496Uploads
163k+Views
70k+Downloads
Physics

OCR A level Physics: Capacitors
OCR A level Physics: 21.1 Capacitors
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Electrical quantities, symbols, and units
SI prefixes and standard form
Definition of a capacitor
Structure of a capacitor
Calculating capacitance, charge, and potential difference.
Bundle

GCSE Physics: P3 Electricity Full Scheme
All resources for P3 Electricity GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Electrostatics
Electrical Current
Electrical Current Practical Activity
Circuit Symbols and Potential Difference
Series and Parallel Circuits
Resistance and Ohm’s Law
Resistance of a wire Practical Activity
I-V Characteristics and Component Graphs
Circuit Calculations
Sensing Circuits
Electrical Power and Energy
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics P4 Magnetism
All resources for P4 Magnetism and Magnetic Fields for GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1.Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
• Magnets and Magnetic Fields
• Currents and Fields
• Right Hand Cork-screw Rule
• Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
• Currents and Forces
• Motors
• Electromagnetic Induction
• Generators
• Transformers
• Speakers and Microphones

OCR AS level Physics: Projectile Motion
OCR AS level Physics: Projective Motion is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Includes:
Resolving vectors in 2D
Pythagoras’ theorem:
Equations of constant acceleration - suvat equations
Projectiles being dropped
Projectiles fired at and angle to the horizontal
Velocity-time graphs

OCR A level Physics: Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
OCR A level Physics: 19.3 Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Definition of luminosity
Usual axis choice of a HR diagram.
Identifying the positions of the main sequence, white dwarfs, red giants, and red supergiants.
Description of how stellar evolution is shown in a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P1 Matter Full scheme
All resources for P1 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1.Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
End of topic test
Scheme of work
Development of the atomic model
Density
Temperature
Specific Latent Heat
Specific Heat Capacity
Pressure and Temperature
Pressure and Area
Pressure are Volume
Atmospheric Pressure
Liquid Pressure
Sinking and Floating

GCSE Physics: Nuclear Fission
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P6.2.2 Nuclear Fission
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Conservation of mass
Uranium as a nuclear fission fuel
Nuclear fission process
Chain reactions in nuclear fission reactions
Control rods and moderators in nuclear reactors
Benefits and disadvantages of nuclear fission reactors.
Mass-Energy Equivalence

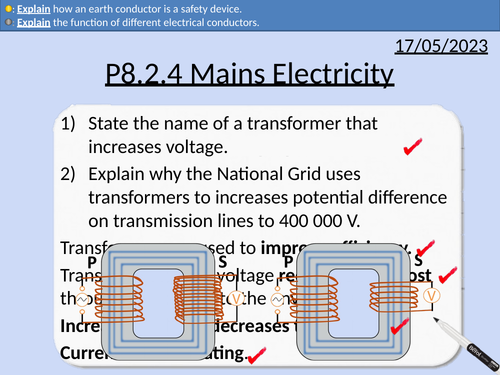
GCSE Physics: Mains Electricity
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.2.4 Mains Electricity
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Domestic Electrical Supply being 230 V, AC at 50 Hz.
Direct potential difference and alternating potential difference.
Reasons for insulation on wires.
Potential Difference between different conductors.
Function of the earth conductor.
Double insulation and no earth wire.
Reasons the live wire is dangerous.
Reasons why live to earth is dangerous.

OCR AS level Physics: Resistance and Resistivity
OCR AS level Physics: Resistance and Resistivity is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Factors affecting resistance
Calculating resistivity
Resistivity and temperature
Experimentally determining resistivity
Using a graph to calculate resistivity

GCSE Physics: Hooke's Law Practical
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of Hooke’s Law
• Converting from centimeters to meters
• Converting from millimeters to meters
• Calculating the spring constant from a gradient of a force-extension graph
• The parallax effect and good experimental practice
• Data analysis (calculating mean and significant figures).

