497Uploads
167k+Views
71k+Downloads
Physics

OCR A level Physics: Electric Fields
OCR A level Physics: 22.1 Electric Fields
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Electric field line pattern from point charges, uniformly charged objects, and capacitors.
Rules for electric field lines
Interacting field lines for attraction and repulsion
Detecting electric fields with a charged gold leaf
Definition of electric field strength
Explaining that electric field strength is a vector with magnitude and direction
Apply the equation for electric field strength

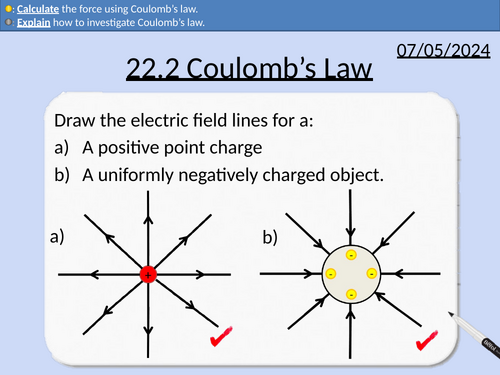
OCR A level Physics: Coulomb’s Law
OCR A level Physics: 22.2 Coulomb’s Law
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Electric force related to the product of charge and square of the separation
The constant of proportionality 𝑘
Permittivity of free space
Experiment for investigating Coulomb’s Law
Electric Field Strength and Coulomb’s Law

OCR A level Physics: Charged particles in uniformed electric fields
OCR A level Physics: 22.4 Charged particles in uniformed electric fields
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Equations for constant acceleration
Maximum kinetic energy of a charged particle in a uniformed field
Sketching trajectories for charged particles in uniformed fields
Calculating velocities for horizontal and vertical components

OCR A level Physics: Uniformed electric fields & capacitance
OCR A level Physics: 22.3 Uniformed electric fields & capacitance
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Liquid crystal displays (LCDs)
Electric field between two charged parallel plates
Deriving an equation for electric field strength of a parallel plate capacitor.
Accelerating charged particles in a uniformed electric field
Capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with an insulating (dielectric) material - relative permittivity
Millikan’s experiment

OCR A level Physics: Electric Potential and Energy
OCR A level Physics: 22.5 Electric Potential and Energy
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Definition of electric potential energy
Definition of electric potential.
Definition of electric potential difference.
Using a force-distance graph to determine electric potential energy
Using electron-volts and joules in calculations
Capacitance of an isolated charged sphere
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Electric Fields
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 22 Electric Fields is apart of the Module 6: Particle and Medical Physics
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
22.1 Electric Fields
22.2 Coulomb’s Law
22.3 Uniform electric fields and capacitance
22.4 Charged particles in uniformed electric fields
22.5 Electric potential and energy
Electric field line pattern from point charges, uniformly charged objects, and capacitors.
Rules for electric field lines
Interacting field lines for attraction and repulsion
Detecting electric fields with a charged gold leaf
Definition of electric field strength
Explaining that electric field strength is a vector with magnitude and direction
Apply the equation for electric field strength
Electric force related to the product of charge and square of the separation
The constant of proportionality 𝑘
Permittivity of free space
Experiment for investigating Coulomb’s Law
Electric Field Strength and Coulomb’s Law
Liquid crystal displays (LCDs)
Electric field between two charged parallel plates
Deriving an equation for electric field strength of a parallel plate capacitor.
Accelerating charged particles in a uniformed electric field
Capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with an insulating (dielectric) material - relative permittivity
Millikan’s experiment
Equations for constant acceleration
Maximum kinetic energy of a charged particle in a uniformed field
Sketching trajectories for charged particles in uniformed fields
Calculating velocities for horizontal and vertical components
Definition of electric potential energy
Definition of electric potential.
Definition of electric potential difference.
Using a force-distance graph to determine electric potential energy
Using electron-volts and joules in calculations
Capacitance of an isolated charged sphere

OCR A level Physics: Magnetic Fields
OCR A level Physics: 23.1 Magnetic Fields
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Attraction and repulsion of magnets
Rules for magnetic field lines
The magnetic field of Earth
Applying the right-hand cork screw rule
How to create uniformed magnetic fields
Solenoids

OCR A level Physics: Understanding Magnetic Fields
OCR A level Physics: 23.2 Understanding Magnetic Fields
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Fleming’s left hand rule
Determining the direction of force on a current carrying conductor
Calculating the magnitude of force on a current carrying conductor
Angles between the magnetic field and current carrying conductor
An experiment to determine the magnetic flux density of a field.

GCSE Physics: Speakers and Microphones
This lesson presentations covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P4.2.6 Speakers and Microphones.
Definition of sound waves.
Structure and operation of a speaker.
Fleming’s left hand rule.
Structure and operation of a microphone.
Electromagnetic induction.
Comparison of speakers and motors.
Comparison of microphone and generators.
Comparing microphones and speakers

OCR A level Physics: Charged Particles in Magnetic Fields
OCR A level Physics: 23.3 Charged Particles in Magnetic Fields
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Apply Fleming’s left-hand rule to charged particles
Deriving an equation for the magnetic force experienced by a single charged particle (F = BQv)
Charged particles describing (moving) in circular paths in magnetic fields.
The velocity selector.
The Hall probe and Hall voltage.

