496Uploads
163k+Views
70k+Downloads
Physics

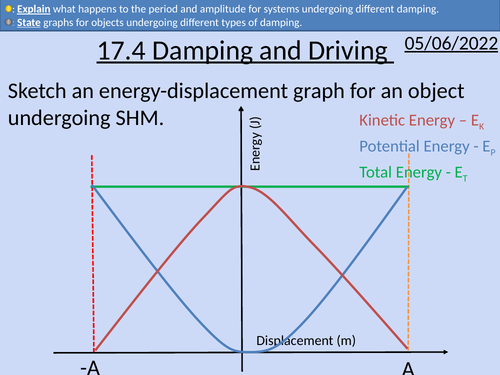
OCR A Level Physics: Damping and Driving
OCR A Level Physics: Damping and Driving presentation with homework and answers

GCSE Physics: Thermal Conducitvity and Cooling Curves
These two lesson presentations covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.2.4 Thermal conductivity and Cooling Curves
Definition for thermal conductivity
Energy transfers and conservation of energy
Reducing energy dissipation
Practical procedure and results analysis

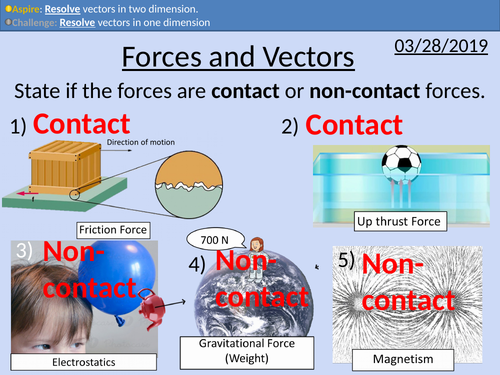
GCSE Physics: Forces and Vectors
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Vector addition in 1D
Vector addition in 2D
Resolving vectors

GCSE Physics: Acceleration Practical
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Acceleration experiment protocol
• Ensuring results are reproducible and repeatable
Spotting and removing anomalies.
Rearranging equations

GCSE Physics: Electrical Resistance
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Ohm’s law and units
• Proportionalities
• Resistance in series
• Rearranging equations
• Calculating resistance with ohm’s law

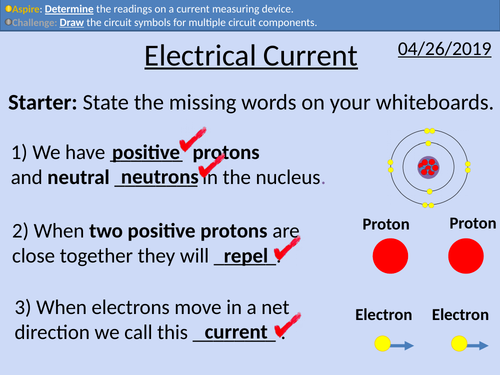
GCSE Physics: Electrical Current
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Circuit symbols
• Conditions for current to flow
• Measuring current in series circuits
• Measuring current in parallel circuits.

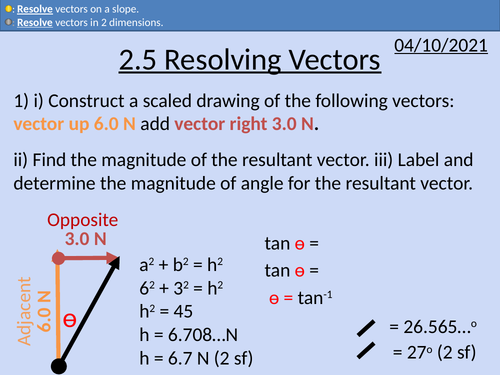
OCR AS level Physics: Resolving Vectors
OCR AS level Physics: Resolving Vectors is a part of the Module 2: Foundations of Physics
Full lesson PowerPoint with worked examples and homework with complete worked answers.
Using trigonometry to solve vector problems
Vectors in 2 D
Resolving vectors on a slope

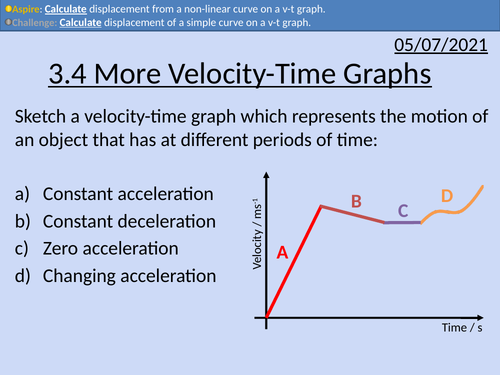
OCR AS level Physics: More Velocity-Time Graphs
OCR AS level Physics: More Velocity-time Graphs is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

OCR AS level Physics: Free fall and g
OCR AS level Physics: Free fall and g is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Definition of free fall and gravitational force.
Dimensional analysis of units for acceleration and g.
Determining g with equations of constant acceleration (suvat equations).
Determining g with finding the gradient of graphs.
Determining g experimentally with stopwatches, trap doors, light gates, and cameras with strobes.

