36Uploads
18k+Views
10k+Downloads
All resources

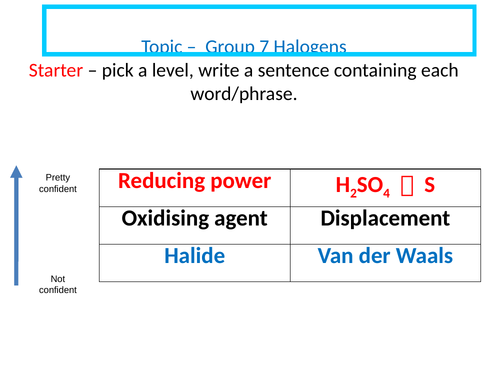
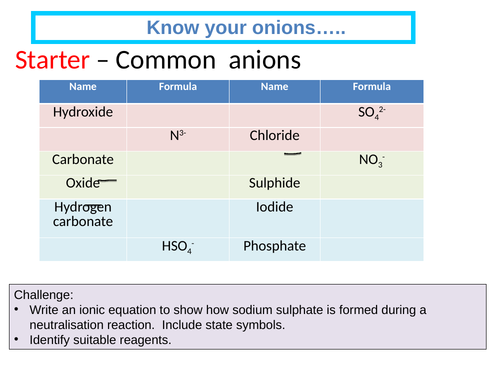
Group 7 Halogens
Describe the trend in boiling points and oxidising ability of the halogens.
Predict observations for a displacement reaction between aqueous halogens and aqueous halides.
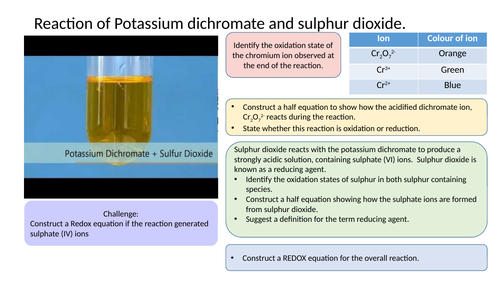
Construct equations for chlorine disproportion chemistry

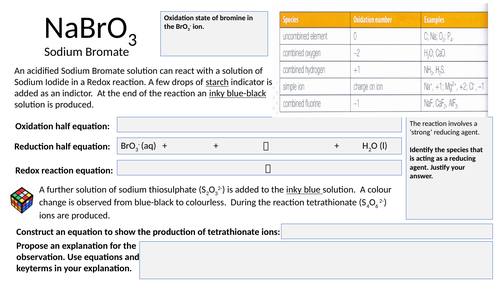
Redox equation activity
Structured activity that allows student’s to apply their knowledge and understanding of REDOX chemistry.

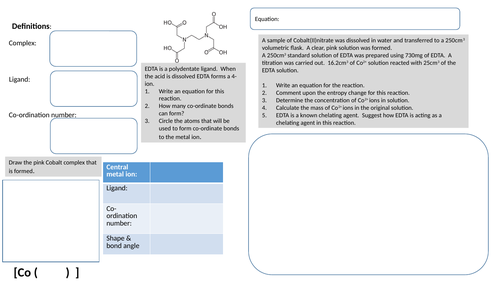
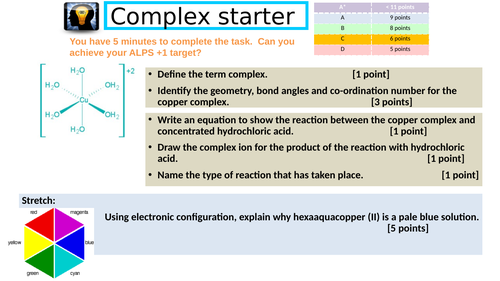
Complex chemistry activity
Activity that involves transition metal complex and aqueous reactions, Born-Haber cycle, entropy and titration.

