497Uploads
167k+Views
71k+Downloads
Chemistry

OCR Applied Science: 2.1 Mixtures and Alloys
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 2.1 of Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Types of mixtures to include solutions, colloids and suspensions
Difference between colloids and suspensions in terms of particle size
Uses of common colloids in nature and medicine
Types of colloids to include aerosols, emulsions, foams, gels and sols
Significance of colloids in nature and medicine
Alloys as mixtures of metals
The character and features of alloys
Uses of common alloys to include amalgam, solder, bronze, titanium alloy

OCR Applied Science: 1.1 The Atom
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 1.1 of Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
nucleus contains protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons
relative masses and charges
nuclear and atomic diameters
nucleon number, proton number and isotopes
proton number defines the type of atom
nuclear notation
attractive and repulsive forces within the nucleus

OCR Applied Science: 2.2 Reactions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 2.2 of Module 1: Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Oxidation and reduction (redox) reactions
Addition reactions of alkenes to include full balanced symbol equations
Substitution reactions of alkanes and haloalkanes to include full balanced
equations
Addition polymerisation to include identification of monomers and repeating units
Condensation polymerisation to include identification of monomers and repeating units
Definition of a radical
The role played by UV light in producing chlorine radicals from CFCs in the
depletion of the ozone layer
Equations to show how chlorine radicals can destroy many ozone molecules
Displacement reactions to include full balanced equations for metals and halogens.

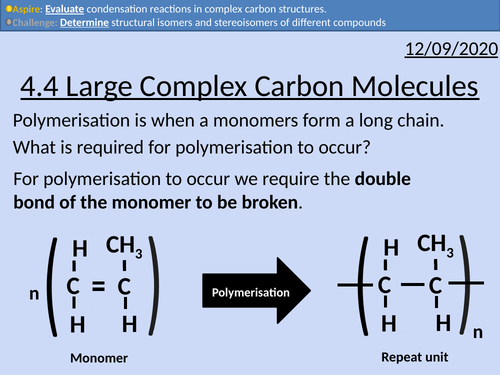
OCR Applied Science: 4.4 Large Complex Carbon Molecules
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 4.4 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Complex carbohydrates (starch, glycogen, cellulose)
• Carbohydrates found as monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides (monomers, dimers or polymers)
• Monomers held together by glycosidic bonds to form dimers and polymers, via condensation reactions
• Monosaccharides include glucose, fructose and galactose
• Disaccharides include maltose, sucrose and lactose
• Polysaccharides include starch, glycogen and cellulose
• Cellulose is found in plant cell walls where it provides strength/support and pliability
• Starch and glycogen are energy sources
Proteins and peptides from amino acids
• Dipeptides are formed from two amino acids joined by a peptide bond, via a condensation reaction
• Polypeptides are chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
• Proteins/polypeptides have physiological or functional roles, including enzymes, carrier proteins in the plasma membrane, and structural roles, including collagen and elastin fibres in connective tissue
Lipids from fatty acids, glycerol and phosphorus compounds
• Monoglycerides, diglycerides and triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and glycerol
• An ester bond forms between each fatty acid and the glycerol, via condensation reactions
• Phospholipids contain glycerol plus two fatty acids and a phosphate group
• Lipids act as an energy source within cells, as an insulation layer around animal organs, in the myelin sheath (found around some nerve fibres/axons) to increase speed of nerve transmission
• Phospholipids form a bilayer in the plasma membrane
Protein synthesis (transcription, translation) RNA, messenger, ribosomal and transfer
• The nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, are polymers of nucleotides
• Peptide bonds form between amino acids to create polypeptide chains/proteins
• Recall a simple description of protein synthesis

OCR Applied Science: 4.1 Principles of Carbon Chemistry
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 4.1 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
• Alkanes as saturated hydrocarbons containing single C-C and C-H bonds
• Alkenes as unsaturated hydrocarbons containing a C=C double bond
• Alkynes as unsaturated hydrocarbons containing a C ≡ C triple bond
• Name and draw structural and skeletal formulae of the first four members of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes
• Aldehydes and ketones as organic compounds containing the C=O group
• Name and draw the structural formulae of the first four aldehydes and the first two ketones
• Alcohols as organic compounds containing the OH group
• Name and draw structural and skeletal formulae of the first four alcohols
• Conversion of alcohols to form aldehydes and ketones is classified as an oxidation reaction
• Name and draw structural and skeletal formulae of the first four carboxylic acids
• Reaction of carboxylic acids with an alkali, to include full equations using structural formulae
• Name and draw structural and skeletal formulae of the four C4H8O2 esters
• How an ester can be made from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry C2.1 Purity and Separating Mixtures
All resources for P2.1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Relative Formula Mass
Empirical Formula
Pure and Impure Substances
Filtration and Crystallisation
Simple Distillation
Paper Chromatography
Gas and Think Layer Chromatography
Purification and Checking Purity

