496Uploads
163k+Views
70k+Downloads
All resources

GCSE Chemistry: Filtration and Crystallisation
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Definitions for solution, solute, solvent, insoluble, soluble.
The technique of filtration
The technique of crystallisation

GCSE Chemistry: Pure and Impure Substances
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Definitions of pure and impure substances
Definition of an alloy
Identification of purity with melting points
Plotting graphs and data analysis

GCSE Chemistry: Paper Chromatography & Rf Values
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of technique for paper chromatography
• Experimental procedure
• Definitions of stationary and mobile phase
• Application of Rf equation with examples and answers

OCR Applied Science: 6.2 Physico-chemical Properties of Materials
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 6.2 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Structure of metals, giant covalent, and simple molecular structures.
Properties of metals, giant covalent, and simple molecular structures.
Forces and bonds of metals, giant covalent, and simple molecular structures.
Phase diagrams – interpreting and calculating changes.
Sublimation and phase diagrams.

GCSE Chemistry: Simple Distillation
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Changes of state
• The technique of simple distillation
• Concentration of solute increasing in distillation
• Jobs related to chemistry
• Key word test Insoluble, Soluble, Solvent, Solute, Solution, Distillation, Filtration, and Crystallisation

GCSE Chemistry: Purification and Checking Purity
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Choosing the correct separation technique
• Comparisons of mobile and stationary phases for chromatography
• Rf Values
• Analysing chromatographs in gas chromatography

GCSE Chemistry: Thin Layer and Gas Chromatography
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Experimental Procedure for Thin Layer Chromatography
• Analysing and calculating Rf Values
• Pros and cons of paper and TL chromatography
• Experimental procedure for Gas Chromatography
• Persuasive writing and embedding literacy in science

OCR Applied Science: 4.2 Polymers and Carbon Compounds
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 4.2 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Determining the empirical formula for compounds
Draw monomers and repeat units using structural and skeletal formula of the following polymers:
Polyethene
Polypropene
Polylactate
Polystyrene
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)

GCSE Chemistry: Electronic Structures
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Electrons reside in energy levels (shells) around the nucleus
• The electronic configuration of elements up to 20 is 2,8,8,2
• Groups and periods of the periodic table
• Drawing electron configurations

GCSE Chemistry: Metals and Non-metals
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Using the periodic table to identify metals and non-metals
• Different properties of metal and non-metals (Appearance, melting and boiling point, state of matter at room temperature, ductility, and malleability).
• Exceptions of physical properties (mercury being liquid and carbon conducting electricity).

GCSE Chemistry: Simple Molecules
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Dot and cross diagrams of simple molecules
• Simple molecules form covalent bonds
• The group number on the periodic table informs us how many electrons are in the outer shell.
• Groups on the periodic table

GCSE Chemistry: Ionic Compounds
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Filled outer shells result in more stable electronic structures.
• The electronic configuration ionic compounds
• Models of giant ionic structures

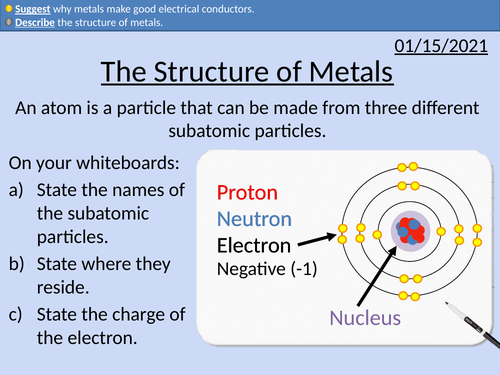
GCSE Chemistry: The Structure of Metals
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• State a use for metals
• Describe the structure of metals
• Why metals make good electrical conductors.
• Metals on the periodic table

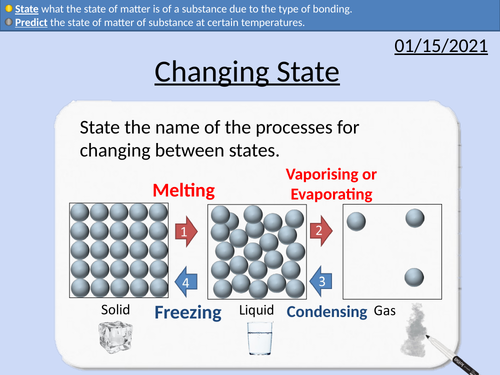
GCSE Chemistry: Changing State
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Define melting and boiling point of a pure substance.
• Predict the state of matter of substance at certain temperatures.
• State what the state of matter is of a substance due to the type of bonding.
• Metals, covalent structures, ionic structures and simple molecules.

GCSE Chemistry: Bulk Properties
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Jobs in Material Science
• Bulk properties of metals - malleable and conductors of electricity
• Bulk properties of ionic and covalent structures - brittle
• Explain why substances conducting electricity depends upon the state of matter

OCR Applied Science: 21.1 Regulatory Bodies
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 1.1 and 1.2 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
Understand the influence of regulatory bodies on development of consumer products.
1.1 The relevant governing bodies that oversee product safety for
manufacturers and consumers of products.
1.2 How governing bodies influence how quality control is applied.

OCR Applied Science: 21.2.2 Testing During Development
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 2.2 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.2 Laboratory testing during development i.e.:
• formulation
• production
• quality control and assurance
• after sale monitoring.

GCSE Chemistry: Carbon
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• State processes of the carbon cycle.
• Define the word allotrope.
• Explain why allotropes have different properties.
• Graphite, graphene, and fullerenes

OCR Applied Science: 21.2.1 Types of Testing
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 2.1 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.1 Types of testing i.e.:
• in-vitro
• in-vivo
• titration
• extraction and separation
Bundle

OCR Applied Science: 21.2 Product Testing of Consumer Products
OCR Applied Science Level 3 - Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
2.1 Types of testing i.e.:
• in-vitro
• in-vivo
• titration
• extraction and separation
2.2 Laboratory testing during development i.e.:
• formulation
• production
• quality control and assurance
• after sale monitoring.
2.3 Effectiveness of test i.e.:
• Appropriate test method
• Data collection validity and reliability
• Consistent chemical composition
• Hazards and risks of use (e.g. toxicity, possible mutagenic and
teratogenic effects, microbiological safety)