497Uploads
167k+Views
71k+Downloads
Physics
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Particle Physics
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 24 Particle Physics is apart of the Module 6: Particle and Medical Physics
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
24.1 Alpha-particle scattering experiment
24.2 The Nucleus
24.3 Antiparticles, Leptons, & Hadrons
24.4 Quarks
24.5 Beta decay
Developments of scientific models
Thompson’s plum-pudding model
Rutherford’s nuclear (planetary) model
Rutherford’s experiment, observations, and conclusions
Using Coulomb’s law to find the minimum distance between particles
Nucleons
Isotopes
Nuclear notation
Atomic mass units (u)
Radius for atomic nucleus equation
Volume and density of atomic nuclei
The strong nuclear force
Antiparticles, their properties, and symbols
Particle and antiparticle annihilation
The four fundamental forces (strong nuclear, weak nuclear, electromagnetic, and gravitational forces) and their properties.
Definition and examples of hadrons and leptons.
The Standard Model of particle physics
Quarks, anti-quarks and their charges
Baryons and mesons
Properties of neutrinos
Nuclear notation
Nuclear decay equations
Beta-plus and beta-minus decays
Quark transformation

GCSE Physics: Speakers and Microphones
This lesson presentations covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P4.2.6 Speakers and Microphones.
Definition of sound waves.
Structure and operation of a speaker.
Fleming’s left hand rule.
Structure and operation of a microphone.
Electromagnetic induction.
Comparison of speakers and motors.
Comparison of microphone and generators.
Comparing microphones and speakers

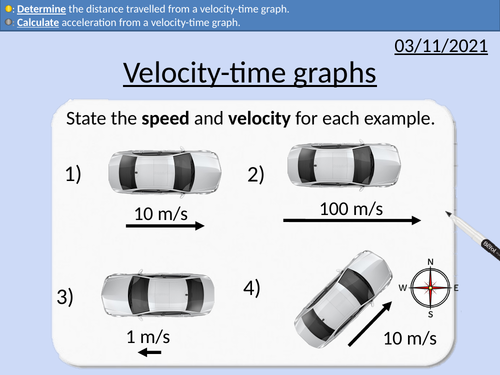
GCSE Physics: Velocity-time graphs
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.1.5
Analysing velocity-time graphs
Calculating the gradient
Acceleration from velocity-time graphs
Distance travelled from velocity-time graphs
Worked problems and solutions

GCSE Physics: Newton's Second Law
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.2.4
Newton’s Second Law in Mathematical Form
Proportionalities
Rearranging Equations
Student’s problems with answers
Exam style questions with solutions
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Forces in Action
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 3: Forces in Action.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
This covers topics from weight as a force to Archimedes’ principle.
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Electrical Circuits
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 4: Energy, Power, and Resistance.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
This covers topics from Kirchhoff’s laws to potential dividers and sensing circuits.

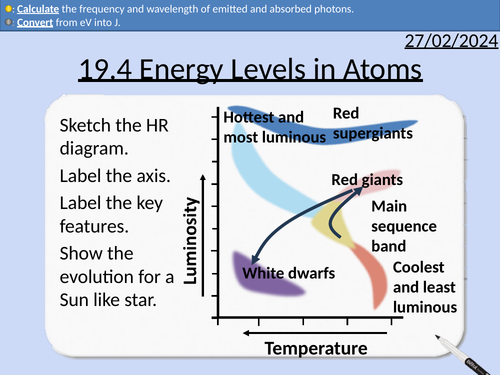
OCR A level Physics: Energy Levels in Atoms
OCR A level Physics: 19.4 Energy Levels in Atoms
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Atoms have different electron arrangements
Ground state energy
Bound electron states being negative
Converting between joules and electronvolts
Calculating the change of energy between energy states
Calculating a photon’s frequency and wavelength

GCSE Physics: Current and Magnetic Fields
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P4.1.2 Current and Magnetic Fields.
Current Produces Magnetic Fields
Experiment to Demonstrate Magnetic Field Lines
Right-hand Corkscrew Explanation
Solenoids
MRI imaging

