497Uploads
167k+Views
71k+Downloads
All resources

GCSE Physics: Energy Sources
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.2.1 Energy Sources
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Types of different energy sources
Renewable and non-renewable definitions
Different uses of energy sources - transport, heating, and generating electricity
Advantages and disadvantages of different energy sources
Fossil fuels – oil, coal, and natural gas.
Nuclear fuel – Uranium
Biofuels – wood, biodiesel, and biogas.
The sun - solar (PV) panels and solar heating panels
Tides,
Waves,
Hydroelectricity
Wind
Geothermal

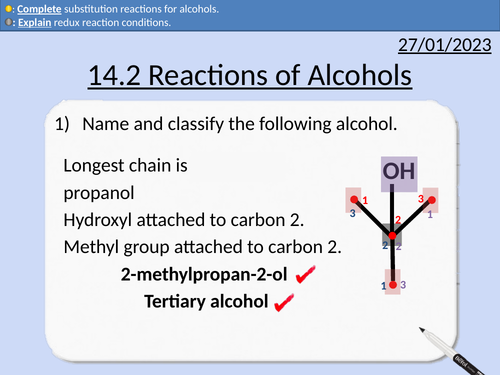
OCR AS Chemistry: Reactions of Alcohols
OCR AS Chemistry: 14.2 Reactions of Alcohols
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Combustion of alcohols
Reflux condition for reactions
Primary alcohol to aldehydes
Primary alcohols to carboxylic acids
Secondary alcohols to ketones
Dehydration of alcohols
Substitution reactions for alcohols
Bundle

GCSE OCR Physics: P8.3 Beyond Earth
All resources for P8.2 Powering Earth GCSE OCR Physics Gateway 9-1. Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Key facts about the Big-Bang model
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB, CMBR)
Doppler Red shift of light from stars in galaxies
Hubble’s evidence of absorption spectra being red shifted
Structure of the solar system
Nuclear Fusion
Evolution of large stars
Evolution of Sun like stars
Gravitational force and force from nuclear fusion
Natural Satellites
Geostationary Satellites
Low Polar Orbit Satellites
Speed is constant and velocity is changing in stable orbits.
Changing speed and radius
Gravitational force, acceleration, and speed.
Plotting data and describing relationships
All objects emit electromagnetic radiation
Describe how changing temperature changes frequency, wavelength, and intensity of the radiation produced.
Explain why objects change temperature by absorbing and emitting radiation.
Explain why the temperature of the Earth changes due to greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
S and P waves
Structure of the Earth
Reflection, absorption, and refraction of waves
Sonar to map the ocean floor

GCSE Physics: Imaging with Electromagnetic Waves
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.2.3 Imaging with Electromagnetic waves. Includes student activities and full worked answers.
Careers: Medical Physicist
X-rays
CT scans
Gamma imaging
Thermogram
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Precautions for using ionising radiation

GCSE Physics: EM waves - Uses and Dangers
This presentation cover the OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.2.2 Uses and Dangers of EM radiation. PowerPoint includes student activities with full worked answers.
Recall that light is an electromagnetic wave
Give examples of some practical uses of electromagnetic waves in the radio, micro-wave, infra-red, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray and gamma-ray regions
Describe how ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays can have hazardous effects, notably on human bodily tissues.
Explain that electromagnetic waves transfer energy from source to absorber to include examples from a range of electromagnetic waves
Precautions for ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays

OCR A level Physics: Life Cycles of Stars
OCR A level Physics: 19.2 Life Cycles of Stars
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Calculating mass in kg from solar mass
Life cycle of stars with a mass between 0.5 and 10 solar masses
Life cycle of stars with a mass above 10 solar masses
Pauli exclusion principle and electron degeneracy pressure
Red giants and white dwarfs
The Chandrasekhar limit
Red supergiants to black holes and neutron stars
Stellar nucleosynthesis

OCR A level Physics: Faraday's Law and Lenz's Law
OCR A level Physics: 23.5 Faraday’s Law and Lenz’s Law
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Magnetic flux density and magnetic flux linkage
Faraday’s Law
Lenz’s Law
Alternators and induced e.m.f.
Graphs of flux linkage and induced e.m.f.

