497Uploads
169k+Views
72k+Downloads
Physics

GCSE Physics: Forces and Large Acclerations
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Road safety
Force and acceleration equations
How large forces produce dangerous accelerations

GCSE Physics: Energy Resources
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.2.2 Energy Resources
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
How use of energy resources have changed over time. (Biofuels, Fossil Fuels, Nuclear, Renewable).
How energy use has increased (increase population and development of technology)
Explain patterns and trends in the use of energy resources.
Fossil fuels are finite and will run out at current consumption levels.

GCSE Physics: Satellites
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.3.3 Satellites
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Natural Satellites
Geostationary Satellites
Low Polar Orbit Satellites
Speed is constant and velocity is changing in stable orbits.
Changing speed and radius
Gravitational force, acceleration, and speed.
Plotting data and describing relationships

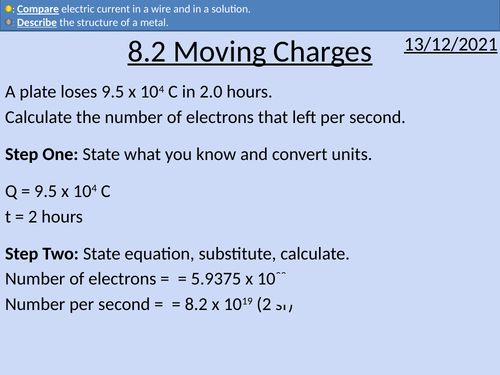
OCR AS level Physics: Moving Charges
OCR AS level Physics: Moving Charges is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Structure of a metal
Conventional current and electron flow
Measuring current with an ammeter
Ionic solutions with cations and anions.
Ions, relative charge and absolute charge
Comparing ionic solutions and metal conductors

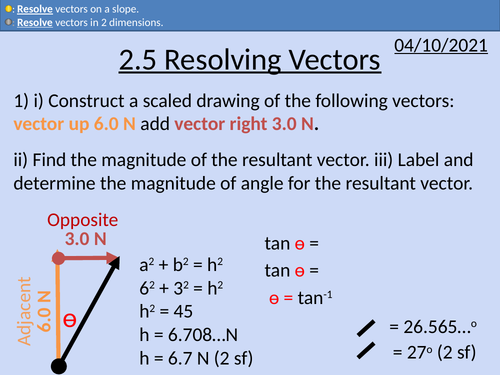
OCR AS level Physics: Resolving Vectors
OCR AS level Physics: Resolving Vectors is a part of the Module 2: Foundations of Physics
Full lesson PowerPoint with worked examples and homework with complete worked answers.
Using trigonometry to solve vector problems
Vectors in 2 D
Resolving vectors on a slope

OCR AS level Physics: Adding Vectors
OCR AS level Physics: Adding Vectors is a part of the Module 2: Foundations of Physics
Full lesson PowerPoint with worked examples and homework with complete worked answers.
Adding vectors in 1 D
Adding vectors in 2 D
Vector triangles
Using Pythagoras’ theorem to determine the magnitude
Using trigonometry to determine the direction

OCR AS level Physics: Acceleration
OCR AS level Physics: Acceleration is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

OCR AS level Physics: Conservation of Energy
OCR AS level Physics: Conservation of Energy is a part of the Module 3: Work, Energy and Power.
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

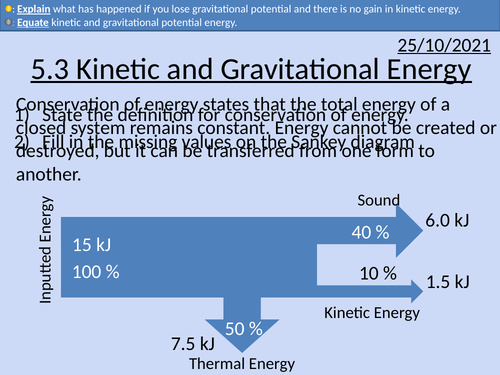
OCR AS level Physics: Kinetic and Gravitational Potential Energy
OCR AS level Physics: Kinetic and Gravitational Potential Energy is a part of the Module 3: Work, Energy and Power.
Presentation come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

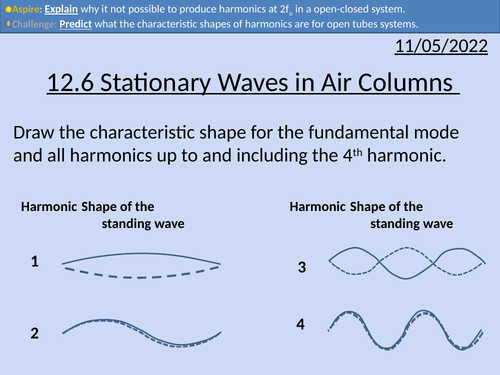
OCR AS level Physics: Stationary Waves in Air Columns
OCR AS level Physics: Stationary Waves in Air Columns is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

OCR AS level Physics: Stationary Waves
OCR AS level Physics: Stationary Waves is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

OCR AS level Physics: Einstein's Photoelectric Equation
OCR AS level Physics: Einstein’s Photoelectric Effect Equation is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
Full lesson PowerPoint with worked examples and homework with complete worked answers.
The photoelectric equation
Work function and Kinetic Energy
Determining work function from a graph
Determining threshold frequency from a from graphical analysis.
Determining Plank’s constant from graphical analysis.

