497Uploads
167k+Views
71k+Downloads
All resources

OCR A level Physics: Einstein's Mass-Energy Equation
OCR A level Physics: 26.1 Einstein’s Mass-Energy Equation
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Mass-energy is a conserved quantity
Einstein’s mass-energy equation
Particle and antiparticle annihilate each other
Rest mass and increasing mass with increased kinetic energy
Interpretation of mass-energy equivalence

GCSE Biology: DNA
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.2.1 DNA
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid.
DNA is found in the nucleus of cells.
DNA is packaged into a thread-like structure called chromosomes.
Humans typically have 46 chromosomes shared from their parents.
Genes are sections of DNA that code for physical characteristics.
The structure of DNA.
DNA is comprised of monomers called nucleotides.
A nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a sugar (deoxyribose), and an organic base.
There are four organic bases: Adenine, A. Thymine, T. Cytosine, C. Guanine, G.
Hydrogen bonds in DNA.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Biology: B1.1 Cell Structures
All resources for B1.1 Cell Structures GCSE OCR Biology Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Cells are the building blocks of living objects.
Definition of eukaryotic cells
Typical size of eukaryotic cells
Subcellular structure of animal cells
Subcellular structure of plant cells
Organelles and their functions
Revision activities (Look, Cover, Write, Check)
Print out of animal and plant cells
Typical size of bacterial cells
Subcellular structure of bacterial cells
Functions of subcellular structure of bacterial cells
Comparing animal, plant, and bacterial cells
Revision activity - flash cards
Print out of bacterial cell
Labeling a light microscope
Defining magnification and resolution.
Explaining why stains are used for light microscope.
Calculating total magnification, objective lens magnification and eyepiece lens magnification.
Calculating actual size, magnification, and magnified size of objects.
Converting from from micrometre (µm) to millimetres (mm)
Rearranging equations
Comparing sizes of different cells
Using standard form
Using SI prefixes (nano, micro, milli, kilo, mega)
Comparing electron microscopes and light microscopes.

GCSE Biology: Aerobic Respiration
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.3.2 Aerobic Respiration
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Word equation for aerobic respiration
Balanced symbol equation for aerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration is an exothermic reaction
The structure of mitochondria
ATP and its uses
Why blood flow increases to muscles when exercising
Bundle

GCSE OCR Biology: B1.3 Respiration
All resources for B1.3 Respiration GCSE OCR Biology Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
The three main macronutrients - carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
Names of enzymes - carbohydrase, amylase, protease, lipase
What the macronutrients are broken down into - simple sugars, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol.
Metabolic rate
Food tests and the positive results
Word equation for aerobic respiration
Balanced symbol equation for aerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration is an exothermic reaction
The structure of mitochondria
ATP and its uses
Why blood flow increases to muscles when exercising
Conditions for anaerobic respiration
Word equation for anaerobic respiration in mammals
Lactic acid and its affects.
Oxygen debt
Comparing aerobic and anaerobic respiration in mammals.
Anaerobic respiration in plants - fermentation.
Fermentation word equation and symbol equation.
Exam questions.

GCSE Biology: Photosynthesis
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.4.1 Photosynthesis
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Word and symbol equation for photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide diffuses from the air through the stomata.
Water travels by osmosis through the root hair cells.
Photosynthesis occurs inside the plant’s chloroplast.
Chloroplasts contain a green pigment called chlorophyll.
Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction.
The two main stages of photosynthesis.
Comparing photosynthesis and aerobic respiration.

