484Uploads
144k+Views
63k+Downloads
Physics

OCR A level Physics: Life Cycles of Stars
OCR A level Physics: 19.2 Life Cycles of Stars
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Calculating mass in kg from solar mass
Life cycle of stars with a mass between 0.5 and 10 solar masses
Life cycle of stars with a mass above 10 solar masses
Pauli exclusion principle and electron degeneracy pressure
Red giants and white dwarfs
The Chandrasekhar limit
Red supergiants to black holes and neutron stars
Stellar nucleosynthesis

OCR A level Physics: Objects in the Universe
OCR A level Physics: 19.1 Objects in the Universe
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The size of astronomical objects: Universe, Galaxies, Solar systems, Stars, Planets, Planetary satellites, Comets, Artificial planetary satellites
Comparing planets and comets
The birth of stars
Stars in equilibrium during the main sequence

OCR A level Physics: Spectra
OCR A level Physics: 19.5 Spectra
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The electromagnetic spectrum and wavelengths
Definition of spectroscopy
Electrons and energy levels
Continuous spectra
Emission spectra from gases
Absorption spectra from gases

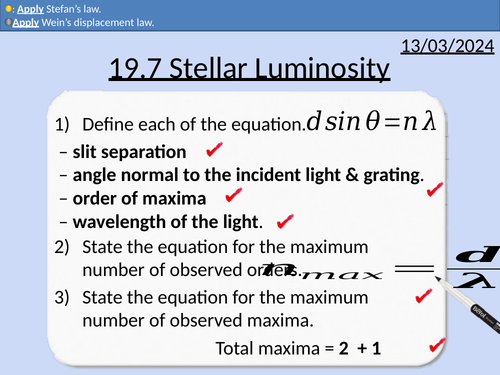
OCR A level Physics: Stellar Luminosity
OCR A level Physics: 19.7 Stellar Luminosity
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The electromagnetic spectrum, frequency/wavelength, and temperature
Black body radiation
Wein’s displacements law
Stefan’s law (Stefan-Boltzmann law)

OCR A level Physics: Capacitors
OCR A level Physics: 21.1 Capacitors
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Electrical quantities, symbols, and units
SI prefixes and standard form
Definition of a capacitor
Structure of a capacitor
Calculating capacitance, charge, and potential difference.

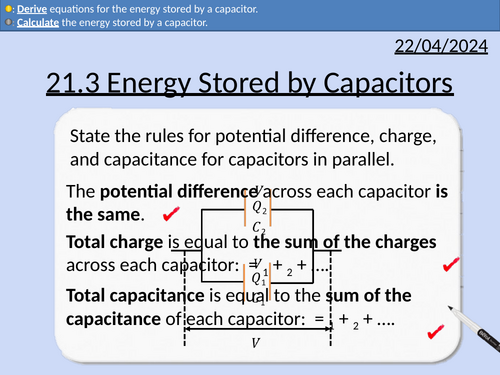
OCR A level Physics: Energy Stored by Capacitors
OCR A level Physics: 21.3 Energy Stored by Capacitors
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Work done of a capacitor depends upon the initial potential difference and capacitance.
Work done is provided by the source of potential difference.
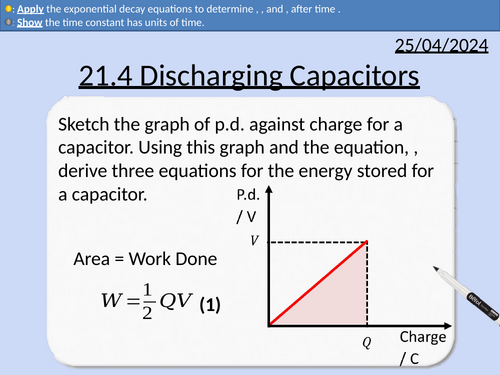
Deriving three equations for work done of a capacitor.

OCR A level Physics: Discharging Capacitors
OCR A level Physics: 21.4 Discharging Capacitors
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Exponential increase and exponential decay
Explaining how capacitors discharge through a resistor in parallel
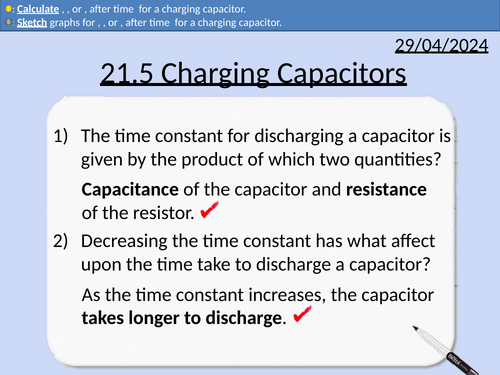
Definition of time constant for a capacitor
Showing that time constant has units of seconds
Iterative method for finding how capacitors discharge
Using exponentials and logs.
Solving a differential equation (needed for A-level Maths).

