496Uploads
162k+Views
70k+Downloads
All resources
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P2.1 Motion
All resources for P2.1 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1.Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Distance, time and speed
Vectors and Scalars
Acceleration
Distance-time graphs
Velocity-time graphs
Equations of motion
Kinetic Energy

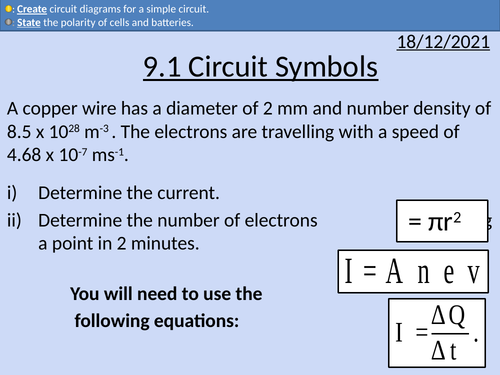
OCR AS level Physics: Circuit Symbols
OCR AS level Physics: Circuit Symbols is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
All circuit symbols required for OCR A level physics
Polarity of cells and batteries
Electron flow and conventional current
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Quantum Physics
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 4: Quantum Physics.
All presentations are full lesson PowerPoints with worked examples and homeworks with complete worked answers.
The Photon Model
Energy of a single photon
Converting from electron-volts to Joules.
Frequency of the electromagnetic spectrum
Determining Plank’s constant with LEDs
Threshold potential difference difference
Photoelectric Effect
Threshold frequency
Producing photoelectrons
Kinetic energy of photoelectrons
Linking frequency and wavelength
The electromagnetic spectrum, frequency and energy.
Einstein’s Photoelectric Equation
The photoelectric equation
Work function and Kinetic Energy
Determining work function from a graph
Determining threshold frequency from a from graphical analysis.
Determining Plank’s constant from graphical analysis.
Wave Particle Duality
deBroglie wavelength equation
Diffraction of electrons and protons
Comparing wavelengths of particles with different masses
Kinetic energy and wavelength

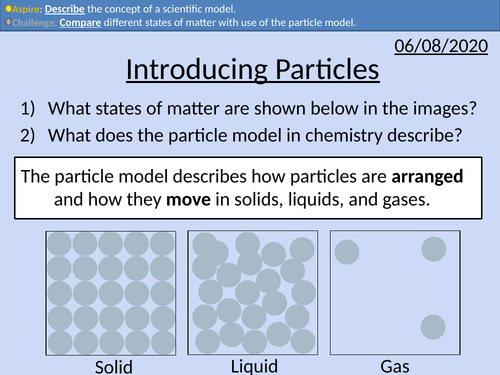
GCSE Chemistry: Introducing Particles
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Solids, liquids, and gases
• Scientific models as a concept
Bundle

GCSE OCR Chemistry: P1.2 Atomic Structure
All resources for P1.2 GCSE OCR Chemistry Gateway 9-1 Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Atomic Structure
Isotopes and Ions
Developing the Atomic Model

GCSE Chemistry: Empirical Formula
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Calculate empirical formula and by finding the simplest whole-number ratio
• Calculate relative formula mass from balanced equations.

OCR Applied Science: 2.2 Reactions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 2.2 of Module 1: Science Fundementals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Oxidation and reduction (redox) reactions
Addition reactions of alkenes to include full balanced symbol equations
Substitution reactions of alkanes and haloalkanes to include full balanced
equations
Addition polymerisation to include identification of monomers and repeating units
Condensation polymerisation to include identification of monomers and repeating units
Definition of a radical
The role played by UV light in producing chlorine radicals from CFCs in the
depletion of the ozone layer
Equations to show how chlorine radicals can destroy many ozone molecules
Displacement reactions to include full balanced equations for metals and halogens.

