496Uploads
163k+Views
70k+Downloads
Chemistry

GCSE Chemistry: Electrolysis of Water
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Pure water being made partially of ions (hydrogen and hydroxide).
• PANIC convention for electrodes
• OILRIG convention for redox reactions
• Electron transfers at electrodes
• Half-equations for anode and cathode
• Balancing half-equations

GCSE Chemistry: Detecting Cations
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Flame tests for lithium, sodium, potassium, calcium, and copper.
Electron energy levels and emitting radiation.
Precipitate tests for iron(II)), iron(III), copper(II), calcium, and zinc.

OCR AS Chemistry: Introduction to Reaction Mechanisms
OCR AS Chemistry: 11.5 Introduction to Reaction Mechanisms
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Covalent bonds
Homolytic fission and heterolytic reactions
Curly arrows in reaction mechanisms
Identifying addition, substitution, and elimination reactions.

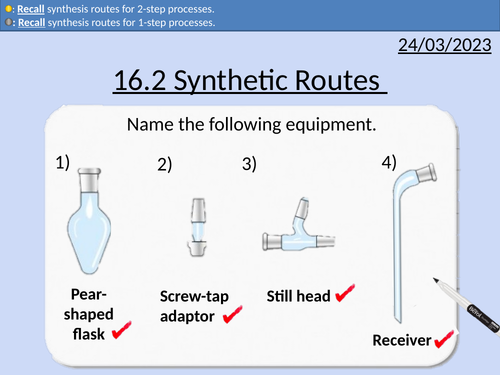
OCR AS Chemistry: Synthetic Routes
OCR AS Chemistry: 16.2 Synthetic Routes
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Functional Groups - Alkane, Alkene, Haloalkane, Alcohols, Carboxylic Acid, Ketone, Aldehyde, Ester, Amine, Nitrile.
One-step synthetic routes with reagents and conditions
Two-step synthetic routes with reagents and conditions

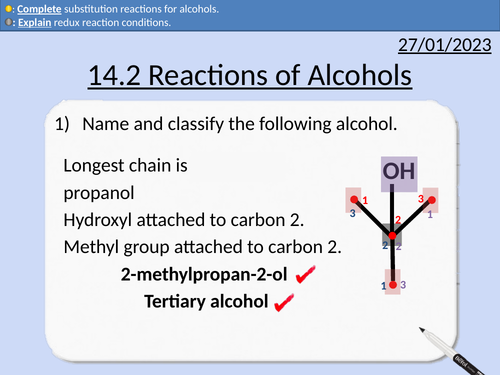
OCR AS Chemistry: Reactions of Alcohols
OCR AS Chemistry: 14.2 Reactions of Alcohols
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Combustion of alcohols
Reflux condition for reactions
Primary alcohol to aldehydes
Primary alcohols to carboxylic acids
Secondary alcohols to ketones
Dehydration of alcohols
Substitution reactions for alcohols

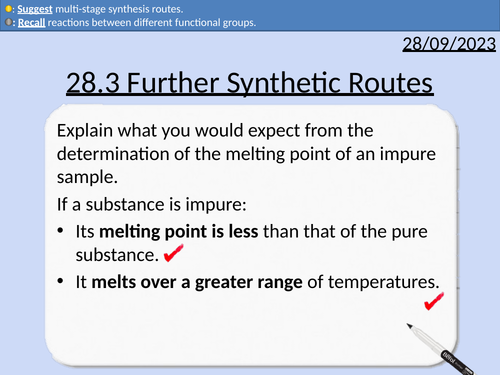
A level Chemistry: Further Synthetic Routes
OCR A level Chemistry: 28.3 Further Synthetic Routes
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Functional groups
Reactions of benzenes
Reactions of phenols
Common reactions between different functional groups
Reaction conditions and reagents

A level Chemistry: Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopy
OCR A level Chemistry: 29.3 Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopyy
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Identifying different carbon environments
The types of carbon environment
The amount of chemical shift ẟ / ppm

GCSE Chemistry: Empirical Formula
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Calculate empirical formula and by finding the simplest whole-number ratio
• Calculate relative formula mass from balanced equations.

OCR Applied Science: 1.2 The Periodic Table
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 1.2 of Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Elements are based on atomic structure and can be classified by the Periodic Table i.e.:
organisation of elements within the table
groups
periods
atomic number
atomic mass atomic radius

OCR Applied Science: 6.2 Physico-chemical Properties of Materials
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 6.2 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Structure of metals, giant covalent, and simple molecular structures.
Properties of metals, giant covalent, and simple molecular structures.
Forces and bonds of metals, giant covalent, and simple molecular structures.
Phase diagrams – interpreting and calculating changes.
Sublimation and phase diagrams.

