Avogadro’s constant
• Relative Atomic Mass, Relative Formula Mass and Molar Mass
• Rearranging Equations
• Calculating the number of moles present

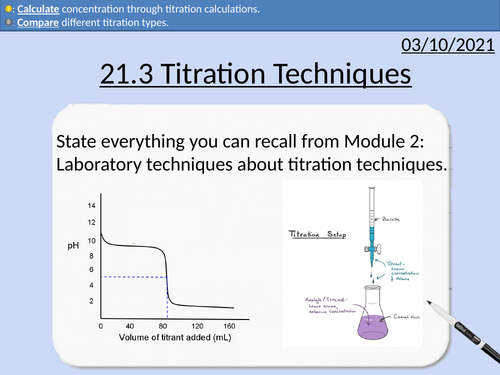
OCR Applied Science: 21.3 Titration Techniques
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
3.1 Titration techniques on consumer products
• Acid-base titration (e.g. limescale removers, eco-disinfectants)
• Precipitation titration (e.g. contact lens saline solution)
• Redox titration, (e.g. bleach, tooth whitener; vitamin C tablets).
• Complexometric titrations (e.g. Milk of Magnesia)
Including explanation and activities on:
Titration calculations
Moles and molar mass
Rearranging Equations
State symbols
Significant Figures
Comparing Data

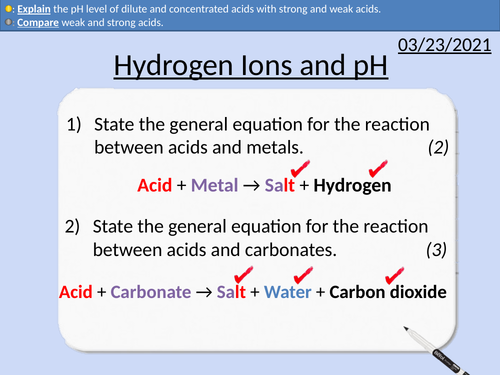
GCSE Chemistry: Hydrogen Ions and pH
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Concentration of fruit squash
• Comparing strong and weak acids
• pH and hydrogen ion concentration
• Titration curves

GCSE Chemistry: Electrolysis of Water
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Pure water being made partially of ions (hydrogen and hydroxide).
• PANIC convention for electrodes
• OILRIG convention for redox reactions
• Electron transfers at electrodes
• Half-equations for anode and cathode
• Balancing half-equations

GCSE Chemistry: Detecting Cations
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Flame tests for lithium, sodium, potassium, calcium, and copper.
Electron energy levels and emitting radiation.
Precipitate tests for iron(II)), iron(III), copper(II), calcium, and zinc.

OCR AS Chemistry: Organic Chemistry
OCR AS Chemistry: 11.1 Organic Chemistry
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Definition of hydrocarbons
What organic chemistry is
Saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons
Definition of functional groups
Definition of homologous group
Bundle

OCR AS level Chemistry: Alkanes
OCR AS level Chemistry: Alkanes is apart of the Module 4: Core Organic Chemistry and Analysis
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks

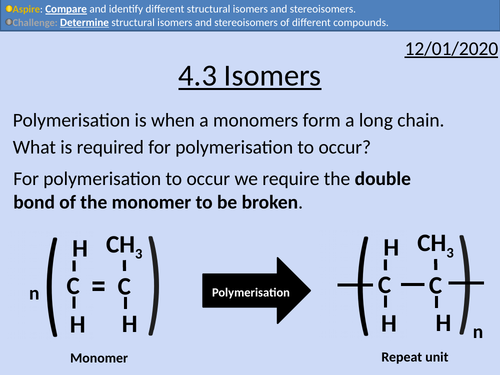
OCR Applied Science: 4.3 Isomers
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 4.3 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
• Stating definitions and comparing structural isomers and stereoisomers.
• Condensed structural formula
• Lines of symmetry for structural isomers
• Cis- and Trans isomers
• Optical isomers as non-superimposable mirror images.
• Wedge and Dash Notation
• Identifying chiral centres (asymmetric carbons)
• Le Bel-van’t Hoff rule
• Determining the maximum number of isomers.

OCR AS Chemistry: Properties of Alcohols
OCR AS Chemistry: 14,1 Properties of Alcohols
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Naming alcohols
Classifying alcohols (primary, secondary, tertiary)
Electronegativity
Polar and non-polar molecules
Explaining physical properties of alcohols compared to alkanes
Volatility
Solubility
Melting points
Chain length and London forces

OCR AS Chemistry: The Chemistry of Haloalkanes
OCR AS Chemistry: The Chemistry of Haloalkanes
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Naming Haloalkanes
Classifying Haloalkanes (primary, secondary, tertiary)
Electronegativity
Reaction mechanism for hydrolysis
Rates of reactions for hydrolysis
Reaction conditions for hydrolysis
Bundle

OCR AS level Chemistry: Organic Synthesis
OCR AS level Chemistry: Organic Synthesis is apart of the Module 4: Core Organic Chemistry and Analysis
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
Heating under reflux
Distillation
Re-distillation
Purifying Organic Products
Removing impure acids from organic compounds
Drying agents
Functional Groups - Alkane, Alkene, Haloalkane, Alcohols, Carboxylic Acid, Ketone, Aldehyde, Ester, Amine, Nitrile.
One-step synthetic routes with reagents and conditions
Two-step synthetic routes with reagents and conditions
Bundle

