496Uploads
163k+Views
70k+Downloads
All resources

GCSE Physics: Half-life
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P6.1.4 Half life
All presentations come with student activities and worked solutions.
Definition of half-life
Radioactive decays are random
Finding half-life from a graph
Constructing a half-life graph
Finding the number of half-lives past using ratios

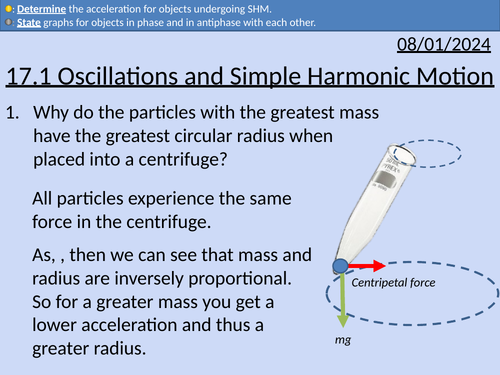
OCR A Level Physics: Simple Harmonic Motion and Oscillations
OCR A Level Physics: Simple Harmonic Motion and Oscillations presentation, homework and answers.

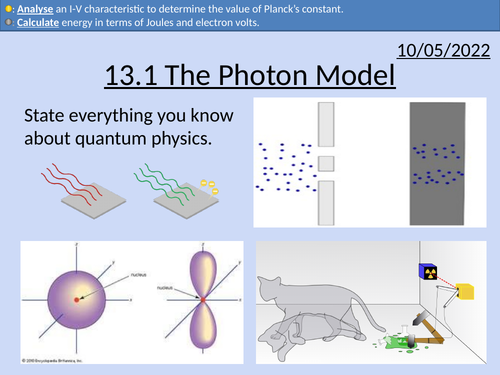
OCR AS Physics: The Photon Model
OCR AS Physics A: The Photon Model is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
Full lesson PowerPoint with worked examples and homework with complete worked answers.
Energy of a single photon
Converting from electron-volts to Joules.
Frequency of the electromagnetic spectrum
Determining Plank’s constant with LEDs
Threshold potential difference difference

GCSE Physics: The National Grid
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.2.3 The National Grid
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Structure of the National Grid
Step-up and Step-down transformers
How transformers increase the efficiency of the National Grid
Number of turns and potential difference
Current and potential difference in primary and secondary coils

GCSE Physics: The Big-Bang
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.3.1 The Big-Bang
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Key facts about the Big-Bang model
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB, CMBR)
Doppler Red shift of light from stars in galaxies
Hubble’s evidence of absorption spectra being red shifted

OCR AS level Physics: The Electron Gun
OCR AS level Physics: The electron gun is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
The structure of an electron gun.
The electron gun in the history of science (J.J. Thomson).
Rearranging equations to equate kinetic energy and work done.
Accelerating potential differences
Comparing the protons and electrons accelerated in a potential difference.

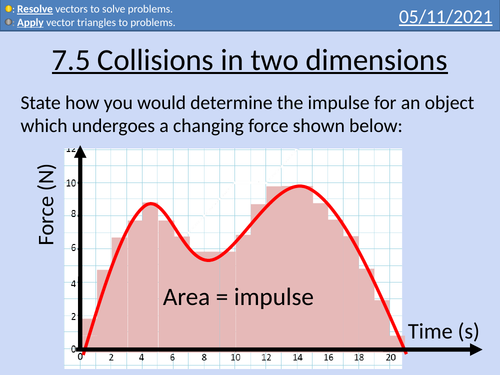
OCR AS level Physics: Collisions in two dimensions
OCR AS level Physics: Collisions in 2D is a part of the Module 3: Laws of Motion and Momentum. Presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

OCR AS level Physics: Superposition
OCR AS level Physics: Superposition of Waves is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

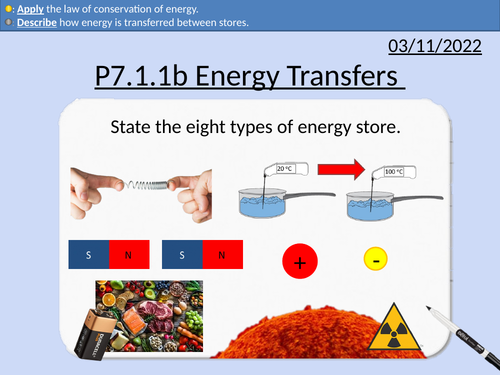
GCSE Physics: Energy transfers and Conservation of energy
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.1.1b Energy stores transfers and Conservation of energy.
This PowerPoint covers while including student activities and worked answers:
The law of conservation of energy.
The energy transfer pathways:
Mechanically – with forces
Electrically – with current
Heating by particles
Heating by radiation
Describing stores and transfers for:
Object projected upwards or up a slope,
A moving object hitting an obstacle,
An object being accelerated by a constant force,
A vehicle slowing down,
Bringing water to a boil in an electric kettle