OCR AS Physics: Potential Dividers
OCR AS Physics A: Potential Divider is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Application of the ratio of resistances
Application of the potential divider circuit
Deriving the potential divider equation
Rearranging the potential divider equation

GCSE Physics: Absorption and Emission Spectra
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P6.1.5 Radiation in and out of atoms.
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Arrangements of electrons and distance from the nucleus
Electron energy levels
Absorbing electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation and energy
Absorption spectra
Emission spectra
Discovery of helium
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P6 Radiation
All resources for GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1 P6 Radiation.
Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Atoms and Isotopes
Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Radiation
Nuclear Equations
Half-life
Radiation and the body
Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear Fission
Radiation in and out of atoms

OCR A Level Physics: Kepler’s Laws
OCR A level Physics: 18.4 Kepler’s Laws
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The terms: eccentricity, aphelion, perihelion, astronomical unit
Kepler’s First Law
Kepler’s Second Law
Kepler’s Third Law
Graphs of T^2 against r^3 to determine the gradient (constant of proportionality, k).
Equating (4π)^2/𝐺𝑀 to the gradient (constant of proportionality, k)

OCR A level Physics: Spectra
OCR A level Physics: 19.5 Spectra
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The electromagnetic spectrum and wavelengths
Definition of spectroscopy
Electrons and energy levels
Continuous spectra
Emission spectra from gases
Absorption spectra from gases

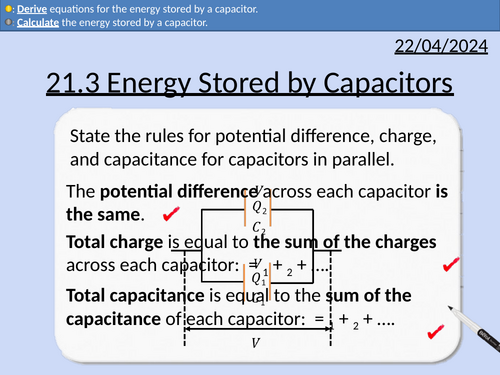
OCR A level Physics: Energy Stored by Capacitors
OCR A level Physics: 21.3 Energy Stored by Capacitors
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Work done of a capacitor depends upon the initial potential difference and capacitance.
Work done is provided by the source of potential difference.
Deriving three equations for work done of a capacitor.

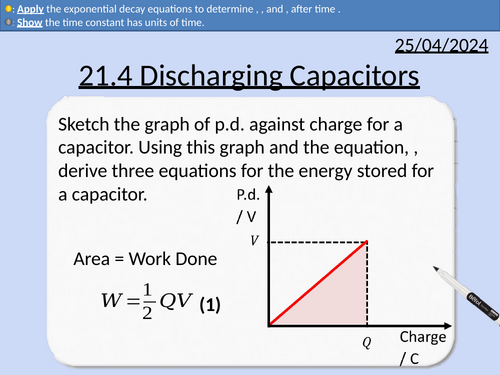
OCR A level Physics: Discharging Capacitors
OCR A level Physics: 21.4 Discharging Capacitors
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Exponential increase and exponential decay
Explaining how capacitors discharge through a resistor in parallel
Definition of time constant for a capacitor
Showing that time constant has units of seconds
Iterative method for finding how capacitors discharge
Using exponentials and logs.
Solving a differential equation (needed for A-level Maths).

GCSE Physics: Speakers and Microphones
This lesson presentations covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P4.2.6 Speakers and Microphones.
Definition of sound waves.
Structure and operation of a speaker.
Fleming’s left hand rule.
Structure and operation of a microphone.
Electromagnetic induction.
Comparison of speakers and motors.
Comparison of microphone and generators.
Comparing microphones and speakers

OCR A Level Physics: Gravitational Potential
OCR A level Physics: 18.6 Gravitational Potential
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Center of mass and treating spherical objects as point masses
Gravitational fields
Definition of gravitational potential
Applying the gravitational potential equation
Graph of gravitational potential against distance (V against r)
Combining gravitational potentials from more than one mass

GCSE Physics: Momentum
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.2.6
Momentum Equation
Rearranging the momentum equation
Momentum as a vector
Vector addition with momentum
Exam question with worked solutions
Student problems with answers
Proportionalities