OCR AS level Chemistry: Alcohols
OCR AS level Chemistry: Alcohols is apart of the Module 4: Core Organic Chemistry and Analysis
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks
Naming alcohols
Classifying alcohols (primary, secondary, tertiary)
Electronegativity
Polar and non-polar molecules
Explaining physical properties of alcohols compared to alkanes
Volatility
Solubility
Melting points
Chain length and London forces
Combustion of alcohols
Reflux condition for reactions
Primary alcohol to aldehydes
Primary alcohols to carboxylic acids
Secondary alcohols to ketones
Dehydration of alcohols
Substitution reactions for alcohols

A Level Chemistry: The Chemistry of Phenol
OCR A level Chemistry: 25.3 The Chemistry of Phenol
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Naming phenols
Distinguishing between phenols and alcohols
Distinguishing between phenols and alkenes
Distinguishing between phenols and carboxylic acids
Phenol as a weak acid
Electrophilic reactions with phenols
Comparing and explaining the reactivity of phenols and benzene

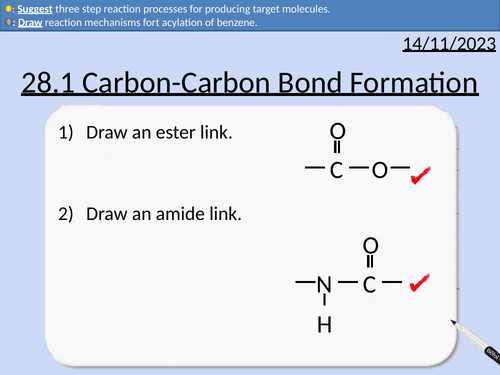
A level Chemistry: Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Forming nitriles from haloalkanes
Forming nitriles from aldehydes and ketones
Forming amines from nitriles (reduction)
Forming carboxylic acids from nitriles (hydrolysis)
Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene
Acylation of benzene with acyl chloride

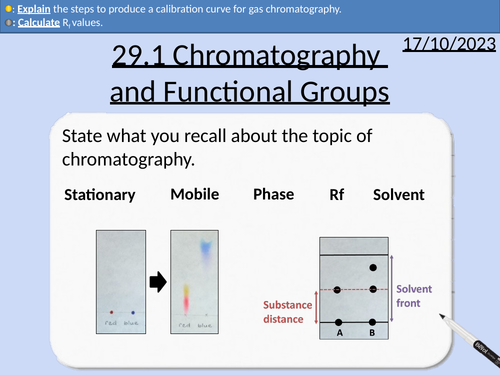
A level Chemistry: Chromatography and Functional Group Analysis
OCR A level Chemistry: 29.1 Chromatography and Functional Group Analysis
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Thin layer chromatography (TLC)
Rf values
Gas chromatography (GC)
Gas chromatograms
Retention time and peak integrations
Calibration curves from retention time and relative peak area
Differentiation of functional groups: alkene, primary and secondary alcohols, aldehydes, cabonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, and haloalkes.

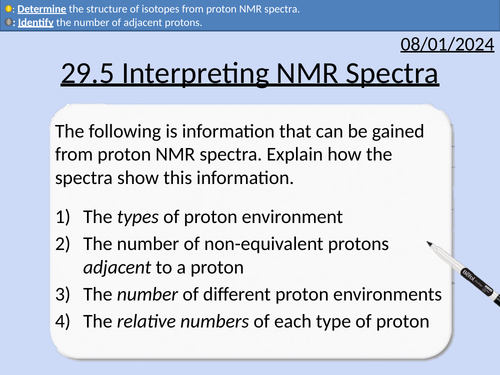
A level Chemistry: Interpreting Proton NMR Spectra
OCR A level Chemistry: 29.5 Interpreting Proton NMR Spectra
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Predicting proton NMR spectra for molecules
Identifying the number of different proton environments
Identifying the types of proton environment and chemical shifts
Integration traces (area of peaks) and relative number of protons
The spin-spin splitting pattern (n + 1)

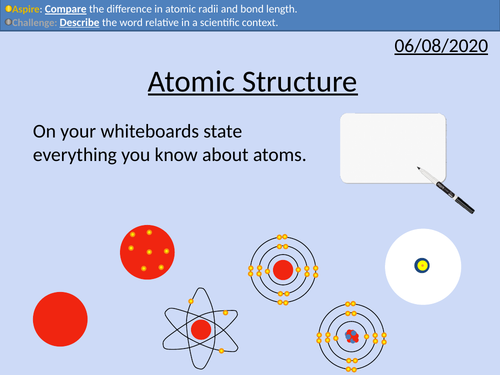
GCSE Chemistry: Atomic Structure
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Scientific models as a concept
• Structure of the atom
• Relative mass and charge of subatomic particles
• Bond length of atoms and molecules

GCSE Chemistry: Development of the Atomic Model
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford and Bohr’s models
• Comparing different scientific models of the atom

OCR Applied Science: 1.3 Ionic and Covalent Bonding
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 1.3 of Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Elements react together to form compounds by i.e.
ionic bonding
covalent bonding