496Uploads
163k+Views
70k+Downloads
Physics

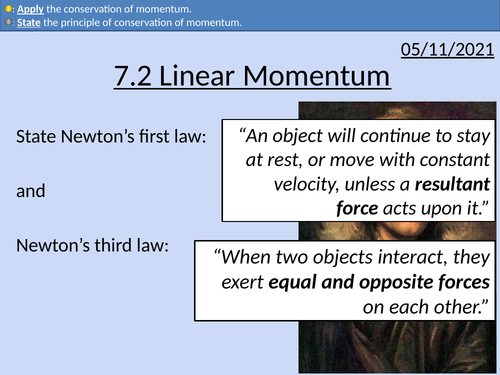
OCR AS level Physics: Linear Momentum
OCR AS level Physics: Linear Momentum is a part of the Module 3: Laws of Motion and Momentum. Presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

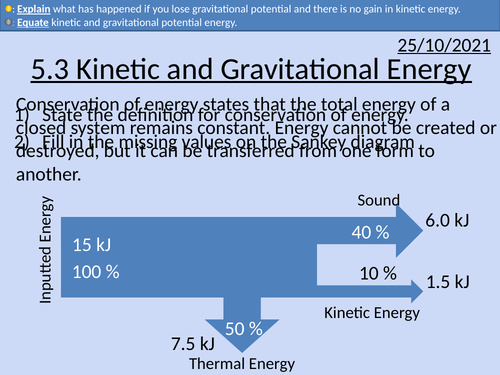
OCR AS level Physics: Kinetic and Gravitational Potential Energy
OCR AS level Physics: Kinetic and Gravitational Potential Energy is a part of the Module 3: Work, Energy and Power.
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

OCR AS level Physics: Einstein's Photoelectric Equation
OCR AS level Physics: Einstein’s Photoelectric Effect Equation is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
Full lesson PowerPoint with worked examples and homework with complete worked answers.
The photoelectric equation
Work function and Kinetic Energy
Determining work function from a graph
Determining threshold frequency from a from graphical analysis.
Determining Plank’s constant from graphical analysis.

OCR Applied Science: 21.1 Regulatory Bodies
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 1.1 and 1.2 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
Understand the influence of regulatory bodies on development of consumer products.
1.1 The relevant governing bodies that oversee product safety for
manufacturers and consumers of products.
1.2 How governing bodies influence how quality control is applied.

OCR Physics P2 Forces Revision
This revision PowerPoint should take approximately 5 hours of class time to complete.
This PowerPoint covers GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
** P2.1 Motion:**
Distance, time and speed
Vectors and Scalars
Acceleration
Distance-time graphs
Velocity-time graphs
Kinetic Energy
** P2.2 Newton’s Laws:**
Forces and Interactions
Free Body Diagrams
Newton’s First Law
Newton’s Second Law
Everyday Forces
Momentum
Work Done and Power
P2.3 Forces in Action:
Stretching springs
Stretching materials and storing energy
Gravitational Fields and Potential Energy
Turning Forces
Simple Machines
Hydraulics

OCR A level Physics: Angular Acceleration
OCR A level Physics: Angular Acceleration and the Radian is a part of the Module 5: Newtonian world and astrophysics.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks with answers.

OCR A level Physics: Angular Velocity and the Radian
OCR A level Physics: Angular Velocity and the Radian is a part of the Module 5: Newtonian world and astrophysics.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks with answers.

OCR A level Physics: Exploring Centripetal Forces
OCR A level Physics: Centripetal Force and the Radian is a part of the Module 5: Newtonian world and astrophysics.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks with answers.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics P5.2 Electromagnetic Spectrum
Resources for P5.2 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1 Triple and Combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each lesson includes student activities and full worked answers.
Order of the electromagnetic spectrum
Wavelength and frequency relationship
Application of wave speed equation
Rearranging equation
Producing and detecting radio waves
Recall that light is an electromagnetic wave
Give examples of some practical uses of electromagnetic waves in the radio, micro-wave, infra-red, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray and gamma-ray regions
Describe how ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays can have hazardous effects, notably on human bodily tissues.
Explain that electromagnetic waves transfer energy from source to absorber to include examples from a range of electromagnetic waves
Precautions for ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays
Careers: Medical Physicist
X-rays
CT scans
Gamma imaging
Thermogram
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Precautions for using ionising radiation

GCSE Physics: Electromagnetic Refraction
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.3.2a Electromagnetic Reflection.
Includes student activities and full worked answers.
Refraction the change of velocity - speed and direction
Magnitude of refraction depending on wavelength
Magnitude of refraction depending on optical density
Refraction practical activity instructions
Wave speed, wavelength, and frequency relationship in refraction

OCR AS Physics: Diodes
OCR AS Physics A: Diodes is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Polarity of diodes
Conventional current and diodes
Plotting I-V curves for diodes
Describing I-V curves for diodes

OCR AS Physics: Combining Resistors
OCR AS Physics A: Combining Resistors is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Rules for adding resistors in series and parallel
Applying adding resistors in series and parallel

OCR AS Physics: Analysing Circuits
OCR AS Physics: Analysing Circuits is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Drawing and labeling circuit diagrams
Adding Resistors in Series and Parallel
Ohm’s Law
Kirchhoff’s Laws
The Electrical Power Equation

OCR AS Physics: Wave Properties
OCR AS Physics: Wave Properties is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

GCSE OCR Physics: Circuit Calculations
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P3.2.6 Circuit Calculations.
Measuring current and potential difference
Adding resistors in series and parallel
Rearranging Ohm’s Law
Rules for series circuits
Worked solutions to series circuit exam questions
Rules for parallel circuits
Worked solutions to parallel circuit exam questions

GCSE Physics: Atomic Model 2
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.1.2
Scientific Models
Dalton’s model
Rutherford’s model
Bohr’s model

GCSE Physics: Density
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.2.1
Presentation includes
Calculating volume for regular shapes
Conversion from grams (g) to kilograms (kg) and centimetres (cm) to meters (m) with exercise and answers
Converting with standard form with examples and solutions
Applying the density equation with examples and solutions
Proportionalities
Plenary exam question and solution

GCSE Physics: Density Practical
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.2.1
Presentation includes
Conversion from grams (g) to kilograms (kg) and centimetres (cm) to meters (m) with exercise and answers
Finding volume of regular and irregular shapes
Plenary Exam Question and Answer

GCSE Physics: Specific Heat Capacity
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.2.3
Presentation includes:
Definition of SHC
Real life examples of SHC
SHC equation with example
SHC equation questions with worked solutions
Exam question with solution

GCSE Physics: Pressure and Surface Area
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.3.2 Pressure and Volume
This presentation includes:
Calculating surface area
Pressure equation with worked example
Rearranging pressure equation
Pressure equation problems with full solutions