497Uploads
167k+Views
71k+Downloads
Chemistry

OCR Applied Science: 1.3 Ionic and Covalent Bonding
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 1.3 of Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Elements react together to form compounds by i.e.
ionic bonding
covalent bonding

OCR Applied Science: 6.2 Physico-chemical Properties of Materials
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 6.2 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Structure of metals, giant covalent, and simple molecular structures.
Properties of metals, giant covalent, and simple molecular structures.
Forces and bonds of metals, giant covalent, and simple molecular structures.
Phase diagrams – interpreting and calculating changes.
Sublimation and phase diagrams.

GCSE Chemistry: Electronic Structures
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Electrons reside in energy levels (shells) around the nucleus
• The electronic configuration of elements up to 20 is 2,8,8,2
• Groups and periods of the periodic table
• Drawing electron configurations

GCSE Chemistry: Simple Molecules
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Dot and cross diagrams of simple molecules
• Simple molecules form covalent bonds
• The group number on the periodic table informs us how many electrons are in the outer shell.
• Groups on the periodic table

GCSE Chemistry: Covalent Structures
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of giant covalent structures
• An empirical formula shows the simplest whole-number ratio of the atoms of each compound.
• Melting and boiling point of simple molecules
• Compare physical properties of simple molecules and giant covalent lattices.

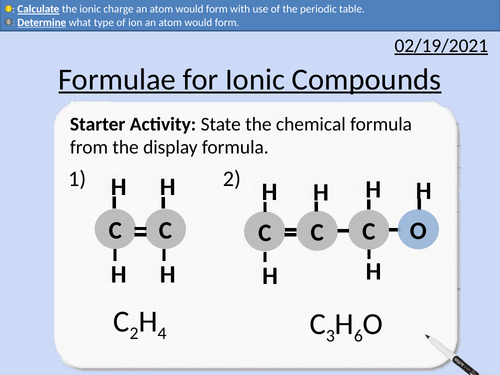
GCSE Chemistry: Formulae for Ionic Compounds
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• State the number of electrons in each energy level.
• Determine what type of ion an atom would form.
• Calculate the ionic charge an atom would form with use of the periodic table.
• Groups number, outer shell electrons, dot and cross diagrams

GCSE Chemistry: The pH scale
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• pH 0 - 14 scale with household examples
• Definitions for acids, bases and alkali substances
• Universal indicator and pH probes
• Using equalities and inequalities

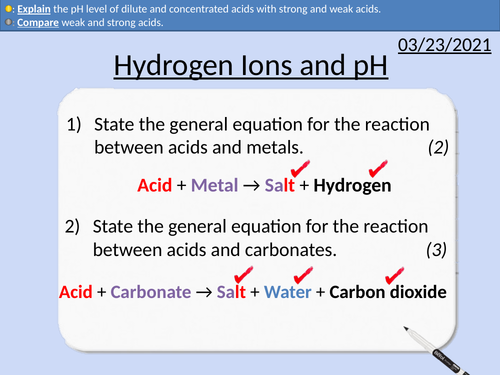
GCSE Chemistry: Hydrogen Ions and pH
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Concentration of fruit squash
• Comparing strong and weak acids
• pH and hydrogen ion concentration
• Titration curves

GCSE Chemistry: Reactivity of Elements
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Group 1, 2, 7, 0 electron structures
• Reactivity series for metals
• Equation for metals and water
• Equation for metals and acid
• Displacement reactions for metals

GCSE Chemistry: Condensation Polymers
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Block notation for hydrocarbons
Amino acids functional groups
Amino acids forming proteins through condensation reactions
Forming polyesters through condensation reactions
Forming polyamides through condensation reactions
Comparing polyesters and polyamides
Conditions for condensation polymers

OCR AS Chemistry: Introduction to Reaction Mechanisms
OCR AS Chemistry: 11.5 Introduction to Reaction Mechanisms
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Covalent bonds
Homolytic fission and heterolytic reactions
Curly arrows in reaction mechanisms
Identifying addition, substitution, and elimination reactions.

OCR Applied Science: 1.2 The Periodic Table
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 1.2 of Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Elements are based on atomic structure and can be classified by the Periodic Table i.e.:
organisation of elements within the table
groups
periods
atomic number
atomic mass atomic radius

GCSE Chemistry: Carbon
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• State processes of the carbon cycle.
• Define the word allotrope.
• Explain why allotropes have different properties.
• Graphite, graphene, and fullerenes

GCSE Chemistry: Bond Energies and Energy Changes
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of bond energies
• Calculating bond energies per mole
• Calculating change in bond energies in reactions
• Determining if a reaction is exothermic or endothermic from the change in bond energy.

GCSE Chemistry: Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition for exothermic and endothermic
• Examples of exothermic and endothermic reactions
• Practical procedure for NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
• Determining if experimental evidence show a exothermic or endothermic reaction

GCSE Chemistry: Group 1 - Alkali Metals
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of Alkali Metals
• Properties of Alkali Metals
• Trends and anomalies in Group 1 (Density, Melting Point)
• Reactivity of Group 1 Alkali Metals
• Electron configuration of Group 1 Alkali Metals

GCSE Chemistry: Halogen Displacement Reactions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of halides displacement reactions
• Definition of displacement reactions
• Identifying displaced products
• Completing displacement reactions
• Explaining experimental evidence for displacement reactions.

GCSE Chemistry: Group 0 - Noble Gases
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Properties of Noble gases
• Trends and anomalies in Group 0 (Density, Melting Point)
• Reactivity of Group 0 Noble gases
• Electron configuration of Group 0 Noble gases

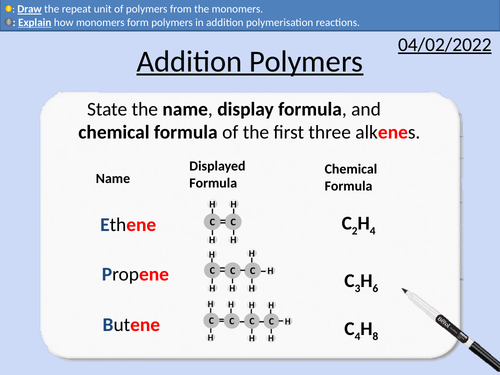
GCSE Chemistry: Addition Polymers
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Prefixes mono- and poly-
Alkanes and alkenes functional groups
Saturated and unsaturated carbon bonds
Addition polymerisation reactions
Conditions needed for polymerisation reactions
How monomers form polymers
Repeat units and monomers

OCR AS Chemistry: Structural Isomerism
OCR AS Chemistry: 11.4 Structural Isomerism
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Definition for Structural Isomers
Moving functional group to form isomers
Aldehydes and ketones being structural isomers
Skeletal formula and structural formula