GCSE Chemistry: Ionic Compounds
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Filled outer shells result in more stable electronic structures.
• The electronic configuration ionic compounds
• Models of giant ionic structures

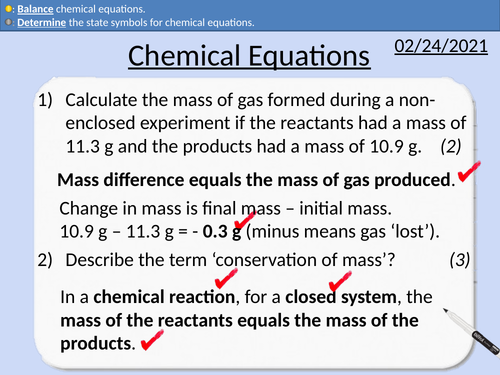
GCSE Chemistry: Chemical Equations
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Pathways into medical chemistry
• State the number of atoms from a chemical formula.
• Properties of metals and non-metals
• Determine state symbols for chemical equations
• Balancing chemical equations

GCSE Chemistry: Alkenes
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Unsaturated hydrocarbons
• Comparing alkanes and alkenes
• Mnemonic device for naming alkenes
• General formula for alkenes
• Completing addition reactions for alkenes

OCR AS Chemistry: Alkanes
OCR AS Chemistry: 12.1 Alkanes
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Sigma bonds (σ-bonds).
Tetrahedral shape and bond angles
Fractional distillation
Chain length and boiling point
Branching and boiling point
London Forces

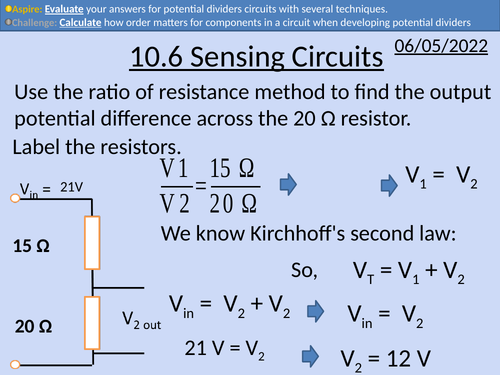
OCR AS Physics: Sensing Circuits
OCR AS Physics: Analysing Circuits is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Kirchhoff’s Laws for potential difference
Thermistors and LDRs in sensing circuits
Ratio of resistances and ratio of potential differences

OCR A level Physics: The Nucleus
OCR A level Physics: 24.2 The Nucleus
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Nucleons
Isotopes
Nuclear notation
Atomic mass units (u)
Radius for atomic nucleus equation
Volume and density of atomic nuclei
The strong nuclear force

OCR A level Physics: Antiparticles, Leptons, & Hadrons
OCR A level Physics: 24.3 Antiparticles, Leptons, & Hadrons
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Antiparticles, their properties, and symbols
Particle and antiparticle annihilation
The four fundamental forces (strong nuclear, weak nuclear, electromagnetic, and gravitational forces) and their properties.
Definition and examples of hadrons and leptons.

GCSE OCR Physics P1 Scheme of Work
Middle term plan for OCR Gateway Physics P1
This coveres:
Code
Combined or Triple
Number of lessons
Math Skills
Equations Introduced
Skills Developed
Content Covered
Practical or Demo

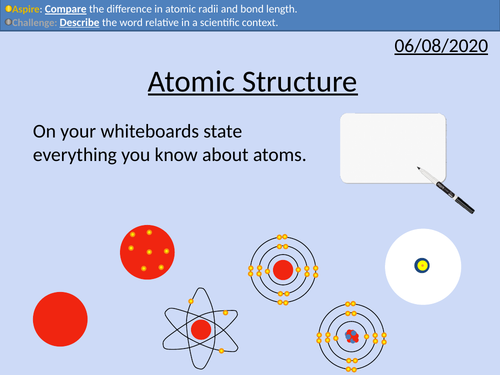
GCSE Chemistry: Atomic Structure
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Scientific models as a concept
• Structure of the atom
• Relative mass and charge of subatomic particles
• Bond length of atoms and molecules

GCSE Chemistry: Simple Molecules
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Dot and cross diagrams of simple molecules
• Simple molecules form covalent bonds
• The group number on the periodic table informs us how many electrons are in the outer shell.
• Groups on the periodic table

GCSE Chemistry: Nanoparticles
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Relative size of nanoparticles
• Convert nanometres using standard form
• Uses and dangers of nanoparticles

GCSE Chemistry: Covalent Structures
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Definition of giant covalent structures
• An empirical formula shows the simplest whole-number ratio of the atoms of each compound.
• Melting and boiling point of simple molecules
• Compare physical properties of simple molecules and giant covalent lattices.

GCSE OCR Physics: Circuit Calculations
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P3.2.6 Circuit Calculations.
Measuring current and potential difference
Adding resistors in series and parallel
Rearranging Ohm’s Law
Rules for series circuits
Worked solutions to series circuit exam questions
Rules for parallel circuits
Worked solutions to parallel circuit exam questions