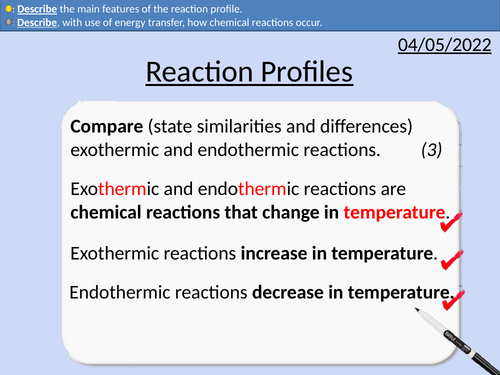
GCSE Chemistry: Reaction Profiles
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Reaction profiles for exothermic and endothermic
• Energy stores of particles and surroundings
• Activation energy
• Describing the main features of reaction profiles.

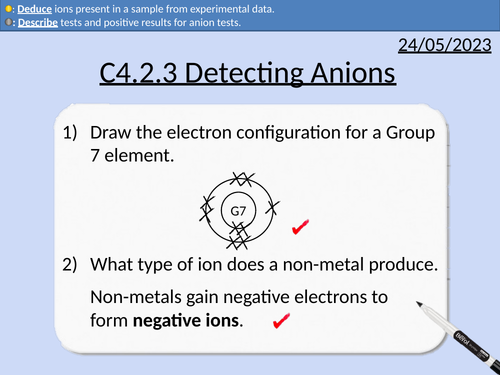
GCSE Chemistry: Detecting Anions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Definitions for anions, cations, anodes, cathodes.
Tests for carbonate ions
Tests for sulfate ions
Tests for halide ions

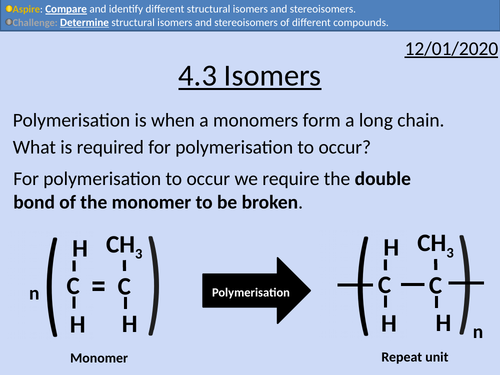
OCR Applied Science: 4.3 Isomers
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 4.3 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
• Stating definitions and comparing structural isomers and stereoisomers.
• Condensed structural formula
• Lines of symmetry for structural isomers
• Cis- and Trans isomers
• Optical isomers as non-superimposable mirror images.
• Wedge and Dash Notation
• Identifying chiral centres (asymmetric carbons)
• Le Bel-van’t Hoff rule
• Determining the maximum number of isomers.

OCR AS Chemistry: Polymerisation of Alkenes
OCR AS Chemistry: 13.5 Polymerisation of Alkenes
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Monomers and repeat units
Addition Polymerisation for:
Polyethene
Polypropene
Polylactate
Polystyrene
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Environmental Concerns from polymers including:
Combustion of polymers
recycling PVC
biogradeable bioplastics
photodegradable polymers
feedstock recycling

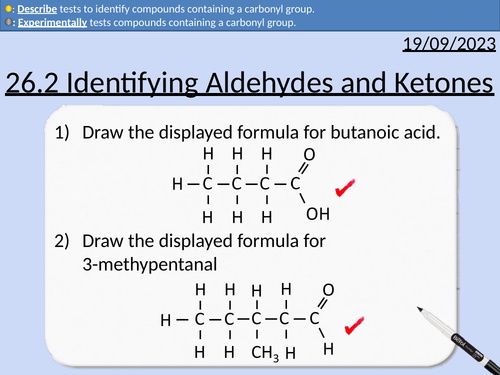
A level Chemistry: Identifying Aldehydes and Ketones
OCR A level Chemistry: 26.2 Identifying Aldehydes and Ketones
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Testing for Carbonyl Groups
Brady’s reagent - 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine - 2,4-DNP
Distinguishing between Aldehydes and Ketones
Tollen’s reagent - silver nitrate in aqueous ammonia

OCR Applied Science: 6.1 Mechanical Properties of Materials
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 6.1 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
• Interpreting laboratory tests for stress-strain graphs and Young’s modulus
• Awareness that repeated loading cycles may cause failure by fatigue below the yield strength
• Use of diagrams to understand that the way molecules are arranged in polymers determines the properties: chain length, crosslinking, use of plasticizers and crystallinity.
• Use and rearranging of the density equation.

