484Uploads
145k+Views
63k+Downloads
All resources

A Level Chemistry: Introducing Benzene
OCR A level Chemistry: 25.1 Introducing Benzene
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Molecular, empirical, skeletal formula for benzene.
The Kekulé model for benzene
Evidence against the Kekule model
The delocalised model for benzene
Nomenclature for benzene rings and aromatic (arene) compounds
Naming benzene containing compounds
Drawing benzene containing compounds
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Capacitance
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 21 Capacitance is apart of the Module 6: Particle and Medical Physics
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
21.1 Capacitors
21.2 Capacitors in circuits
21.3 Energy stored by capacitors
21.4 Discharging capacitors
21.5 Charging capacitors
21.6 Uses of capacitors
Electrical quantities, symbols, and units
SI prefixes and standard form
Definition of a capacitor
Structure of a capacitor
Calculating capacitance, charge, and potential difference.
Uses of capacitors in circuits.
Rules for capacitors in parallel (potential difference, charge, and capacitance).
Rules for capacitors in series (potential difference, charge, and capacitance).
Applying the rules in series and parallel.
Creating a circuit to calculate the charge stored on the capacitor.
Work done of a capacitor depends upon the initial potential difference and capacitance.
Work done is provided by the source of potential difference.
Deriving three equations for work done of a capacitor.
Exponential increase and exponential decay
Explaining how capacitors discharge through a resistor in parallel
Definition of time constant for a capacitor
Showing that time constant has units of seconds
Iterative method for finding how capacitors discharge
Using exponentials and logs.
Solving a differential equation (needed for A-level Maths).
Explaining how capacitors charge with a resistor in series
Explaining how 𝑉, 𝐼, or 𝑄, change with time 𝑡 for a charging capacitor.
Sketching graphs for 𝑉, 𝐼, or 𝑄, after time 𝑡 for a charging capacitor.
Calculating 𝑉, 𝐼, or 𝑄, change with time 𝑡 for a charging capacitor.
Calculating power output from a circuit containing a capacitor
A rectifier circuit - changing an alternating input to a smooth output

A level Chemistry: Combined Techniques
OCR A level Chemistry: 29.6 Combined Techniques
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Percentage yield to determine empirical formula
Mass spectra
Infrared spectra
Carbon-13 NMR spectra
Proton NMR spectra

OCR AS Physics: Diffraction and Polarisation
OCR AS Physics: Diffraction and Polarisation is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

OCR AS Physics: Refractive Index
OCR AS Physics: Refractive Index is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

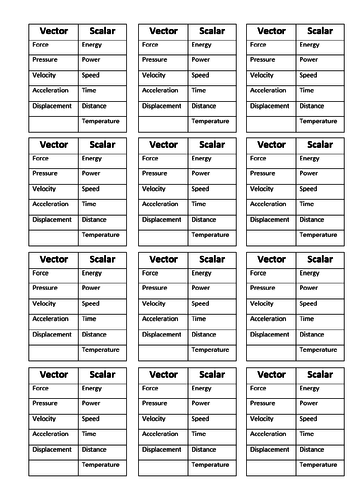
GCSE Physics: Vectors and Scalars
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.2.2.
Content covered:
Definition for vector and scalar
Vector addition in 1 D
Vector addition in 2 D
Scaled drawings and Pythagoras’ theorem
Worked examples and student problems with answers included

GCSE Physics: Newton's Second Law
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.2.4
Newton’s Second Law in Mathematical Form
Proportionalities
Rearranging Equations
Student’s problems with answers
Exam style questions with solutions

GCSE Physics: Simple Machines and Gears
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.3.5 Simple Machines
• Uses of simple machines
• Simple machines as force multipliers
• Mechanical advantage equation
• Gears – ratios, speed, direction
• Rearranging equations
• Exam style questions with solutions
• Student problems with answers

GCSE Physics: Nuclear Fission
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P6.2.2 Nuclear Fission
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Conservation of mass
Uranium as a nuclear fission fuel
Nuclear fission process
Chain reactions in nuclear fission reactions
Control rods and moderators in nuclear reactors
Benefits and disadvantages of nuclear fission reactors.
Mass-Energy Equivalence

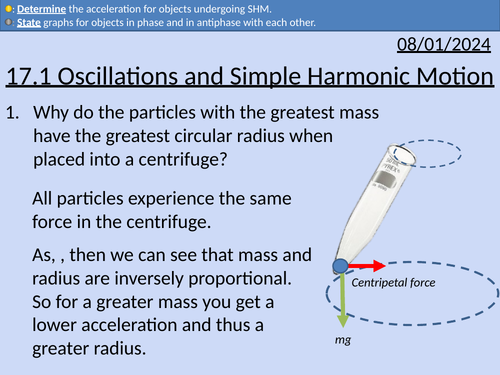
OCR A Level Physics: Simple Harmonic Motion and Oscillations
OCR A Level Physics: Simple Harmonic Motion and Oscillations presentation, homework and answers.