OCR Applied Science: 6.3 Electrical Properties
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 6.3 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
Current as flow of charge in a conductor.
Use the equation: I = ΔQ ÷ Δt
Ohm’s law illustrates the relationship of V ∝ I
Use the equation: potential difference (V) = current (A) × resistance
Use the equations for adding resistors in series and parallel
Compare electromotive force and potential difference
Use the equation: charge © = current (A) × time (s)
Use and recognise the equation for mean drift velocity
Use the equation: energy transferred (work done) (J) = charge © × potential difference (V)
Use the equation: energy transferred (J, kWh) = power (W, kW) × time (s, h)
Use the equation: power (W) = energy (J) ÷ time (s)

OCR Applied Science: 21.1 Regulatory Bodies
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers: Topic 1.1 and 1.2 of Module 21: Product Testing Techniques.
Understand the influence of regulatory bodies on development of consumer products.
1.1 The relevant governing bodies that oversee product safety for
manufacturers and consumers of products.
1.2 How governing bodies influence how quality control is applied.

OCR Physics P2 Forces Revision
This revision PowerPoint should take approximately 5 hours of class time to complete.
This PowerPoint covers GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
** P2.1 Motion:**
Distance, time and speed
Vectors and Scalars
Acceleration
Distance-time graphs
Velocity-time graphs
Kinetic Energy
** P2.2 Newton’s Laws:**
Forces and Interactions
Free Body Diagrams
Newton’s First Law
Newton’s Second Law
Everyday Forces
Momentum
Work Done and Power
P2.3 Forces in Action:
Stretching springs
Stretching materials and storing energy
Gravitational Fields and Potential Energy
Turning Forces
Simple Machines
Hydraulics

OCR A level Physics: Angular Acceleration
OCR A level Physics: Angular Acceleration and the Radian is a part of the Module 5: Newtonian world and astrophysics.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks with answers.

OCR A level Physics: Angular Velocity and the Radian
OCR A level Physics: Angular Velocity and the Radian is a part of the Module 5: Newtonian world and astrophysics.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks with answers.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics P5.2 Electromagnetic Spectrum
Resources for P5.2 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1 Triple and Combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each lesson includes student activities and full worked answers.
Order of the electromagnetic spectrum
Wavelength and frequency relationship
Application of wave speed equation
Rearranging equation
Producing and detecting radio waves
Recall that light is an electromagnetic wave
Give examples of some practical uses of electromagnetic waves in the radio, micro-wave, infra-red, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray and gamma-ray regions
Describe how ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays can have hazardous effects, notably on human bodily tissues.
Explain that electromagnetic waves transfer energy from source to absorber to include examples from a range of electromagnetic waves
Precautions for ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays
Careers: Medical Physicist
X-rays
CT scans
Gamma imaging
Thermogram
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Precautions for using ionising radiation
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics P5 Waves
Resources for P5 GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1 Triple and Combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each lesson includes student activities and full worked answers.
Definition of a wave
Mechanical waves
Electromagnetic waves
Transverse waves
Longitudinal waves
Amplitude
Wavelength
Frequency
Time period
Calculating frequency and equation
Relationship between frequency and wavelength when speed is constant.
Calculating time period from frequency with equations
The speed equation
Measuring distance and time
Simple experiment for the speed of sound
Improving experiments
Echoes
Speed of sound experiment with microphones and oscilloscope.
Ray diagrams
Absorption, reflection and transmission
Sonar
Ultrasound
Rearranging equation
Refraction
Relationship between wave speed and wavelength
Structure of the ear.
Frequency range of human hearing.
Explanation of the limited frequency range of humans.
Explanation for hearing deteriorating with age.
Order of the electromagnetic spectrum
Wavelength and frequency relationship
Application of wave speed equation
Rearranging equation
Producing and detecting radio waves
Recall that light is an electromagnetic wave
Give examples of some practical uses of electromagnetic waves in the radio, micro-wave, infra-red, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray and gamma-ray regions
Describe how ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays can have hazardous effects, notably on human bodily tissues.
Explain that electromagnetic waves transfer energy from source to absorber to include examples from a range of electromagnetic waves
Precautions for ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays
Careers: Medical Physicist
X-rays
CT scans
Gamma imaging
Thermogram
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Precautions for using ionising radiation
Law of reflection
Labeling and measuring angles of incidence and reflection
Practical activity instructions - fully animated.
Reflection, absorption, and refraction is affected by wavelength of electromagnetic wave.
Refraction the change of velocity - speed and direction
Magnitude of refraction depending on wavelength
Magnitude of refraction depending on optical density
Refraction practical activity instructions
Wave speed, wavelength, and frequency relationship in refraction
Convex and Concaves lenses
Eyes and corrective lenses
Refraction and wavelength
Focal points for lenses
Determining the type of images produced through a lens
Names of colours for the visible spectrum
Coloured filters
Coloured objects acting as a coloured filters
White light and refracting prism
Refraction and wavelength
Specular reflection
Diffuse scattering
Scattering - Why the sky is blue and milk is white.

OCR AS Physics: Thermistor
OCR AS Physics A: Thermistor is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.
Thermistor uses
Thermistors with negative temperature coefficients
Plotting I-V curves for thermistors
Creating an experiment to test thermistors.