497Uploads
167k+Views
71k+Downloads
Physics

OCR A Level Physics: Newton's Law of Gravitation
OCR A Level Physics:Newton’s Law of Gravitation presentation, homework and answers.

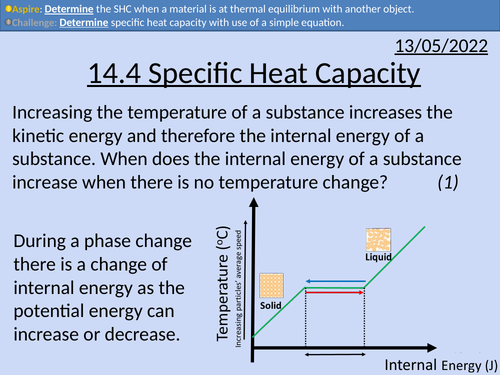
OCR A level Physics: Specific Heat Capacity
OCR A level Physics: Specific Heat Capacity is a part of the Module 5: Newtonian World and Astrophysics. The PowerPoint presentation includes worked examples, solutions and a homework.

GCSE Physics: Gravitational Energy
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.1.5 Gravitational Energy
Gravitational fields
Rearranging Gravitational Energy Equation
Exam question with worked solutions
Practice questions with worked solutions
Analysing graphs and gradients.

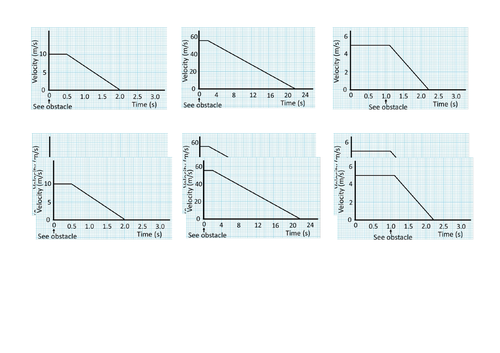
GCSE Physics: Braking and Stopping Distances
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.1.3 Braking and Stopping Distances. All presentations come with student activities and worked solutions.
Factors affecting braking distance
Total stopping distances
Calculating area of a velocity-time graph for displacement (distance traveled).
Rearranging equations
MOT testing
(Final velocity)2 – (Initial velocity)2 = 2 x Acceleration x Distance
v2 – u2 = 2 a s
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P8.2 Powering Earth
All resources for P8.2 Powering Earth GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Types of different energy sources
Renewable and non-renewable definitions
Different uses of energy sources - transport, heating, and generating electricity
Advantages and disadvantages of different energy sources
Fossil fuels – oil, coal, and natural gas.
Nuclear fuel – Uranium
Biofuels – wood, biodiesel, and biogas.
The sun - solar (PV) panels and solar heating panels
Tides
Waves
Hydroelectricity
Wind
Geothermal
How use of energy resources have changed over time. (Biofuels, Fossil Fuels, Nuclear, Renewable).
How energy use has increased (increase population and development of technology)
Explain patterns and trends in the use of energy resources.
Fossil fuels are finite and will run out at current consumption levels.
Structure of the National Grid
Step-up and Step-down transformers
How transformers increase the efficiency of the National Grid
Number of turns and potential difference
Current and potential difference in primary and secondary coils
Domestic Electrical Supply being 230 V, AC at 50 Hz.
Direct potential difference and alternating potential difference.
Reasons for insulation on wires.
Potential Difference between different conductors.
Function of the earth conductor.
Double insulation and no earth wire.
Reasons the live wire is dangerous.
Reasons why live to earth is dangerous.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P2.3 Forces in action
All resources for P2.3 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1.Triple and comined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
• Stretching springs
• Stretching materials and storing energy
• Gravitational Fields and Potential Energy
• Turning Forces
• Simple Machines
• Hydraulics

GCSE Physics: Electrical Current Practical Activity
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P3.1.2 Electrical Current
Electron flow and conventional current
Measuring current with ammeters
Series and parallel circuits
Comparing current at junctions

OCR A level Physics: Electric Fields
OCR A level Physics: 22.1 Electric Fields
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Electric field line pattern from point charges, uniformly charged objects, and capacitors.
Rules for electric field lines
Interacting field lines for attraction and repulsion
Detecting electric fields with a charged gold leaf
Definition of electric field strength
Explaining that electric field strength is a vector with magnitude and direction
Apply the equation for electric field strength

OCR A level Physics: Radioactive Dating
OCR A level Physics: 25.6 Radioactive Dating
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
State what isotopes of carbon are used in carbon dating.
Explain how carbon dating works.
Calculate the age of objects with carbon dating.

OCR A level Physics: Modelling Radioactive Decay
OCR A level Physics: 25.5 Modelling Radioactive Decay
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Iterative Method
Selecting appropriate time intervals
Comparing answers from the iterative method and exact solution.

OCR A level Physics: Nuclear Fusion
OCR A level Physics: 26.4 Nuclear Fusion
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Nuclear equations
Conditions for nuclear fusion
Binding energy and released energy

OCR A level Physics: Nuclear Fission
OCR A level Physics: 26.3 Nuclear Fission
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Fuels in nuclear fission reactors
Moderators and thermal neutrons
Conservation of mass-energy
Energy released in fission reactions
Control rods
Nuclear waste management

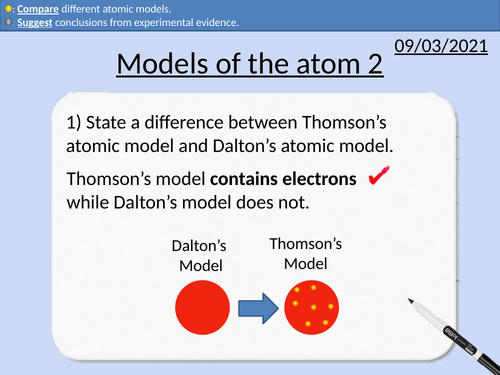
GCSE Physics: Development of the Atomic Model 2
This presentation includes:
Why scientific models change over time
Electric charge
Rutherford’s atomic model
Rutherford’s experiment
Bohr’s atomic model