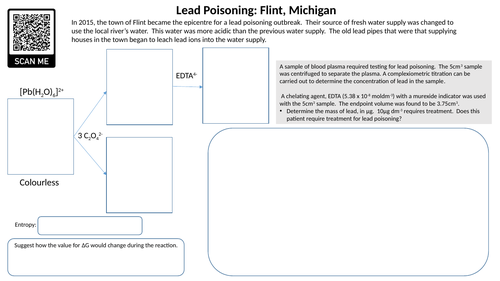
Complex ions: Lead poisoning starter
Starter activity that involves application of complex ion chemistry, stereoisomerism, entropy and titration

Period 3
Write equations for the reactions of Period 3 elements to form their oxides.
Describe the structure and bonding of period 3 oxides
Explain why period 3 oxides react differently in water to for ionic / covalent structure and the equations.
Explain how period 3 oxides react with simple acids and alkali

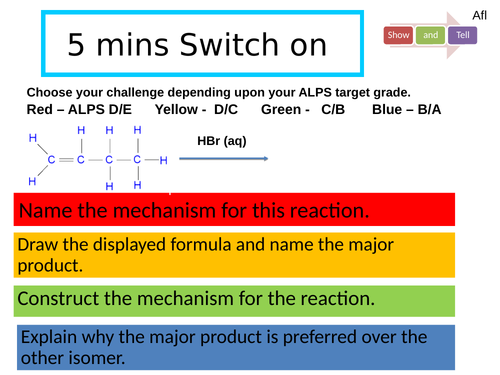
Revision: Alkenes
Describe E/Z stereoisomerism.
Explain how to use CIP rules to classify an isomer E or Z.
Recall polymerisation of alkenes
Outline the two mechanisms that alkenes undergo and justify why the major product is formed.

Revision: Transition metals
Describe the features of a complex ion.
Explain how a complex is coloured.
Determine the formula of a complex using colorimetry.
Determine the concentration of a complex using colorimetry and titrations.

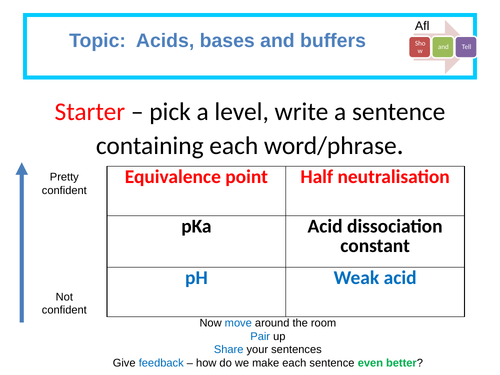
Determining the pKa of aspirin: Required practical
Calculating the pH of a weak acid.
Describe how to produce a standard solution.
Propose a suitable experimental method that could be used to determine the pKa of aspirin.
Use Excel to create a calibration curve and to generate a calibrated data set. (Included)
Analysis of a pH curve to determine pKa.

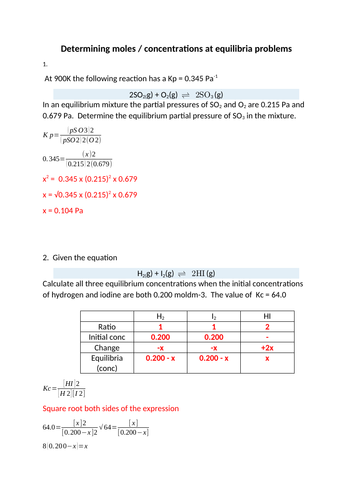
Constructing Redox equations activity
Starter activity for year 13 students practicing constructing half equations and REDOX equations.

Titration and standard solution - required practical
Describe how to prepare a standard solution of sodium hydrogensulphate.
Suggest suitable techniques that will help a student to carryout an accurate titration.
Development of exam technique when approaching titration how science works questions

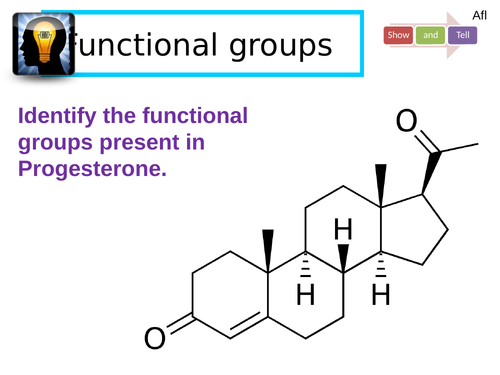
Aldehydes and ketones
Recall how alcohol FG can be oxidised into carbonyl containing FG.
Identify a suitable reducing agent for reducing a carbonyl into an alcohol.
Construct a mechanism to show the reduction of a carbonyl.
Explain how racemic mixtures can be formed.