A level Chemistry: Carboxylic Acids
OCR A level Chemistry: 26.3 Carboxylic Acids
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The Carboxyl Group and polarity of bonds.
Naming carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acids as weak acids
Reactions of carboxylic acids with:
Metals
Metal oxides
Alkali
Carbonates
Changing solubility of carboxylic acids in water due to carbon chain length.

OCR AS Chemistry: Practical Techniques in Organic Chemistry
OCR AS Chemistry: 16.1 Practical Techniques in Organic Chemistry
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Heating under reflux
Distillation
Re-distillation
Purifying Organic Products
Removing impure acids from organic compounds
Drying agents
Bundle

OCR A Level Chemistry: Module 6 Organic Chemistry and Analysis
This bundle includes all PowerPoint lessons for Module 6 Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All PowerPoints are whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
C25 Aromatic Chemistry
Introducing Benzene
Electrophilic substitution Reactions
The Chemistry of Phenol
Directing Groups
C26 Carbonyls and Carboxylic Acids
Carbonyl Compounds
Identifying Aldehydes and ketones
Carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acid derivatives
C27 Amines, Amino Acids and Polymers
Amines
Amino acids, amides and chirality
Condensation Polymers
C28 Organic Synthesis
Carbon-carbon bond formation
Further Practical Techniques
Further Synthetic Routes
C29 Chromatography and Spectroscopy
Chromatography and functional group analysis
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopy
Proton NMR Spectroscopy
Interpreting NMR Spectra
Combining Techniques

A level Chemistry: Combined Techniques
OCR A level Chemistry: 29.6 Combined Techniques
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Percentage yield to determine empirical formula
Mass spectra
Infrared spectra
Carbon-13 NMR spectra
Proton NMR spectra
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Chromatography and Spectroscopy
OCR A level Chemistry: Chromatography and Spectroscopy is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
29.1 Chromatography and Functional Group Analysis
29.2 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
29.3 Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopyy
29.4 Proton NMR Spectroscopy
29.5 Interpreting Proton NMR Spectra
29.6 Combined Techniques
Thin layer chromatography (TLC)
Rf values
Gas chromatography (GC)
Gas chromatograms
Retention time and peak integrations
Calibration curves from retention time and relative peak area
Differentiation of functional groups: alkene, primary and secondary alcohols, aldehydes, cabonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, and haloalkes.
Nuclear Spin
Resonance
Tetramethylsilane (TMS)
Chemical Shift ẟ
Identifying different carbon environments
The types of carbon environment
The amount of chemical shift ẟ / ppm
Identifying the number of different proton environments
Identifying the types of proton environment and chemical shifts
Integration traces (area of peaks) and relative number of protons
The spin-spin splitting pattern (n + 1)
Predicting proton NMR spectra for molecules
Identifying the number of different proton environments
Identifying the types of proton environment and chemical shifts
Integration traces (area of peaks) and relative number of protons
Percentage yield to determine empirical formula
Mass spectra
Infrared spectra
Carbon-13 NMR spectra
Proton NMR spectra

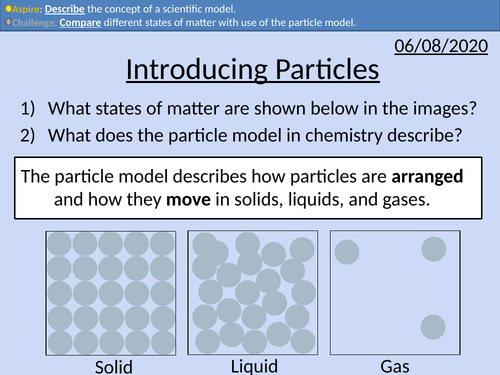
GCSE Chemistry: Introducing Particles
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Solids, liquids, and gases
• Scientific models as a concept

GCSE Chemistry: Chemical and Physical Changes
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Differences between physical and chemical changes
• Explain why physical changes are generally easier to reverse

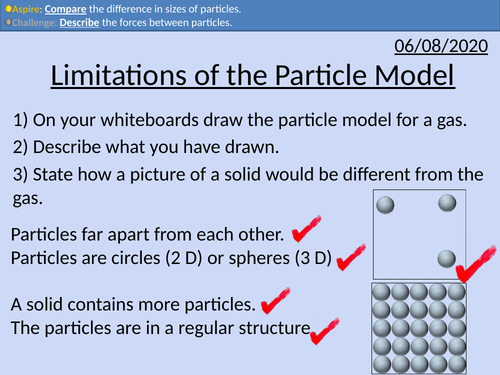
GCSE Chemistry: Limitations of the Particle Model
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Describing the limitations of the model: lack of forces between particles, size of particles, and space between the particles.
• Mathematically comparing sizes and distances of particles