GCSE Physics: Energy Stores
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.1.1 Energy stores
Examples, units, and equations of each energy store:
Kinetic
Gravitational potential
Elastic
Thermal
Magnetic
Electrostatic
Chemical
Nuclear
Student activities with full worked answers also included.

GCSE Physics: The Big-Bang
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.3.1 The Big-Bang
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Key facts about the Big-Bang model
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB, CMBR)
Doppler Red shift of light from stars in galaxies
Hubble’s evidence of absorption spectra being red shifted

OCR AS level Physics: Moments and Equilibrium
OCR AS level Physics: Moments and Equilibrium is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

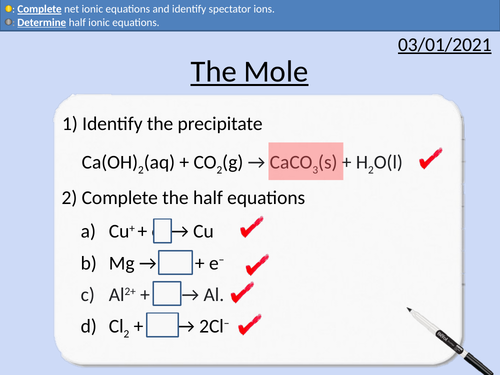
GCSE Chemistry: The Mole
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Using Standard Form
• Avogadro’s constant
• Relative Atomic Mass, Relative Formula Mass and Molar Mass
• Rearranging Equations
• Calculating the number of moles present

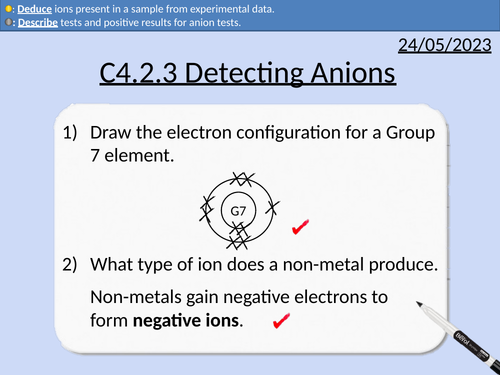
GCSE Chemistry: Detecting Anions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Definitions for anions, cations, anodes, cathodes.
Tests for carbonate ions
Tests for sulfate ions
Tests for halide ions

GCSE Physics: Types of Waves
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.1.1a WaTypes of wave. Includes student activities and full worked answers.
Definition of a wave
Mechanical waves
Electromagnetic waves
Transverse waves
Longitudinal waves

OCR AS Chemistry: Reactions of Alkenes
OCR AS Chemistry: 13.3 Reactions of Alkenes
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Alkene addition reactions:
Hydrogen with a nickel catalyst
Halogens
Hydrogen halide
Steam with an acid catalyst
Test for unsaturated alkenes.
Bond enthalpy for sigma and pi bonds.

OCR AS Physics: Thermistor
OCR AS Physics A: Thermistor is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Thermistor uses
Thermistors with negative temperature coefficients
Plotting I-V curves for thermistors
Creating an experiment to test thermistors.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P8.2 Powering Earth
All resources for P8.2 Powering Earth GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Types of different energy sources
Renewable and non-renewable definitions
Different uses of energy sources - transport, heating, and generating electricity
Advantages and disadvantages of different energy sources
Fossil fuels – oil, coal, and natural gas.
Nuclear fuel – Uranium
Biofuels – wood, biodiesel, and biogas.
The sun - solar (PV) panels and solar heating panels
Tides
Waves
Hydroelectricity
Wind
Geothermal
How use of energy resources have changed over time. (Biofuels, Fossil Fuels, Nuclear, Renewable).
How energy use has increased (increase population and development of technology)
Explain patterns and trends in the use of energy resources.
Fossil fuels are finite and will run out at current consumption levels.
Structure of the National Grid
Step-up and Step-down transformers
How transformers increase the efficiency of the National Grid
Number of turns and potential difference
Current and potential difference in primary and secondary coils
Domestic Electrical Supply being 230 V, AC at 50 Hz.
Direct potential difference and alternating potential difference.
Reasons for insulation on wires.
Potential Difference between different conductors.
Function of the earth conductor.
Double insulation and no earth wire.
Reasons the live wire is dangerous.
Reasons why live to earth is dangerous.

A level Chemistry: Carboxylic Acids
OCR A level Chemistry: 26.3 Carboxylic Acids
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The Carboxyl Group and polarity of bonds.
Naming carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acids as weak acids
Reactions of carboxylic acids with:
Metals
Metal oxides
Alkali
Carbonates
Changing solubility of carboxylic acids in water due to carbon chain length.