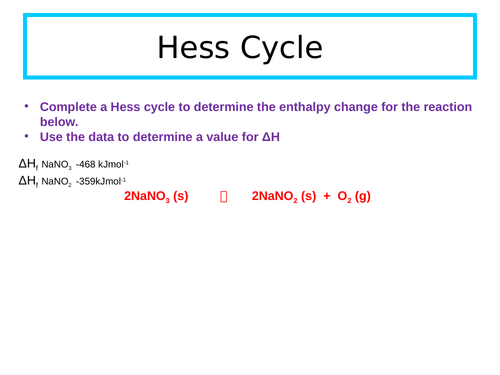
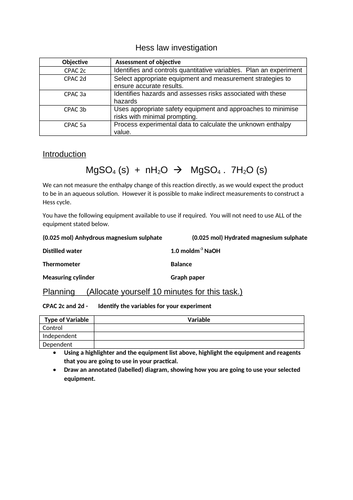
Enthalpy of solution
Define enthalpies of solution, hydration and lattice dissociation.
Construct a Hess cycle for an ionic substance being dissolved in a solvent.
Use experimental data, calculations and Hess law to determine an unknown enthalpy change from a class experiment.

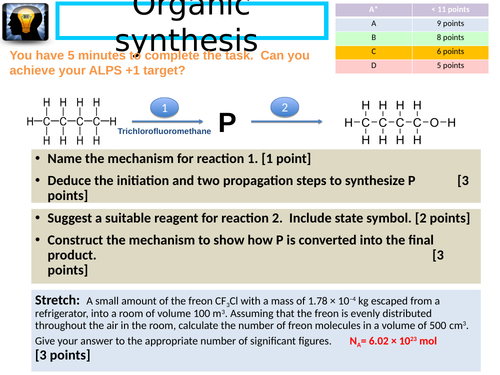
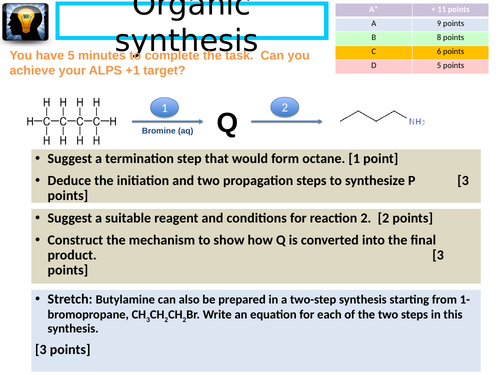
Organic synthesis workmat 2
Recap / Revison workmat. Please note that no answers are provided with this resource.

Haloalkanes - introduction to nucleophilic substitution
Identify the differences between nucleophiles, electrophiles and radicals.
Outline the major stages of free radical substitution.
Construct a diagram to explain how reactions via nucleophilic substitution take place.

Haloalkanes - nucleophilic substitution
Outline a mechanism to show free radical substitution.
Construct nucleophilic substitution mechanisms using curly arrows.
Synthesis of alcohols, nitriles and amines from haloalkanes.

Haloalkanes - elimination
Synthesis of alcohols, nitriles and amines from haloalkanes.
Synthesis of alkenes from haloalkanes.
Comparison of the two reaction mechanisms that haloalkanes undergo.