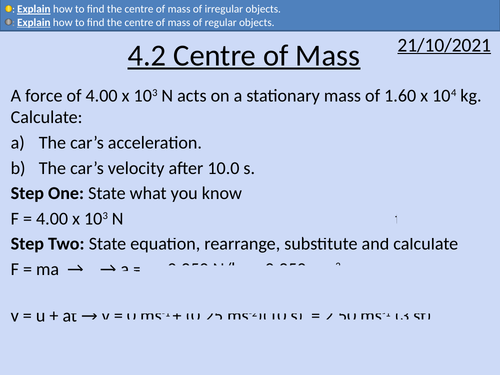
OCR AS level Physics: Centre of Mass
OCR AS level Physics: Centre of mass is a part of the Module 3: Force and Motion
Full lesson PowerPoint with worked examples and homework with complete worked answers.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P8.1 Physics on the move
All resources for P8.1 Physics on the move GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Average speeds of walking, running, cycling, cars, trains, wind, sound, and light.
The speed equation
The acceleration equation
Explaining average speed camera
Explaining instantaneous speed camera
Estimating everyday accelerations
Calculating speed from rotation speed and circumference of wheels
Converting from miles per hour to meters per second
Reaction time definition
Factors that increase reaction time
Simple reaction time experiment
Thinking distance
Rearranging equations
Speed equation
(Final velocity)2 – (Initial velocity)2 = 2 x Acceleration x Distance
v2 – u2 = 2 a s
Factors affecting braking distance
Total stopping distances
Calculating area of a velocity-time graph for displacement (distance traveled).
Rearranging equations
MOT testing
Large accelerations produce large forces.
Values of g that cause severe injury or death
Road Safety
Newton’s First Law and seat belts
Crumple zones
Force = Mass x Acceleration
Acceleration = Change in velocity /Time taken
Estimating speed, accelerations and forces involved in large accelerations for everyday road transport.

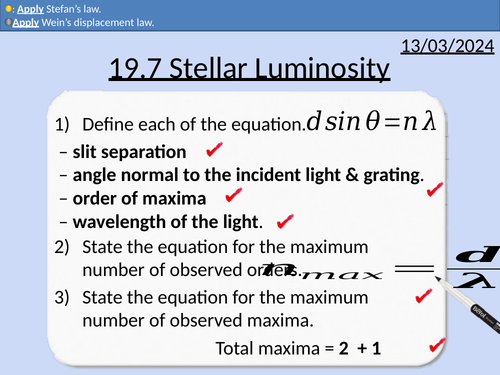
OCR A level Physics: Stellar Luminosity
OCR A level Physics: 19.7 Stellar Luminosity
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The electromagnetic spectrum, frequency/wavelength, and temperature
Black body radiation
Wein’s displacements law
Stefan’s law (Stefan-Boltzmann law)

OCR A level Physics: Half-life and Activity
OCR A level Physics: 25.3 Half-life and Activity
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The reason why radioactive decays are considered random and spontaneous
Rolling dice being a good analogue for radioactive decays
Definition of half-life
Determining half-life from a graph.
Calculating half-life from a table of data.
Activity of a sample in Bq
The decay constant derivation

GCSE Physics: Magnets and Magnetic Fields
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P4.1.1 Magnets and Magnetic Fields.
Rules for repulsion and attraction
Magnetic Field Line Rules
Magnetic field density and magnetic force
Modeling the Earth as a Bar Magnet
Permanent and Induced Magnets
Magnetic Domains

GCSE Physics: Equations of Motion
This presentation covers GCSE Physics OCR Gateway P2.1.6
Introduction of final speed^2 – initial speed^2 = 2 x acceleration x distance
Rearranging of final speed^2 – initial speed^2 = 2 x acceleration x distance
Derivation of final speed^2 – initial speed^2 = 2 x acceleration x distance
Three different methods for rearranging equations
Kinetic energy, acceleration and speed problems with answers