GCSE Chemistry: Purification and Checking Purity
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Choosing the correct separation technique
• Comparisons of mobile and stationary phases for chromatography
• Rf Values
• Analysing chromatographs in gas chromatography

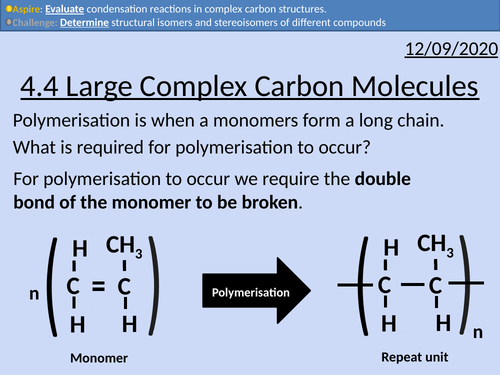
OCR Applied Science: 4.4 Large Complex Carbon Molecules
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 4.4 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Complex carbohydrates (starch, glycogen, cellulose)
• Carbohydrates found as monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides (monomers, dimers or polymers)
• Monomers held together by glycosidic bonds to form dimers and polymers, via condensation reactions
• Monosaccharides include glucose, fructose and galactose
• Disaccharides include maltose, sucrose and lactose
• Polysaccharides include starch, glycogen and cellulose
• Cellulose is found in plant cell walls where it provides strength/support and pliability
• Starch and glycogen are energy sources
Proteins and peptides from amino acids
• Dipeptides are formed from two amino acids joined by a peptide bond, via a condensation reaction
• Polypeptides are chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
• Proteins/polypeptides have physiological or functional roles, including enzymes, carrier proteins in the plasma membrane, and structural roles, including collagen and elastin fibres in connective tissue
Lipids from fatty acids, glycerol and phosphorus compounds
• Monoglycerides, diglycerides and triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and glycerol
• An ester bond forms between each fatty acid and the glycerol, via condensation reactions
• Phospholipids contain glycerol plus two fatty acids and a phosphate group
• Lipids act as an energy source within cells, as an insulation layer around animal organs, in the myelin sheath (found around some nerve fibres/axons) to increase speed of nerve transmission
• Phospholipids form a bilayer in the plasma membrane
Protein synthesis (transcription, translation) RNA, messenger, ribosomal and transfer
• The nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, are polymers of nucleotides
• Peptide bonds form between amino acids to create polypeptide chains/proteins
• Recall a simple description of protein synthesis

GCSE Chemistry: Ionic Compounds
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Filled outer shells result in more stable electronic structures.
• The electronic configuration ionic compounds
• Models of giant ionic structures
Bundle

OCR Applied Science: 21.2 Product Testing of Consumer Products
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.1 Types of testing i.e.:
• in-vitro
• in-vivo
• titration
• extraction and separation
2.2 Laboratory testing during development i.e.:
• formulation
• production
• quality control and assurance
• after sale monitoring.
2.3 Effectiveness of test i.e.:
• Appropriate test method
• Data collection validity and reliability
• Consistent chemical composition
• Hazards and risks of use (e.g. toxicity, possible mutagenic and
teratogenic effects, microbiological safety)

GCSE Chemistry: Conservation of Mass
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• State the number of atoms from a chemical formula.
• Relative Atomic masses and relative formula mass
• Practical activity of non-closed chemical reactions.

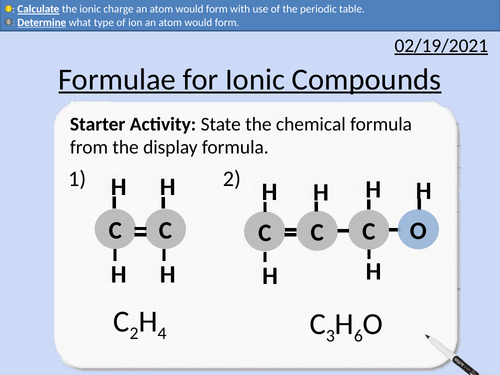
GCSE Chemistry: Formulae for Ionic Compounds
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• State the number of electrons in each energy level.
• Determine what type of ion an atom would form.
• Calculate the ionic charge an atom would form with use of the periodic table.
• Groups number, outer shell electrons, dot and cross diagrams

GCSE Chemistry: Group 1 - Alkali Metals
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of Alkali Metals
• Properties of Alkali Metals
• Trends and anomalies in Group 1 (Density, Melting Point)
• Reactivity of Group 1 Alkali Metals
• Electron configuration of Group 1 Alkali Metals

GCSE Chemistry: Reactivity of Elements
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Group 1, 2, 7, 0 electron structures
• Reactivity series for metals
• Equation for metals and water
• Equation for metals and acid
• Displacement reactions for metals

GCSE Chemistry: Detecting Gases
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Tests for Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, Chlorine.
Gifs of each gas test
Electron structure for diatomic molecules
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry C4.1 Predicting and identifying reactions and products
C4.1 Predicting and identifying reactions and products
All resources for P4.1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Group 1 - The Alkali Metals
Group 7 - The Halogens
Halogen Displacement Reactions
Group 0 - The Noble Gases
The Transition Metals
Reactivity of Elements