OCR A Level Physics: Gravitational Potential Energy
OCR A level Physics: 18.7 Gravitational Potential Energy
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Radial and uniformed field
Definition of gravitational potential energy
Deriving escape velocity
Force-Distance graphs for gravitational fields

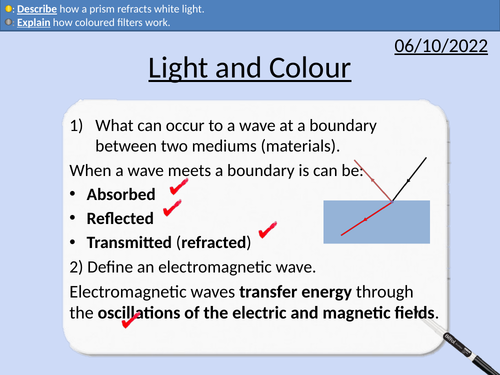
GCSE Physics: Light and Colour
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.3.3 Light and Colour
Includes student activities and full worked answers.
Names of colours for the visible spectrum
Coloured filters
Coloured objects acting as a coloured filters
White light and refracting prism
Refraction and wavelength
Specular reflection
Diffuse scattering
Scattering - Why the sky is blue and milk is white.

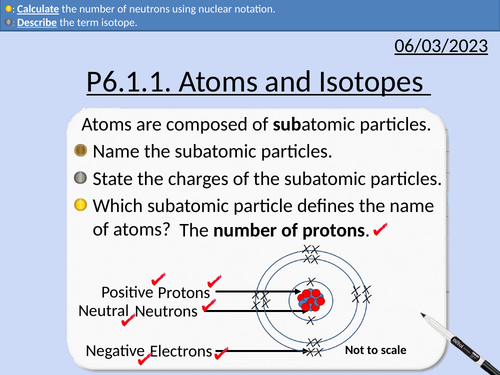
GCSE Physics: Atoms and Isotopes
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P6.1.1 Atoms and Isotopes
All presentations come with student activities and worked solutions.
Structure of atom
Properties of subatomic particles
Atomic Number
Mass Number
Nuclear Notation
Calculating the number of neutrons

GCSE Chemistry: Forming Ions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of ions
• The electronic configuration of ions
• Ions metals and nonmetals form
• Drawing electron configurations
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P8.3 Beyond Earth
All resources for P8.2 Powering Earth GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Key facts about the Big-Bang model
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB, CMBR)
Doppler Red shift of light from stars in galaxies
Hubble’s evidence of absorption spectra being red shifted
Structure of the solar system
Nuclear Fusion
Evolution of large stars
Evolution of Sun like stars
Gravitational force and force from nuclear fusion
Natural Satellites
Geostationary Satellites
Low Polar Orbit Satellites
Speed is constant and velocity is changing in stable orbits.
Changing speed and radius
Gravitational force, acceleration, and speed.
Plotting data and describing relationships
All objects emit electromagnetic radiation
Describe how changing temperature changes frequency, wavelength, and intensity of the radiation produced.
Explain why objects change temperature by absorbing and emitting radiation.
Explain why the temperature of the Earth changes due to greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
S and P waves
Structure of the Earth
Reflection, absorption, and refraction of waves
Sonar to map the ocean floor

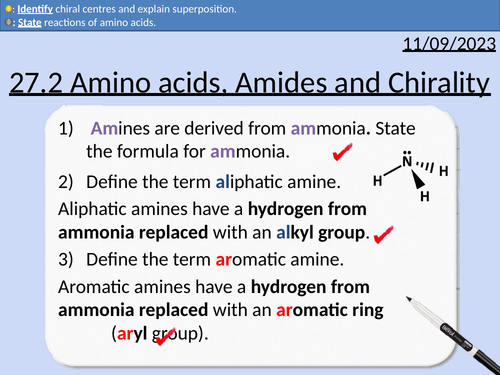
A level Chemistry: Amino acids, Amides and Chirality
OCR A level Chemistry: 27.2 Amino acids, Amides and Chirality
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Locants: alpha, beta, and gamma
Functional groups of amino acids
General formula for amino acids
Reactions of amino acids (alkali and acid)
Esterification of amino acids
Amide functional groups
Naming amide molecules
Drawing optical isomers
Explanation of superimposable and non-superimposable images
Identifying chiral centers

