496Uploads
164k+Views
70k+Downloads
All resources

GCSE Chemistry: Conservation of Mass
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• State the number of atoms from a chemical formula.
• Relative Atomic masses and relative formula mass
• Practical activity of non-closed chemical reactions.

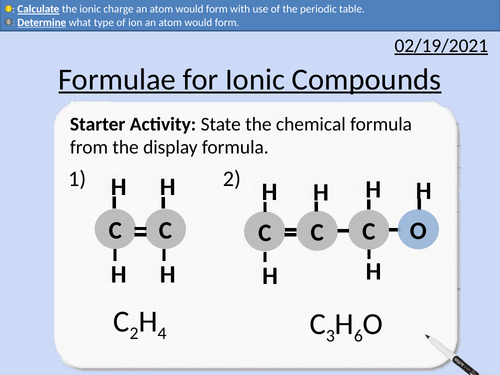
GCSE Chemistry: Formulae for Ionic Compounds
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• State the number of electrons in each energy level.
• Determine what type of ion an atom would form.
• Calculate the ionic charge an atom would form with use of the periodic table.
• Groups number, outer shell electrons, dot and cross diagrams

GCSE Chemistry: Group 1 - Alkali Metals
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of Alkali Metals
• Properties of Alkali Metals
• Trends and anomalies in Group 1 (Density, Melting Point)
• Reactivity of Group 1 Alkali Metals
• Electron configuration of Group 1 Alkali Metals

GCSE Chemistry: Reactivity of Elements
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Group 1, 2, 7, 0 electron structures
• Reactivity series for metals
• Equation for metals and water
• Equation for metals and acid
• Displacement reactions for metals

GCSE Chemistry: Detecting Gases
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Tests for Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, Chlorine.
Gifs of each gas test
Electron structure for diatomic molecules
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry C4.1 Predicting and identifying reactions and products
C4.1 Predicting and identifying reactions and products
All resources for P4.1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Group 1 - The Alkali Metals
Group 7 - The Halogens
Halogen Displacement Reactions
Group 0 - The Noble Gases
The Transition Metals
Reactivity of Elements

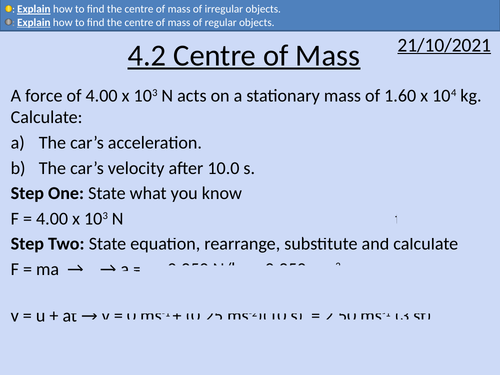
OCR AS level Physics: Centre of Mass
OCR AS level Physics: Centre of mass is a part of the Module 3: Force and Motion
Full lesson PowerPoint with worked examples and homework with complete worked answers.

GCSE Chemistry: Biological Polymers
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Proteins as polymers and amino acids as monomers
Carbohydrates and simple sugars
Comparing simple sugars (glucose, fructose, and sucrose) with complex carbohydrates (starch).
DNA as a polymer and nucleotides as monomers
Structure of nucleotides (phosphate group,
a sugar (deoxyribose), and an organic base).
Base pairing in DNA and hydrogen bonds

OCR AS Chemistry: Alkanes
OCR AS Chemistry: 12.1 Alkanes
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Sigma bonds (σ-bonds).
Tetrahedral shape and bond angles
Fractional distillation
Chain length and boiling point
Branching and boiling point
London Forces
Bundle

OCR AS level Chemistry: Alkanes
OCR AS level Chemistry: Alkanes is apart of the Module 4: Core Organic Chemistry and Analysis
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks

GCSE Physics: Electromagnetic Reflection
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.3.1a Electromagnetic Reflection. Includes student activities and full worked answers.
Law of reflection
Labeling and measuring angles of incidence and reflection
Practical activity instructions - fully animated.
Reflection, absorption, and refraction is affected by wavelength of electromagnetic wave.

OCR AS Physics: Thermistor
OCR AS Physics A: Thermistor is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Thermistor uses
Thermistors with negative temperature coefficients
Plotting I-V curves for thermistors
Creating an experiment to test thermistors.

OCR AS Physics: Paying for Electricity
OCR AS Physics: Paying for Electricity is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Converting time to hours
Using different units for electrical energy
Converting from J to kW hr
Calculating the cost of using different electrical appliances.

GCSE Physics: Generators
This lesson presentations covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P4.2.4 Generators.
Uses of generators
AC and DC definitions
Structure of dynamos and alternators
Comparing dynamos and alternators.
Plotting graphs for induced potential difference from dynamos and alternators
Commercial generators, 230 V at 50 Hz.

OCR A level Physics: Specific Latent Heat
OCR A level Physics: Specific Latent Heat is a part of the Module 5: Newtonian World and Astrophysics. The PowerPoint presentation includes worked examples, solutions and a homework.

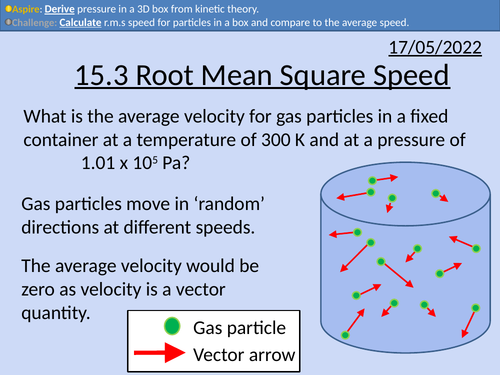
OCR A level Physics: Root mean square speed
OCR A level Physics: Root mean square speed is a part of the Module 5: Newtonian World and Astrophysics. The PowerPoint presentation includes worked examples, solutions and a homework.

OCR A Level Physics: Gravitational Fields
OCR A Level Physics: Gravitational Fields presentation, homework and answers.

GCSE Physics: Kinetic energy and Work done
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.1.1b Kinetic energy and Work done.
PowerPoint includes student activities with fully worked answers included.
Work done and kinetic energy equations
Rearranging equations
Mechanical energy transfer and work done
Kinetic store transfered mechanically to a thermal store through brakes.

GCSE Physics: Gravitational and Elastic Energy
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.1.7 Gravitational and Elastic Energy
Energy transfers with links to sport and PE.
Employer-mentor links with physics and sports
Exam Style Question with worked solutions
Rearranging equations
Practice Questions with worked solutions

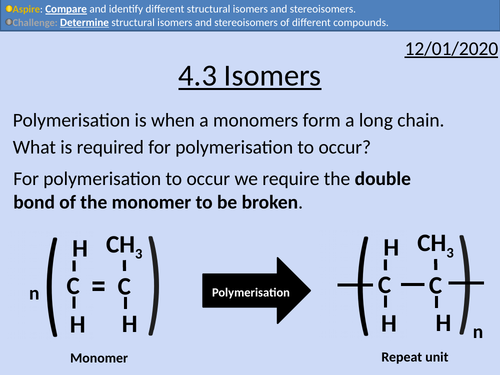
OCR Applied Science: 4.3 Isomers
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 4.3 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
• Stating definitions and comparing structural isomers and stereoisomers.
• Condensed structural formula
• Lines of symmetry for structural isomers
• Cis- and Trans isomers
• Optical isomers as non-superimposable mirror images.
• Wedge and Dash Notation
• Identifying chiral centres (asymmetric carbons)
• Le Bel-van’t Hoff rule
• Determining the maximum number of isomers.