496Uploads
163k+Views
70k+Downloads
Biology

GCSE Biology: Electron Microscopy
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.1.4 Electron Microscopy
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Comparing sizes of different cells
Using standard form
Using SI prefixes (nano, micro, milli, kilo, mega)
Comparing electron microscopes and light microscopes.

GCSE Biology: Light Microscopy
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.1.3 Light Microscopy
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Labeling a light microscope
Defining magnification and resolution.
Explaining why stains are used for light microscope.
Calculating total magnification, objective lens magnification and eyepiece lens magnification.
Calculating actual size, magnification, and magnified size of objects.
Converting from from micrometre (µm) to millimetres (mm)
Rearranging equations

GCSE Biology: Bacterial Cells
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.1.2 Bacterial Cells
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Typical size of bacterial cells
Subcellular structure of bacterial cells
Functions of subcellular structure of bacterial cells
Comparing animal, plant, and bacterial cells
Revision activity - flash cards
Print out of bacterial cell

GCSE Biology: Animal and Plant Cells
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.1.1 Animal and Plant Cells
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Cells are the building blocks of living objects.
Definition of eukaryotic cells
Typical size of eukaryotic cells
Subcellular structure of animal cells
Subcellular structure of plant cells
Organelles and their functions
Revision activities (Look, Cover, Write, Check)
Print out of animal and plant cells
Bundle

OCR Applied Science: 21.2 Product Testing of Consumer Products
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.1 Types of testing i.e.:
• in-vitro
• in-vivo
• titration
• extraction and separation
2.2 Laboratory testing during development i.e.:
• formulation
• production
• quality control and assurance
• after sale monitoring.
2.3 Effectiveness of test i.e.:
• Appropriate test method
• Data collection validity and reliability
• Consistent chemical composition
• Hazards and risks of use (e.g. toxicity, possible mutagenic and
teratogenic effects, microbiological safety)

OCR Applied Science: 21.2.3 Effectiveness of Tests
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 2.3 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.3 Effectiveness of test
• Appropriate test method
• Data collection validity and reliability
• Consistent chemical composition
• Hazards and risks of use

OCR Applied Science: 21.2.2 Testing During Development
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 2.2 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.2 Laboratory testing during development i.e.:
• formulation
• production
• quality control and assurance
• after sale monitoring.

OCR Applied Science: 21.2.1 Types of Testing
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 2.1 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.1 Types of testing i.e.:
• in-vitro
• in-vivo
• titration
• extraction and separation

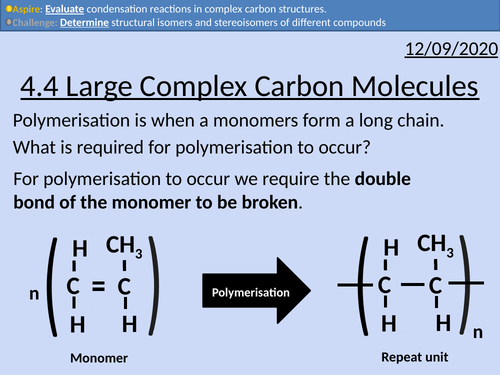
OCR Applied Science: 4.4 Large Complex Carbon Molecules
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 4.4 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Complex carbohydrates (starch, glycogen, cellulose)
• Carbohydrates found as monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides (monomers, dimers or polymers)
• Monomers held together by glycosidic bonds to form dimers and polymers, via condensation reactions
• Monosaccharides include glucose, fructose and galactose
• Disaccharides include maltose, sucrose and lactose
• Polysaccharides include starch, glycogen and cellulose
• Cellulose is found in plant cell walls where it provides strength/support and pliability
• Starch and glycogen are energy sources
Proteins and peptides from amino acids
• Dipeptides are formed from two amino acids joined by a peptide bond, via a condensation reaction
• Polypeptides are chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
• Proteins/polypeptides have physiological or functional roles, including enzymes, carrier proteins in the plasma membrane, and structural roles, including collagen and elastin fibres in connective tissue
Lipids from fatty acids, glycerol and phosphorus compounds
• Monoglycerides, diglycerides and triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and glycerol
• An ester bond forms between each fatty acid and the glycerol, via condensation reactions
• Phospholipids contain glycerol plus two fatty acids and a phosphate group
• Lipids act as an energy source within cells, as an insulation layer around animal organs, in the myelin sheath (found around some nerve fibres/axons) to increase speed of nerve transmission
• Phospholipids form a bilayer in the plasma membrane
Protein synthesis (transcription, translation) RNA, messenger, ribosomal and transfer
• The nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, are polymers of nucleotides
• Peptide bonds form between amino acids to create polypeptide chains/proteins
• Recall a simple description of protein synthesis