OCR AS level Physics: Force, mass, and weight
OCR AS level Physics: Force, mass, and weight is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

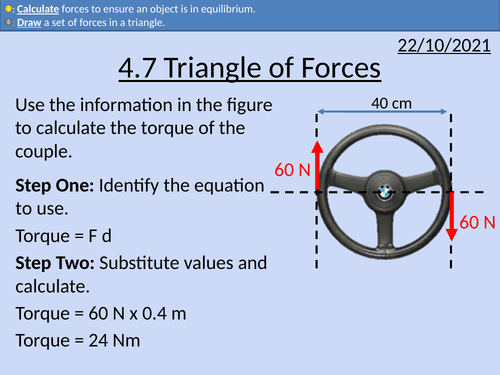
OCR AS level Physics: Triangle of Forces
OCR AS level Physics: Triangle of Forces is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

OCR AS level Physics: Double Slit Experiment
OCR AS level Physics: Double Slit Experiment is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

OCR AS level Physics: Stationary Waves
OCR AS level Physics: Stationary Waves is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

OCR AS level Physics: Wave-Particle Duality
OCR AS level Physics: Wave-Particle Duality is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
Full lesson PowerPoint with worked examples and homework with complete worked answers.
deBroglie wavelength equation
Diffraction of electrons and protons
Comparing wavelengths of particles with different masses
Kinetic energy and wavelength

OCR Applied Science: 6.3 Electrical Properties
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 6.3 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Current as flow of charge in a conductor.
Use the equation: I = ΔQ ÷ Δt
Ohm’s law illustrates the relationship of V ∝ I
Use the equation: potential difference (V) = current (A) × resistance
Use the equations for adding resistors in series and parallel
Compare electromotive force and potential difference
Use the equation: charge © = current (A) × time (s)
Use and recognise the equation for mean drift velocity
Use the equation: energy transferred (work done) (J) = charge © × potential difference (V)
Use the equation: energy transferred (J, kWh) = power (W, kW) × time (s, h)
Use the equation: power (W) = energy (J) ÷ time (s)

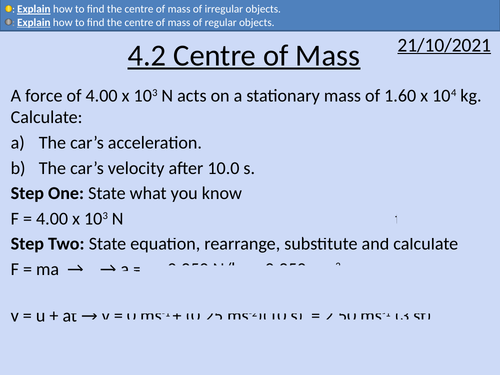
OCR AS level Physics: Centre of Mass
OCR AS level Physics: Centre of mass is a part of the Module 3: Force and Motion
Full lesson PowerPoint with worked examples and homework with complete worked answers.

GCSE Physics: Electromagnetic Reflection
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.3.1a Electromagnetic Reflection. Includes student activities and full worked answers.
Law of reflection
Labeling and measuring angles of incidence and reflection
Practical activity instructions - fully animated.
Reflection, absorption, and refraction is affected by wavelength of electromagnetic wave.

OCR AS Physics: Thermistor
OCR AS Physics A: Thermistor is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Thermistor uses
Thermistors with negative temperature coefficients
Plotting I-V curves for thermistors
Creating an experiment to test thermistors.

OCR AS Physics: Paying for Electricity
OCR AS Physics: Paying for Electricity is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Converting time to hours
Using different units for electrical energy
Converting from J to kW hr
Calculating the cost of using different electrical appliances.

GCSE Physics: Generators
This lesson presentations covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P4.2.4 Generators.
Uses of generators
AC and DC definitions
Structure of dynamos and alternators
Comparing dynamos and alternators.
Plotting graphs for induced potential difference from dynamos and alternators
Commercial generators, 230 V at 50 Hz.