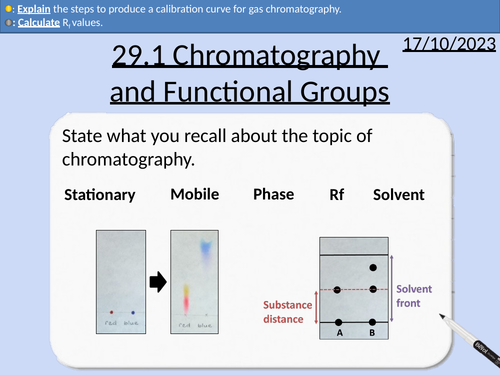
A level Chemistry: Chromatography and Functional Group Analysis
OCR A level Chemistry: 29.1 Chromatography and Functional Group Analysis
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Thin layer chromatography (TLC)
Rf values
Gas chromatography (GC)
Gas chromatograms
Retention time and peak integrations
Calibration curves from retention time and relative peak area
Differentiation of functional groups: alkene, primary and secondary alcohols, aldehydes, cabonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, and haloalkes.

GCSE Physics: EM waves - Uses and Dangers
This presentation cover the OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.2.2 Uses and Dangers of EM radiation. PowerPoint includes student activities with full worked answers.
Recall that light is an electromagnetic wave
Give examples of some practical uses of electromagnetic waves in the radio, micro-wave, infra-red, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray and gamma-ray regions
Describe how ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays can have hazardous effects, notably on human bodily tissues.
Explain that electromagnetic waves transfer energy from source to absorber to include examples from a range of electromagnetic waves
Precautions for ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays

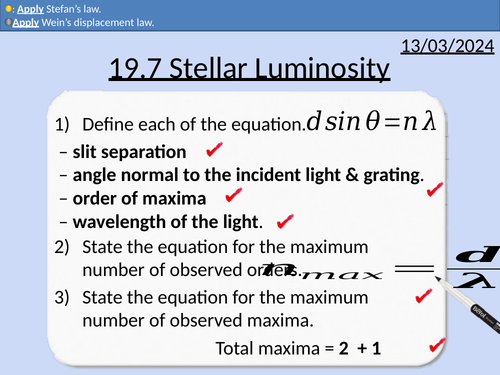
OCR A level Physics: Stellar Luminosity
OCR A level Physics: 19.7 Stellar Luminosity
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The electromagnetic spectrum, frequency/wavelength, and temperature
Black body radiation
Wein’s displacements law
Stefan’s law (Stefan-Boltzmann law)

OCR A level Physics: The Big Bang Theory
OCR A level Physics: 20.4 The Big-bang
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Georges Lemaître’s Theory
Evidence for the Big Bang Model
Hubble’s Law (expanding Universe)
Microwave Background Radiation
Source of the Microwave Background Radiation
Hubble’s constant and the age of the Universe

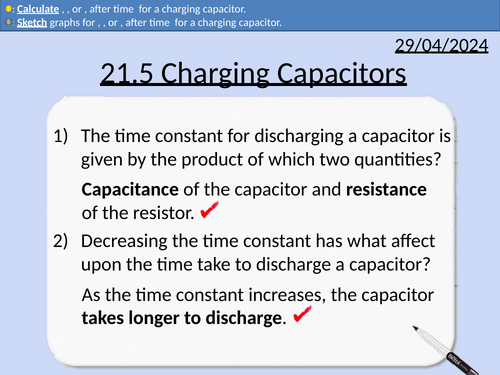
OCR A level Physics: Charging Capacitors
OCR A level Physics: 21.5 Charging Capacitors
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Explaining how capacitors charge with a resistor in series
Explaining how 𝑉, 𝐼, or 𝑄, change with time 𝑡 for a charging capacitor.
Sketching graphs for 𝑉, 𝐼, or 𝑄, after time 𝑡 for a charging capacitor.
Calculating 𝑉, 𝐼, or 𝑄, change with time 𝑡 for a charging capacitor.