GCSE Biology: Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.4.3 Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Definition for rate of photosynthesis
The rate of photosynthesis affects the rate of biomass
Limiting factors include, light level, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature.
Graphs for rate of photosynthesis against light level, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature.
Plotting data graphs.
Exam questions.
Bundle

GCSE OCR Biology: B1.4 Photosynthesis
All resources for B1.4 Photosynthesis GCSE OCR Biology Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Each PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Word and symbol equation for photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide diffuses from the air through the stomata.
Water travels by osmosis through the root hair cells.
Photosynthesis occurs inside the plant’s chloroplast.
Chloroplasts contain a green pigment called chlorophyll.
Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction.
The two main stages of photosynthesis.
Comparing photosynthesis and aerobic respiration.
The positive test for starch
Experimental procedure for testing starch in leaves.
Testing for the need of chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
Testing for the need of light for photosynthesis.
Testing for the need of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
Testing oxygen produced via photosynthesis.
Testing light intensity affects photosynthesis.
Definition for rate of photosynthesis
The rate of photosynthesis affects the rate of biomass
Limiting factors include, light level, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature.
Graphs for rate of photosynthesis against light level, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature.
Plotting data graphs.
Experimental procedures to investigate how the rate of photosynthesis is affected by:
Light level
Temperature
Carbon dioxide concentration
Inverse square law for relative light intensity

GCSE Biology: Osmosis
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B2.1.2 Osmosis
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Definition of osmosis.
Explaining water potential and concentration of solution.
How cells change during osmosis - turgid, lysis, crenated, plasmolysed

A level Chemistry: Combined Techniques
OCR A level Chemistry: 29.6 Combined Techniques
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Percentage yield to determine empirical formula
Mass spectra
Infrared spectra
Carbon-13 NMR spectra
Proton NMR spectra

OCR AS Physics: Diffraction and Polarisation
OCR AS Physics: Diffraction and Polarisation is a part of the Module 4: Electrons, Waves, and Photons. PowerPoint with worked examples and homework.

Physics Display - Science Jobs/Women in Physics
Several word documents with content concerning women in physics and jobs in physics. These displays are in line with IoP recommendations to promote women in physics.

GCSE OCR Physics: Building A Motor
GCSE OCR Physics: Building A Motor powerpoint with instruction on how to construct a motor activity.

GCSE Physics: Floating and Sinking
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.3.5 Floating and Sinking
Content Covered:
Balanced Forces
Rearranging equations
Mass and weight
Gravitational field strength
Pressure
Liquid Pressure
Difference in pressure causing up thrust
Combining two equations
Worked solutions
Exam Style Questions
Problems with answers
Demonstration

GCSE Physics: Atomic Model 1
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.1.1
Covers:
Scientific Models
Ancient Greek Model
Dalton’s Model
JJ Thomson’s model

GCSE Physics: Gravitational Force and Energy
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.3.3 Gravitational Force and Energy
Gravitational fields
Gravitational field strength and mass
Gravitational energy and work done
Exam style questions and solutions
Student problems with answers

GCSE OCR Physics P2 Test
35 mark assessment with mark scheme for P2 from OCR Gateway Physics 9-1.
• 5 multiple choice questions
• Scalars and Vectors
• Speed
• Acceleration
• Equation of Motion
• Velocity-time graph
• Included physics equations
• PIN cover sheet

GCSE OCR Physics P2 Scheme of Work
Middle term plan for OCR Gateway Physics P2
This coveres:
Code
Combined or Triple
Number of lessons
Math Skills
Equations Introduced
Skills Developed
Content Covered
Practical or Demo

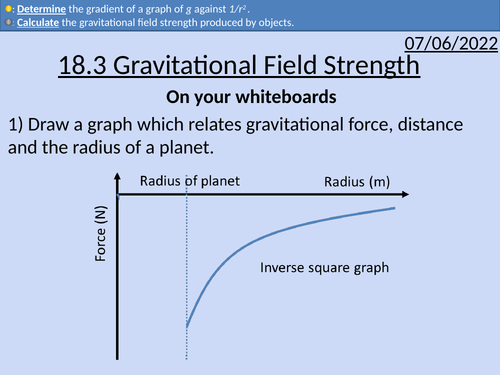
OCR A Level Physics: Gravitational Field Strength
OCR A Level Physics: Gravitational Field Strength presentation with homework and answers

GCSE Physics: Speed Equation
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• The speed equation and units
• Rearranging Equations
• The skill of estimating