OCR A level Physics: Alpha-particle Scattering Experiment
OCR A level Physics: 24.1 Alpha-particle Scattering Experiment
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Developments of scientific models
Thompson’s plum-pudding model
Rutherford’s nuclear (planetary) model
Rutherford’s experiment, observations, and conclusions
Using Coulomb’s law to find the minimum distance between particles

OCR A level Physics: Half-life and Activity
OCR A level Physics: 25.3 Half-life and Activity
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
The reason why radioactive decays are considered random and spontaneous
Rolling dice being a good analogue for radioactive decays
Definition of half-life
Determining half-life from a graph.
Calculating half-life from a table of data.
Activity of a sample in Bq
The decay constant derivation

OCR Applied Science: 6.1 Mechanical Properties of Materials
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student activities covers:
Topic 6.1 of Module 1: Science Fundamentals of the OCR Applied Science Spec.
• Interpreting laboratory tests for stress-strain graphs and Young’s modulus
• Awareness that repeated loading cycles may cause failure by fatigue below the yield strength
• Use of diagrams to understand that the way molecules are arranged in polymers determines the properties: chain length, crosslinking, use of plasticizers and crystallinity.
• Use and rearranging of the density equation.

GCSE Biology: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.3.1 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
The three main macronutrients - carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
Names of enzymes - carbohydrase, amylase, protease, lipase
What the macronutrients are broken down into - simple sugars, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol.
Metabolic rate
Food tests and the positive results

OCR A Level Physics: Satellites
OCR A level Physics: 18.5 Satellites
Module 5 Newtonian World and Astrophysics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Key features of geostationary and low polar orbit satellites
Conditions for stable orbits for satellites
Applying Kepler’s laws to the orbits of satellites

GCSE Physics: Graphs of Current and Potential Difference (I-V)
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P3.2.4 Graphs of potential difference (p.d.) and current.
Linear circuit element
Non-linear circuit element
Diodes and Light emitting diode (LED)
Current against potential difference graphs
How the gradient of a current against potential difference graph relates to resistance
Experimental set-up for determining circuit elements
How temperature affects resistance in lamps and metal conductors (wires)

GCSE Physics: Electrical Power
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P3.2.8 Electrical Power.
Definition of power
Standard form for kW and MW
The three equations for power
Rearranging electrical power equations
Derivation of P = I^2 R with subsitution
Students questions and worked solutions

GCSE Physics: Current and Forces with Equation
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P4.2.1 b Current and Forces.
Units for Magnetic Field Strength
Converting from mT to T
Magnetic Force Equation
Rearranging Equations
Increasing the force on a current carrying conductor in an external magnetic field.
Student questions and worked answers

GCSE Physics: Distance, Time and Speed
This presentation covers material for OCR Physics Gateway 9-1 P2.1.1
Covered:
Measuring and calculating
Accuracy of stop watch vs light gate
Conversion of units
Exam style question
Worked examples
Students questions with answers

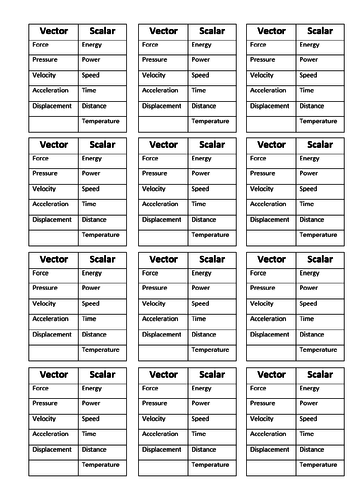
GCSE Physics: Vectors and Scalars
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P1.2.2.
Content covered:
Definition for vector and scalar
Vector addition in 1 D
Vector addition in 2 D
Scaled drawings and Pythagoras’ theorem
Worked examples and student problems with answers included

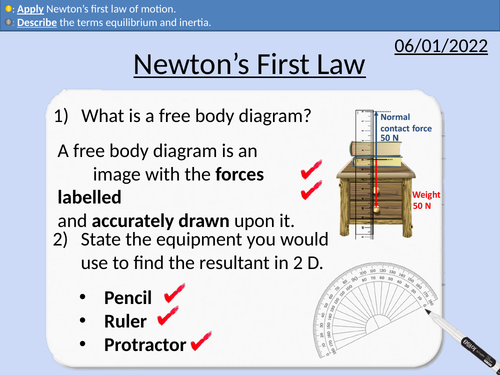
GCSE Physics: Newton's First Law
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.2.3.
PowerPoint with multiple student activities and complete worked answers.
Newton’s First Law definition
Balanced and unbalanced forces producing accelerations
Acceleration being the change in velocity
The principle of inertia
Definition for equilibrium

GCSE Physics: Momentum
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.2.6
Momentum Equation
Rearranging the momentum equation
Momentum as a vector
Vector addition with momentum
Exam question with worked solutions
Student problems with answers
Proportionalities

GCSE Physics: Simple Machines and Gears
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P2.3.5 Simple Machines
• Uses of simple machines
• Simple machines as force multipliers
• Mechanical advantage equation
• Gears – ratios, speed, direction
• Rearranging equations
• Exam style questions with solutions
• Student problems with answers