OCR A level Physics: Charging Capacitors
OCR A level Physics: 21.5 Charging Capacitors
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Explaining how capacitors charge with a resistor in series
Explaining how 𝑉, 𝐼, or 𝑄, change with time 𝑡 for a charging capacitor.
Sketching graphs for 𝑉, 𝐼, or 𝑄, after time 𝑡 for a charging capacitor.
Calculating 𝑉, 𝐼, or 𝑄, change with time 𝑡 for a charging capacitor.
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Radioactivity
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 25 Radioactivity is apart of the Module 6: Particle and Medical Physics
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
25.1 Radioactivity
25.2 Nuclear decay equations
25.3 Half-life and Activity
25.4 Radioactive Decay Calculations
25.5 Modelling Radioactive Decay
25.6 Radioactive Dating
Types of ionising radiation (alpha, beta-plus/beta-minus, gamma)
Penetration power and ionising power
Detecting radiation with a Geiger (GM tube) counter
Background radiation and correct count rates
Electric and magnetic fields affect ionising radiation
Cloud chambers
Typical speeds of radiation produced form nuclear decays
Conservation rules for nuclear decays
Nuclear notation
Alpha decays
Beta-minus and beat-plus decays
Gamma decays
Decay chains
The reason why radioactive decays are considered random and spontaneous
Rolling dice being a good analogue for radioactive decays
Definition of half-life
Determining half-life from a graph.
Calculating half-life from a table of data.
Activity of a sample in Bq
The decay constant derivation
Decay constant and half-life
Using exponentials to calculate activity and number of nuclei present
Solving Differential Equations (beyond A-level Physics course)
Iterative Method
Selecting appropriate time intervals
Comparing answers from the iterative method and exact solution.
State what isotopes of carbon are used in carbon dating.
Explain how carbon dating works.
Calculate the age of objects with carbon dating.

OCR AS level Physics: Resistance
OCR AS Physics A: Resistance is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Definition of an ohm.
Temperature and resistance for metallic conductors (wires)
The ohm in base SI units
I against V graphs and resistance

OCR AS Physics: Electromagnetic Waves
OCR AS Physics A: Electromagnetic Waves is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

GCSE Physics: Simple Circuits
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P3.2.1 Simple Circuits.
Circuit Symbols
Electric field lines and potential difference
Modeling Circuits with Rope
Measuring Potential Difference
Energy Transferred Equation for Electricity
Rearranging Equations

OCR AS Physics: Total Internal Reflection
OCR AS Physics A: Total Internal Reflection is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

GCSE Physics: Resistance and Ohm's Law
This presentations covers the OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P3.2.3 Resistance
Combining resistors in series
Combining resistors in parallel
Modeling resistance, current, and potential difference with a rope.
The relationship between potential difference and current
The relationship between resistance and current
Ohm’s law
Rearranging equations
Worked examples and student questions
Explaining how increasing current increases resistance in a metal conductor and filament lamp.

GCSE Physics: LDRs and Thermistors
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P3.2.5 LDR and Thermistors.
Circuit Symbols
Uses of LDRs and Thermistors
Plotting data and characteristic curves
Conductors, insulators, and semiconductors
Experiment into resistance and temperature of a thermistors
Investigation into resistance and light level of a LDR

GCSE Physics: Current and Forces with Equation
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P4.2.1 b Current and Forces.
Units for Magnetic Field Strength
Converting from mT to T
Magnetic Force Equation
Rearranging Equations
Increasing the force on a current carrying conductor in an external magnetic field.
Student questions and worked answers

GCSE Physics: Free Body Diagrams
This presentation covers GCSE Physics OCR Gateway P2.2.2
Vector Addition 1D
Vector Addition 2D - scaled drawings
Vector Addition 2D - finding angles with a protractor
Resultant vectors and acceleration
Student problems with answers.

GCSE Physics: Stretching Springs
These two lesson presentations covers the OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.3.1 material.
• Number of forces needed to deform an object
• Elastic and Plastic definitions
• Hooke’s Law
• Rearranging equations
• Determining the gradient
• Determining the spring constant
• Experimental procedure
• Exam style questions with solutions

GCSE Physics: Moments and Turning Forces
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.3.4 Turning Forces
Clockwise and anti-clockwise moments
Equation for moments
Rearranging equation
Balancing moments
Principle of moments

GCSE Physics: The Acceleration Equation
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Acceleration equation with units
• Speed-time graphs