496Uploads
163k+Views
70k+Downloads
All resources

GCSE OCR Physics: Building A Motor
GCSE OCR Physics: Building A Motor powerpoint with instruction on how to construct a motor activity.

GCSE Physics: Atomic Model 1
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.1.1
Covers:
Scientific Models
Ancient Greek Model
Dalton’s Model
JJ Thomson’s model

GCSE Physics: Gravitational Force and Energy
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.3.3 Gravitational Force and Energy
Gravitational fields
Gravitational field strength and mass
Gravitational energy and work done
Exam style questions and solutions
Student problems with answers

GCSE OCR Physics P2 Test
35 mark assessment with mark scheme for P2 from OCR Gateway Physics 9-1.
• 5 multiple choice questions
• Scalars and Vectors
• Speed
• Acceleration
• Equation of Motion
• Velocity-time graph
• Included physics equations
• PIN cover sheet

GCSE OCR Physics P2 Scheme of Work
Middle term plan for OCR Gateway Physics P2
This coveres:
Code
Combined or Triple
Number of lessons
Math Skills
Equations Introduced
Skills Developed
Content Covered
Practical or Demo

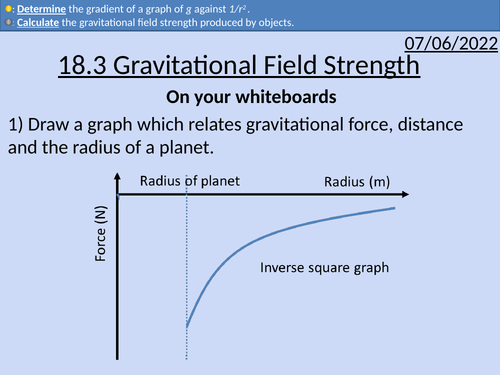
OCR A Level Physics: Gravitational Field Strength
OCR A Level Physics: Gravitational Field Strength presentation with homework and answers

GCSE Physics: Electrical Power and Work Done
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.2.1 Electrical Power and Work Done. All presentations come with student activities and worked solutions.
Definition of power
Converting between W and kW
Converting between seconds, minutes, and hours
Calculating work done in kWh and J
Converting between kWh and J

GCSE Physics: Paying for Electricity
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.2.1 Paying for Electricity
A unit of electricity being a kilo-watt hour (kWh)
Unit cost and calculating costs
Energy bills
Electrical power
Work done = Power x Time
Power = Potential Difference x Current

GCSE Physics: Speed Equation
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• The speed equation and units
• Rearranging Equations
• The skill of estimating

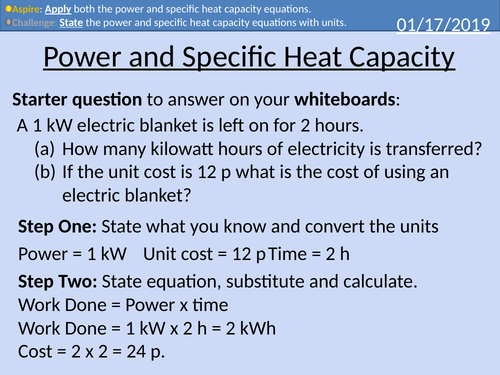
GCSE Physics: Power and Specific Heat Capacity
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.2.3 Power and Specific Heat Capacity.
• Energy Transfers
• Equations and units
• Worked Exam Style Question
• Student questions with numerical solutions

GCSE Physics: Introduciton to Physics
This presentation covers diversity in physics both within the physics community and also with the breadth of what is classified as physics. It contains class activities, a video, and also a research task which could be completed as a class task or as set homework.

GCSE Physics: Introduction to Forces
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Contact and Non-contact forces
Forces and accelerations
Tug of war example

GCSE Physics: Electricity and Subatomic Particles
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Atoms and the particle model for solids, liquids and gases
• Subatomic particles and the property of charge
• Structure of a metal
• Explanations of the Van de Graff and Lightning.

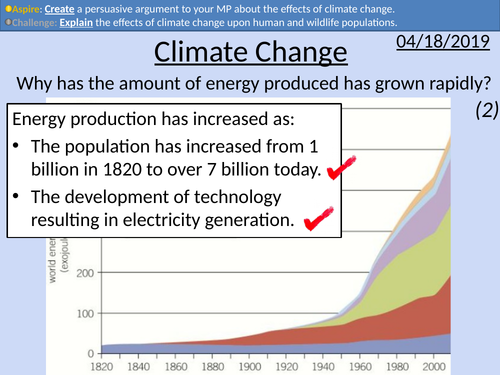
GCSE Physics: Climate Change
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Types of greenhouse gases – carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and water vapour.
• Greenhouse effect with activity
• Class discussion on news report of effects of climate change
• Extended writing task with student friendly mark scheme and scaffolding
• Data analysis task
• Explanation of data collection of CO2 levels
Bundle

GCSE Physics: Physics on the move
This bundle of resources contains 12 lessons for OCR GCSE Physics: Physics on the move.
This is a perfect set of lessons to start your GCSE physics course in year 9 as each lesson builds from the last and doesn’t presuppose any other GCSE physics knowledge.
Scientific definitions from working scientifically
Maths skills and rearranging equations
Planning Experiments
All lessons have worked examples, questions for students, and plenary activities.

GCSE Physics: Balanced Forces
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Balancing forces with vectors
Accelerations and resultant forces

GCSE Physics: Constructing Circuits
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Constructing Series Circuit
• Constructing Parallel Circuits
• Analysing results for Potential Difference
• Analysing results for Current
• Clear resource list, diagrams and photos to aid teaching.

GCSE Physics: Potential Difference
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Modelling potential difference and current
• Circuit symbols and units
• Measuring potential difference
• Series and Parallel circuits

GCSE Physics: Efficiency and Sankey Diagrams
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of efficiency
• Analysing and constructing Sankey diagrams
• Using the efficiency equation
• Rearranging the efficiency equation