GCSE Physics: Specific Latent Heat
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.2.4 Specific Latent Heat
Presentation covers
Changes of State - Phase changes
Interactive Graph
Equation with example
Questions with solutions for SLH equation
Exam style question with answer

GCSE Physics: Resistance and Ohm's Law
This presentations covers the OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P3.2.3 Resistance
Combining resistors in series
Combining resistors in parallel
Modeling resistance, current, and potential difference with a rope.
The relationship between potential difference and current
The relationship between resistance and current
Ohm’s law
Rearranging equations
Worked examples and student questions
Explaining how increasing current increases resistance in a metal conductor and filament lamp.
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Charge and Current
OCR AS level Physics: Charge and Current is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
Fundamental charge and relative charge
Structure of a metal
Conventional current and electron flow
Measuring current with an ammeter
Ionic solutions with cations and anions.
Ions, relative charge and absolute charge
Comparing ionic solutions and metal conductors
Apply Kirchhoff’s First Law
Kirchhoff’s First Law in mathematical form
Kirchhoff’s First Law in written form
Describing conservation laws
Women in Science - Emmy Noether
CERN and jobs in physics
Number density for conductors, semi-conductors, and insulators
Calculating cross-sectional area
Apply the mean drift velocity equation.
Derivation of Mean Drift Velocity Equation
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Energy, Power, and Resistance
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 4: Energy, Power, and Resistance.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
This covers topics from circuit symbols to paying for electricity.
All circuit symbols required for OCR A level physics
Polarity of cells and batteries
Electron flow and conventional current
Calculating the base SI units for volts
Comparing potential difference and electromotive force (emf).
Circuit diagrams for measuring potential difference and emf.
Calculating energy dissipated in a circuit.
The structure of an electron gun.
The electron gun in the history of science (J.J. Thomson).
Rearranging equations to equate kinetic energy and work done.
Accelerating potential differences
Comparing the protons and electrons accelerated in a potential difference
Definition of an ohm.
Temperature and resistance for metallic conductors (wires)
The ohm in base SI units
I against V graphs and resistance
I-V Characteristics curves for ohmic components
I-V Characteristics curves for non-ohmic components
Circuit diagrams used to measure I and V.
Describing I-V Characteristics curves
Polarity of diodes
Conventional current and diodes
Plotting I-V curves for diodes
Describing I-V curves for diodes
Factors affecting resistance
Calculating resistivity
Resistivity and temperature
Experimentally determining resistivity
Using a graph to calculate resistivity
Thermistor uses
Thermistors with negative temperature coefficients
Plotting I-V curves for thermistors
Creating an experiment to test thermistors.
Materials and uses of LDRs
Creating an experiment to understand LDRs
LDRs relationship with light intensity
Converting time to hours
Using different units for electrical energy
Converting from J to kW hr
Calculating the cost of using different electrical appliances.
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Quantum Physics
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 4: Quantum Physics.
All presentations are full lesson PowerPoints with worked examples and homeworks with complete worked answers.
The Photon Model
Energy of a single photon
Converting from electron-volts to Joules.
Frequency of the electromagnetic spectrum
Determining Plank’s constant with LEDs
Threshold potential difference difference
Photoelectric Effect
Threshold frequency
Producing photoelectrons
Kinetic energy of photoelectrons
Linking frequency and wavelength
The electromagnetic spectrum, frequency and energy.
Einstein’s Photoelectric Equation
The photoelectric equation
Work function and Kinetic Energy
Determining work function from a graph
Determining threshold frequency from a from graphical analysis.
Determining Plank’s constant from graphical analysis.
Wave Particle Duality
deBroglie wavelength equation
Diffraction of electrons and protons
Comparing wavelengths of particles with different masses
Kinetic energy and wavelength

GCSE Physics: Efficiency
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.2.5 Efficiency.
All presentations come with student activities and worked solutions.
Efficiency Ratings
Improving efficiency with insulation and lubrication
Maximum efficiency
Efficiency equation
Sankey diagrams