496Uploads
162k+Views
70k+Downloads
All resources
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry C1 Particles
All resources for P1 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Introducing Particles
Chemical and Physical Changes
Limitations of the Particle Model
Atomic Structure
Isotopes and Ions
Developing the Atomic Model

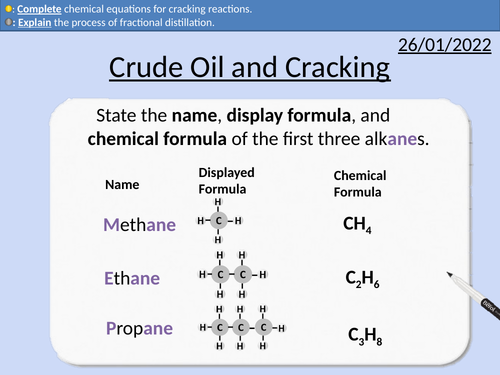
GCSE Chemistry: Crude Oil and Cracking
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of hydrocarbons
• Fossil fuels being finite and non-renewable
• Inter-molecular forces and boiling points
• Fractional distillation of crude oil
• Uses of crude oil
• Cracking equations and reasons to crack hydrocarbons

OCR AS Physics: Electrical Energy & Power
OCR AS Physics: Electrical Energy & Power is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Derive three equations for electrical power
Applying electrical power equations
Create a circuit diagram to calculate power
Base units for V A and W.

OCR AS Physics: Reflection & Refraction
OCR AS Physics A: Reflection & Refraction is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

OCR A level Physics: The Doppler Effect
OCR A level Physics: 20.2 The Doppler Effect
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The definition of the Doppler effect
Changes in pitch of sound waves due to relative motion
Absorption spectra and electron energy levels
Red-shift and blue-shift absorption spectra
The Doppler equation
The condition for velocity for the Doppler equation

GCSE Biology: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.3.1 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
The three main macronutrients - carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
Names of enzymes - carbohydrase, amylase, protease, lipase
What the macronutrients are broken down into - simple sugars, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol.
Metabolic rate
Food tests and the positive results

GCSE Physics: Electrical Power
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P3.2.8 Electrical Power.
Definition of power
Standard form for kW and MW
The three equations for power
Rearranging electrical power equations
Derivation of P = I^2 R with subsitution
Students questions and worked solutions

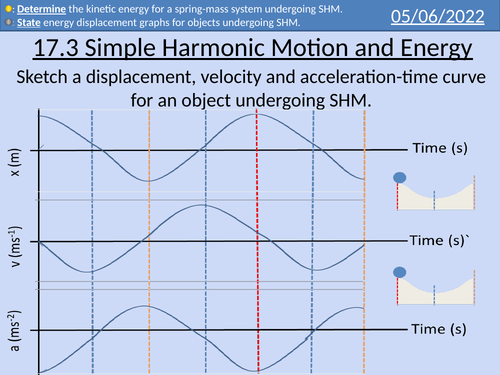
OCR A Level Physics: Simple Harmonic Motion and Energy
OCR A Level Physics: Energy and Simple Harmonic Motion presentation with homework and answers
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Charge and Current
OCR AS level Physics: Charge and Current is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Fundamental charge and relative charge
Structure of a metal
Conventional current and electron flow
Measuring current with an ammeter
Ionic solutions with cations and anions.
Ions, relative charge and absolute charge
Comparing ionic solutions and metal conductors
Apply Kirchhoff’s First Law
Kirchhoff’s First Law in mathematical form
Kirchhoff’s First Law in written form
Describing conservation laws
Women in Science - Emmy Noether
CERN and jobs in physics
Number density for conductors, semi-conductors, and insulators
Calculating cross-sectional area
Apply the mean drift velocity equation.
Derivation of Mean Drift Velocity Equation

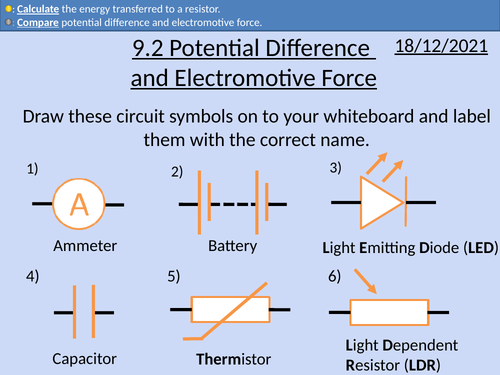
OCR AS level Physics: Potential Difference and Electromotive Force
OCR AS level Physics: Potential Difference and Electromotive Force is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Calculating the base SI units for volts
Comparing potential difference and electromotive force (emf).
Circuit diagrams for measuring potential difference and emf.
Calculating energy dissipated in a circuit.
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Materials
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 3: Materials.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
This covers topics from Hooke’s Law to Young Modulus.

GCSE Chemistry: Group 0 - Noble Gases
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Properties of Noble gases
• Trends and anomalies in Group 0 (Density, Melting Point)
• Reactivity of Group 0 Noble gases
• Electron configuration of Group 0 Noble gases

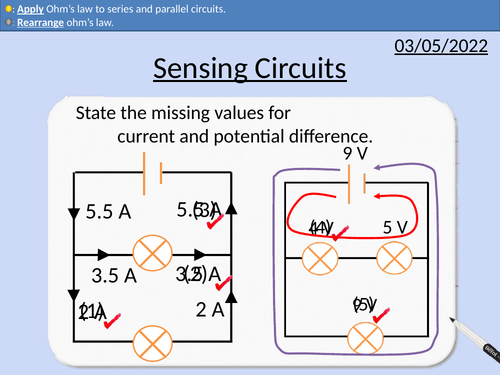
GCSE Physics: Sensing Circuits
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P3.2.7 Sensing Circuits
Potential difference in series and parallel circuits
Lamps in series and parallel
Gravitational potential and potential difference
LDR and Thermistor in potential divider circuits
Using LDRs to control security lights
Using thermistors to control heating/cooling circuits
Exam questions with worked solutions