OCR A level Physics: Electromagnetic Induction
OCR A level Physics: 23.4 Electromagnetic Induction
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Electromagnetic induction produces an induced e.m.f
Conditions to produce electromagnetic induction
How to increase electromagnetic induction
Magnetic flux density, magnetic flux, and magnetic flux linkage
Units of weber (Wb)

OCR A level Physics: Transformers
OCR A level Physics: 23.6 Transformers
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Structure of transformers
Step-up and step-down transformers
The turn-ratio equation
The ideal transformer equation
Why transformers are used in the National Grid
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Magnetic Fields
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 23 Magnetic Fields is apart of the Module 6: Particle and Medical Physics
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
23.1 Magnetic fields
23.2 Understanding magnetic fields
23.3 Charged particles in magnetic fields
23.4 Electromagnetic induction
23.5 Faraday’s law and Lenz’s law
23.6 Transformers
Attraction and repulsion of magnets
Rules for magnetic field lines
The magnetic field of Earth
Applying the right-hand cork screw rule
How to create uniformed magnetic fields
Solenoids
Fleming’s left hand rule
Determining the direction of force on a current carrying conductor
Calculating the magnitude of force on a current carrying conductor
Angles between the magnetic field and current carrying conductor
An experiment to determine the magnetic flux density of a field.
Apply Fleming’s left-hand rule to charged particles
Deriving an equation for the magnetic force experienced by a single charged particle (F = BQv)
Charged particles describing (moving) in circular paths in magnetic fields.
The velocity selector.
The Hall probe and Hall voltage.
Electromagnetic induction produces an induced e.m.f
Conditions to produce electromagnetic induction
How to increase electromagnetic induction
Magnetic flux density, magnetic flux, and magnetic flux linkage
Units of weber (Wb)
Magnetic flux density and magnetic flux linkage
Faraday’s Law
Lenz’s Law
Alternators and induced e.m.f.
Graphs of flux linkage and induced e.m.f.
Structure of transformers
Step-up and step-down transformers
The turn-ratio equation
The ideal transformer equation
Why transformers are used in the National Grid

OCR A level Physics: Faraday's Law and Lenz's Law
OCR A level Physics: 23.5 Faraday’s Law and Lenz’s Law
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Magnetic flux density and magnetic flux linkage
Faraday’s Law
Lenz’s Law
Alternators and induced e.m.f.
Graphs of flux linkage and induced e.m.f.

OCR A level Physics: The Nucleus
OCR A level Physics: 24.2 The Nucleus
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Nucleons
Isotopes
Nuclear notation
Atomic mass units (u)
Radius for atomic nucleus equation
Volume and density of atomic nuclei
The strong nuclear force

OCR A level Physics: Quarks
OCR A level Physics: 24.4 Quarks
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The Standard Model of particle physics
Quarks, anti-quarks and their charges
Baryons and mesons

OCR A level Physics: Radioactivity
OCR A level Physics: 25.1 Radioactivity
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Types of ionising radiation (alpha, beta-plus/beta-minus, gamma)
Penetration power and ionising power
Detecting radiation with a Geiger (GM tube) counter
Background radiation and correct count rates
Electric and magnetic fields affect ionising radiation
Cloud chambers

OCR A level Physics: Beta decay
OCR A level Physics: 24.5 Beta decay
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Properties of neutrinos
Nuclear notation
Nuclear decay equations
Beta-plus and beta-minus decays
Quark transformation
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Particle Physics
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 24 Particle Physics is apart of the Module 6: Particle and Medical Physics
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
24.1 Alpha-particle scattering experiment
24.2 The Nucleus
24.3 Antiparticles, Leptons, & Hadrons
24.4 Quarks
24.5 Beta decay
Developments of scientific models
Thompson’s plum-pudding model
Rutherford’s nuclear (planetary) model
Rutherford’s experiment, observations, and conclusions
Using Coulomb’s law to find the minimum distance between particles
Nucleons
Isotopes
Nuclear notation
Atomic mass units (u)
Radius for atomic nucleus equation
Volume and density of atomic nuclei
The strong nuclear force
Antiparticles, their properties, and symbols
Particle and antiparticle annihilation
The four fundamental forces (strong nuclear, weak nuclear, electromagnetic, and gravitational forces) and their properties.
Definition and examples of hadrons and leptons.
The Standard Model of particle physics
Quarks, anti-quarks and their charges
Baryons and mesons
Properties of neutrinos
Nuclear notation
Nuclear decay equations
Beta-plus and beta-minus decays
Quark transformation

OCR A level Physics: Antiparticles, Leptons, & Hadrons
OCR A level Physics: 24.3 Antiparticles, Leptons, & Hadrons
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Antiparticles, their properties, and symbols
Particle and antiparticle annihilation
The four fundamental forces (strong nuclear, weak nuclear, electromagnetic, and gravitational forces) and their properties.
Definition and examples of hadrons and leptons.