OCR AS Chemistry: Properties of Alcohols
OCR AS Chemistry: 14,1 Properties of Alcohols
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Naming alcohols
Classifying alcohols (primary, secondary, tertiary)
Electronegativity
Polar and non-polar molecules
Explaining physical properties of alcohols compared to alkanes
Volatility
Solubility
Melting points
Chain length and London forces
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P8.1 Physics on the move
All resources for P8.1 Physics on the move GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Average speeds of walking, running, cycling, cars, trains, wind, sound, and light.
The speed equation
The acceleration equation
Explaining average speed camera
Explaining instantaneous speed camera
Estimating everyday accelerations
Calculating speed from rotation speed and circumference of wheels
Converting from miles per hour to meters per second
Reaction time definition
Factors that increase reaction time
Simple reaction time experiment
Thinking distance
Rearranging equations
Speed equation
(Final velocity)2 – (Initial velocity)2 = 2 x Acceleration x Distance
v2 – u2 = 2 a s
Factors affecting braking distance
Total stopping distances
Calculating area of a velocity-time graph for displacement (distance traveled).
Rearranging equations
MOT testing
Large accelerations produce large forces.
Values of g that cause severe injury or death
Road Safety
Newton’s First Law and seat belts
Crumple zones
Force = Mass x Acceleration
Acceleration = Change in velocity /Time taken
Estimating speed, accelerations and forces involved in large accelerations for everyday road transport.

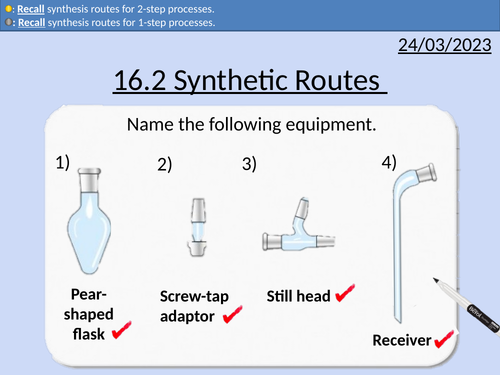
OCR AS Chemistry: Synthetic Routes
OCR AS Chemistry: 16.2 Synthetic Routes
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Functional Groups - Alkane, Alkene, Haloalkane, Alcohols, Carboxylic Acid, Ketone, Aldehyde, Ester, Amine, Nitrile.
One-step synthetic routes with reagents and conditions
Two-step synthetic routes with reagents and conditions

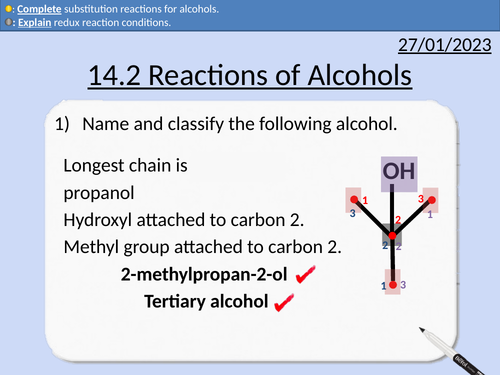
OCR AS Chemistry: Reactions of Alcohols
OCR AS Chemistry: 14.2 Reactions of Alcohols
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Combustion of alcohols
Reflux condition for reactions
Primary alcohol to aldehydes
Primary alcohols to carboxylic acids
Secondary alcohols to ketones
Dehydration of alcohols
Substitution reactions for alcohols
Bundle

GCSE OCR Biology: B1.2 What happens in cells?
All resources for B1.2 What happens in cells? GCSE OCR Biology Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid.
DNA is found in the nucleus of cells.
DNA is packaged into a thread-like structure called chromosomes.
Humans typically have 46 chromosomes shared from their parents.
Genes are sections of DNA that code for physical characteristics.
The structure of DNA.
DNA is comprised of monomers called nucleotides.
A nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a sugar (deoxyribose), and an organic base.
There are four organic bases: Adenine, A. Thymine, T. Cytosine, C. Guanine, G.
Hydrogen bonds in DNA.
The role of proteins and AI
Proteins as polymers
Explaining transcription
mRNA and complementary bases
Explaining translation
Enzymes are made of protein.
Enzymes are biological catalysts.
Catalysts speed up the rate of reaction without being used up themselves.
Enzymes and the lock and key hypothesis.
Enzymes breaking down and bonding substrates.
Enzymes-catalysed reactions
Rate of reaction
Denaturing of enzymes and the active site
Optimum temperature and optimum pH for enzymes
Definition of concentration
Increasing concentration of enzymes and substrates
Saturation of substrates

GCSE Physics: LDRs and Thermistors
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P3.2.5 LDR and Thermistors.
Circuit Symbols
Uses of LDRs and Thermistors
Plotting data and characteristic curves
Conductors, insulators, and semiconductors
Experiment into resistance and temperature of a thermistors
Investigation into resistance and light level of a LDR

GCSE Physics: Graphs of Current and Potential Difference (I-V)
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P3.2.4 Graphs of potential difference (p.d.) and current.
Linear circuit element
Non-linear circuit element
Diodes and Light emitting diode (LED)
Current against potential difference graphs
How the gradient of a current against potential difference graph relates to resistance
Experimental set-up for determining circuit elements
How temperature affects resistance in lamps and metal conductors (wires)